Abstract
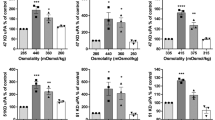
Local recurrence continues to limit survival in medulloblastoma patients, largely related to the persistence of invasive cells at the site of tumour resection and leptomeningeal dissemination. Given the relative dearth of understanding of causative mechanisms behind the invasiveness of medulloblastomas, and a general lack of validated in vitro models with which to study them, our objectives were (1) to obtain quantitative data on the invasiveness of five distinct medulloblastoma cell lines within a 3-dimensional in vitro collagen-based model; and (2) to characterize some of the mechanisms behind invasion, specifically striving to identify proteolytic processes that occur as medulloblastoma cells disrupt and thereby invade the normal tissue surrounding them, and specific inhibitors of these proteolytic enzymes. Five different medulloblastoma cell lines (UW228-1, 2 and 3; Daoy, and Madsen) were implanted onto a 3-dimensional, type I collagen gel assay to assess tumour invasion distance and mean doubling time over 5 days. Proteolytic activity was assessed against collagen types I and IV by measuring the degradation of 3H-collagen I and IV to products soluble in 100% w/v trichloroacetic acid; and general (neutral) proteolytic activity evaluated by measuring the degradation of 3H-albumin. In other experiments, cells were pre-exposed to a variety of protease inhibitors, including inhibitors of metalloproteinases and cysteine, serine and aspartic proteases, and then plated to identify any inhibition of invasion. Inter-group differences in mean invasion distance were assessed by means of Student’s t-tests for non-paired subjects, with P < 0.05 set as the threshold for statistical significance. For the inhibitor studies, an inhibition index, called the inhibitory concentration 50, IC-50, was calculated by performing a regression analysis for each inhibitor tested over a range of concentrations, for each cell line. Within hours of implantation, individual cells readily detached from the surface of the cell aggregates and invaded the collagen matrix, to distances of up to 1,200 μm and at rates of up to 300-μm per day; the UW228-1 cell line clearly was less invasive than the other four cell lines. Proteolytic activity was identified against collagen type I, but not against collagen type IV or albumin; but there was no apparent correlation between invasion distance and either cell doubling time or the amount of collagen type I proteolytic activity. Both metalloproteinase inhibitors suppressed tumour invasion, as did one of two cysteine protease inhibitors; but there was no tumour suppression with either serine or aspartic protease inhibition. MMP-1 and 2, and TIMP-1 and 2 all were detectable by Western blot analysis. Medulloblastoma cell invasiveness within the 3-dimensional model used here appears to depend upon a combination of metalloproteinase and cysteine protease activity, a finding that may suggest areas for potential future clinical investigation and therapy.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Miltenburg D, Louw DF, Sutherland GR (1996) Epidemiology of childhood brain tumors. Can J Neurol Sci 23(2):118–122
Larouche V, Huang A, Bartels U, Bouffet E (2007) Tumors of the central nervous system in the first year of life. Pediatr Blood Cancer 49(7 Suppl):1074–1082
Kopac S, Jereb B (2004) Medulloblastoma in children 0-3 years old: forty years’ experience in slovenia. Pediatr Hematol Oncol 21(1):17–21
Rickert CH (1998) Epidemiological features of brain tumors in the first 3 years of life. Childs Nerv Syst 14(10):547–550
Stiller CA, Bunch KJ (1992) Brain and spinal tumours in children aged under two years: incidence and survival in Britain, 1971-85. Br J Cancer 18(Suppl):S50–S53
Kumar R, Tekkok IH, Jones RA (1990) Intracranial tumours in the first 18 months of life. Childs Nerv Syst 6(7):371–374
