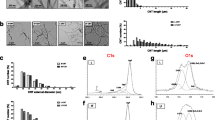
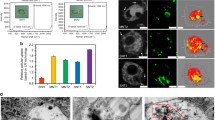
Abstract
The biological response to pristine and annealed multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT) was assessed on murine macrophages (RAW 264.7). First, the physicochemical features of the as-produced MWCNT and annealed at 2125 °C for 1 h were fully characterized. A decrease in structural defects, hydrophobicity and catalytic impurities was detected after annealing. Thereafter, their impact on cytotoxicity, oxidative stress, and pro-inflammatory response was investigated at concentrations ranging from 15 to 120 µg mL−1. No effect of the 2125 °C treatment was detected on the cytotoxicity. In contrast, the annealed carbon nanotubes showed a significant increase of the pro-inflammatory response. We assumed that this behavior was due to the reduction in structural defects that may modify the layer of adsorbed biomolecules. Surprisingly, the purification of metallic catalysts did not have any significant impact on the oxidative stress. We suggested that the structural improvements from the 2125 °C treatment can decrease the carbon nanotube scavenging capacity and thus allow a higher free radical release which may counterbalance the decrease of oxidative stress due to a lower content of metallic impurities.
Graphical Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- B.E.T.:
-
Brunauer–Emmet–Teller method
- CNT:
-
Carbon nanotubes
- CNTa:
-
Annealed carbon nanotubes
- CVD:
-
Chemical vapor deposition
- DCF:
-
2′,7′-Dichlorodihydrofluorescein
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium
- FEG-SEM:
-
Field-emission gun-scanning electron microscopy
- HR-TEM:
-
High-resolution transmission electron microscopy
- H2DCF-DA:
-
2′7′-Dichlorodihydrofluorescein
- LDH:
-
Lactate dehydrogenase
- MWCNT:
-
Multi-walled carbon nanotubes
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- TDS:
-
Thermal desorption
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor α
- XPS:
-
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy
- XRD:
-
X-ray diffraction
References
Baughman RH, Zakhidov AA, de Heer WA (2002) Carbon nanotubes—the route toward applications. Science 297:787–792. doi:10.1