Janish W, Haas JF, Schreiber D, Gerlach H (1984) Primary central nervous system tumors in stillborns and infants. Epidemiological considerations. J Neurooncol 2(2):113–116
Agerlin N, Gjerris F, Brincker H, Haase J, Laursen H, Moller KA et al (1999) Childhood medulloblastoma in Denmark 1960-1984. A population-based retrospective study. Childs Nerv Syst 15(1):29–36 (discussion, 37)
Chan MY, Teo WY, Seow WT, Tan AM (2007) Epidemiology, management and treatment outcome of medulloblastoma in Singapore. Ann Acad Med Singapore 36(5):314–318
Farinotti M, Ferrarini M, Solari A, Filippini G (1998) Incidence and survival of childhood CNS tumours in the Region of Lombardy, Italy. Brain 121(Pt 8):1429–1436
Feltbower RG, Picton S, Bridges LR, Crooks DA, Glaser AW, McKinney PA (2004) Epidemiology of central nervous system tumors in children and young adults (0-29 years), Yorkshire, United Kingdom. Pediatr Hematol Oncol 21(7):647–660
Johannesen TB, Langmark F, Lote K (2003) Cause of death and long-term survival in patients with neuro-epithelial brain tumours: a population-based study. Eur J Cancer 39(16):2355–2363
McNeil DE, Coté TR, Clegg L, Rorke LB (2002) Incidence and trends in pediatric malignancies medulloblastoma/primitive neuroectodermal tumor: a SEER update. Surveillance epidemiology and end results. Med Pediatr Oncol 39(3):190–194
Kadri H, Mawla AA, Murad L (2005) Incidence of childhood brain tumors in Syria (1993-2002). Pediatr Neurosurg 41(4):173–177
Lang O, Kondas O, Torok S, Hauser P, Bognar L, Schuler D (2002) [Incidence of pediatric brain tumors in Hungary between 1989 and 1999]. Orv Hetil 143(9):451–454 [Article in Hungarian]
Chi JG, Khang SK (1989) Central nervous system tumors among Koreans—a statistical study on 697 cases. J Korean Med Sci 4(2):77–90
Roberts RO, Lynch CF, Jones MP, Hart MN (1991) Medulloblastoma: a population-based study of 532 cases. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 50(2):134–144
Di Rocco C, Iannelli A, Papacci F, Tamburrini G (1997) Prognosis of medulloblastoma in infants. Childs Nerv Syst 13(7):388–396
Koeller KK, Rushing EJ (2003) From the archives of the AFIP: medulloblastoma: a comprehensive review with radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiographics 23(6):13–37
Ayan I, Kebudi R, Bayindir C, Darendeliler E (1997) Microscopic local leptomeningeal invasion at diagnosis of medulloblastoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 39(2):461–466
Laerum OD (1997) Local spread of malignant neuroepithelial tumors. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 139(6):515–522
Mulhern RK, Merchant TE, Gajjar A, Reddick WE, Kun LE (2004) Late neurocognitive sequelae in survivors of brain tumours in childhood. Lancet Oncol 5(7):399–408
Palmer SL, Reddick WE, Gajjar A (2007) Understanding the cognitive impact on children who are treated for medulloblastoma. J Pediatr Psychol 32(9):1040–1049
Spiegler BJ, Bouffet E, Greenberg ML, Rutka JT, Mabbott DJ (2004) Change in neurocognitive functioning after treatment with cranial radiation in childhood. J Clin Oncol 22(4):706–713
Tamaki M, McDonald W, Amberger V, Moore E, DelMaestro R (1997) Implantation of C6 astrocytoma cells into collagen type I gels: invasive, proliferative and enzymatic characterizations. J Neurosurg 87(4):602–609
Vaithilingham IS, McDonald W, Stroude EC, Cook RA, DelMaestro R (1992) Proteolytic activity during growth of C6 astrocytoma in the murine spheroid implantation model. Can J Neurol Sci 19(1):17–22
Engbraaten R, Schwachenwald H, Valen H, Bjerkvig R, Laerum OD, Backlund EO (1992) Effects of high and low single dose irradiation on glioma spheroid invasion into normal rat brain tissue in vitro. Anticancer Res 12(5):1501–1506
Mohanam S, Wang SW, Rayford A, Yamamoto M, Sawaya R, Nakajima M et al (1995) Expression of tissue inhibitors of metalloproteases: negative regulators of human glioblastoma invasion in vivo. Clin Exp Metastasis 13(1):57–62
Sivaparvathi M, McCutcheon I, Sawaya R, Nicolson GL, Rao JS (1996) Expression of cysteine protease inhibitors in human gliomas and meningiomas. Clin Exp Metastasis 14(4):344–350
Rempel SA, Rosenblum ML, Mikkelsen T, Yan PS, Ellis KD, Golembieski WA et al (1994) Cathepsin B expression and localization in glioma progression and invasion. Cancer Res 54(23):6027–6031
Sivaparvathi M, Sawaya R, Chintala SK, Go Y, Gokaslan ZL, Rao JS (1996) Expression of cathepsin D during the progression of human gliomas. Neurosci Lett 208(3):171–174
Mikkelsen T, Yan PS, Ho KL, Sameni M, Sloane BF, Rosenblum ML (1995) Immunolocalization of cathepsin B in human glioma: implications for tumor invasion and angiogenesis. J Neurosurg 83(2):285–290
Sivaparvathi M, Yamamoto M, Nicolson GL, Gokaslan ZL, Fuller GN, Liotta LA et al (1996) Expression and immunolocalization of cathepsin L during the progression of human gliomas. Clin Exp Metastasis 14(1):27–34
Uhm JH, Dooley NP, Villemure JG, Yong VW (1997) Mechanisms of glioma invasion: role of matrix metalloproteases. Can J Neurol Sci 24(1):3–15
Giese A, Loo MA, Tran N, Haskett D, Coons SW, Berens ME (1996) Dichotomy of astrocytoma migration and proliferation. Int J Cancer 67(2):275–282
Thorsen F, Enger PO, Wang J, Bjerkvig R, Pedersen PH (2007) Human glioblastoma biopsy spheroids xenografted into the nude rat brain show growth inhibition after stereotactic radiosurgery. J Neurooncol 82(1):1–10
Keles GE, Berger MS, Srinivasin J, Kolstoe DD, Bobola MS, Silber JR (1995) Establishment and characterization of four human medulloblastoma-derived cell lines. Oncol Res 7(10–11):493–503
Rooprai HK, Kyriazis I, Nuttall RK, Edwards DR, Zicha D, Aubyn D et al (2007) Inhibition of invasion and induction of apoptosis by selenium in human malignant brain tumour cells in vitro. Int J Oncol 30(5):1263–1271
Jacobs W, Mikkelsen T, Smith R, Nelson K, Rosenblum ML, Kohn EC (1997) Inhibitory effects of CAI in glioblastoma growth and invasion. J Neurooncol 32(2):93–101
Louis DN, Posner JB, Kaplan R, Jacobs T, all other members of the Brain Tumor Progress Review Group (2000) Report of the Brain Tumor Progress Review Group
Peris-Bonet R, Martinez-Garcia C, Lacour B, Petrovich S, Giner-Ripoll B, Navajas A et al (2006) Childhood central nervous system tumours—incidence and survival in Europe (1978-1997): report from Automated Childhood Cancer Information System project. Eur J Cancer 42(13):2064–2080
Hong TS, Mehta MP, Boyett JM, Donahue B, Rorke LB, Yao MS et al (2004) Patterns of failure in supratentorial primitive neuroectodermal tumors treated in Children’s Cancer Group Study 921, a phase III combined modality study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 60(1):204–213
Paulino AC, Cha DT, Barker JL Jr, Lo S, Manera RB (2004) Patterns of failure in relation to radiotherapy fields in supratentorial primitive neuroectodermal tumor. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 58(4):1171–1176
Kaatsch P, Rickert CH, Kuhl J, Schuz J, Michaelis J (2001) Population-based epidemiologic data on brain tumors in German children. Cancer 92(12):3155–3164
Magnani C, Aareleid T, Viscomi S, Pastore G, Berrino F, EUROCARE Working Group (2001) Variation in survival of children with central nervous system (CNS) malignancies diagnosed in Europe between 1978 and 1992: the EUROCARE study. Eur J Cancer 37(6):711–721
Gilles FH, Sobel EL, Leviton A, Tavare CJ (1998) Clusters of histologic characteristics in children with infratentorial neuroglial tumors. The Childhood Brain Tumor Consortium. J Neurooncol 39(1):51–63
Ibayashi N, Herman M, Boyd JC, Rubinstein LJ (1990) Relationship of invasiveness to proliferating activity and to cytoskeletal protein production in human neuroepithelial tumors maintained in an organ culture system: use of human cortex and dura as supporting matrices. Neurosurgery 26(4):629–637
Kaczarek E, Zapf S, Bouterfa H, Tonn JC, Westphal M, Giese A (1999) Dissecting glioma invasion: interrelation of adhesion, migration and intercellular contacts determine the invasive phenotype. Int J Dev Neurosci 17(5–6):625–641
Massova I, Kotra LP, Fridman R, Mobashery S (1998) Matrix metalloproteinases: structures, evolution, and diversification. FASEB J 12(12):1075–1095
Malemud CJ (2006) Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in health and disease: an overview. Front Biosci 11:1696–1701
Seiki M (2003) Membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase: a key enzyme for tumor invasion. Cancer Lett 194(1):1–11
Golubkov VS, Strongin AY (2007) Proteolysis-driven oncogenesis. Cell Cycle 6(2):147–150
Liang Y, Diehn M, Bollen AW, Israel MA, Gupta N (2008) Type I collagen is overexpressed in medulloblastoma as a component of tumor microenvironment. J Neurooncol 86(2):133–141
Keppler D, Sameni M, Moin K, Mikkelsen T, Diglio CA, Sloane BF (1996) Tumor progression and angiogenesis: cathepsin B & co. Biochem Cell Biol 74(6):799–810
Beliveau R, Delbecchi L, Beaulieu E, Mousseau N, Kachra Z, Berthelet F et al (1999) Expression of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in human brain tumors. Ann N Y Acad Sci 886:236–239
Fillmore HL, VanMeter TE, Broaddus WC (2001) Membrane-type matrix metalloproteinases (MT-MMPs): expression and function during glioma invasion. J Neurooncol 53(2):187–202
Lampert K, Machein U, Machein MR, Conca W, Peter HH, Volk B (1998) Expression of matrix metalloproteases and their tissue inhibitors in human brain tumors. Am J Pathol 153(2):429–437
Nuttall RK, Pennington CJ, Taplin J, Wheal A, Yong VW, Forsyth PA et al (2003) Elevated membrane-type matrix metalloproteinases in gliomas revealed by profiling proteases and inhibitors in human cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res 1(5):333–345
Ozen O, Krebs B, Hemmerlein B, Pekrun A, Kretzschmar H, Herms J (2004) Expression of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in medulloblastomas and their prognostic relevance. Clin Cancer Res 10(14):4746–4753
Rooprai HK, McCormick D (1997) Proteases and their inhibitors in human brain tumors: a review. Anticancer Res 17(6B):4151–4162
Tonn JC, Kerkau S, Hanke A, Bouterfa H, Mueller JG, Wagner S et al (1999) Effect of synthetic matrix-metalloproteinase inhibitors on invasive capacity and proliferation of human malignant gliomas in vitro. Int J Cancer 80(5):764–772
VanMeter TE, Rooprai HK, Kibble MM, Fillmore HL, Broaddus WC, Pilkington GJ (2001) The role of matrix metalloproteinase genes in glioma invasion: co-dependent and interactive proteolysis. J Neurooncol 53(2):213–235
Yamamoto M, Ueno Y, Hayashi S, Fukushima T (2002) The role of proteolysis in tumor invasiveness in glioblastoma and metastatic brain tumors. Anticancer Res 22(6C):4265–4268
Kim SY, Jung SH, Kim HS (2005) Curcumin is a potent broad spectrum inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase gene expression in human astroglioma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 337(2):510–516
Annabi B, Rojas-Sutterlin S, Laflamme C, Lachambre MP, Rolland Y, Sartelet H et al (2008) Tumor environment dictates medulloblastoma cancer stem cell expression and invasive phenotype. Mol Cancer Res 6(6):907–916
Acknowledgements
We express our sincere appreciation to Dr. John R. Silber of the University of Washington, in Seattle, and to Dr. Richard Youle of the National Institutes of Health, in Washington, DC for kindly providing us with four of the five cell lines used in this research; and to Dr. William Stetler-Stevenson, of the Center for Cancer Research, Bethesda MD, for providing us with MMP-1 and -2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ranger, A., McDonald, W., Moore, E. et al. The invasiveness of five medulloblastoma cell lines in collagen gels. J Neurooncol 96, 181–189 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-009-9962-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-009-9962-9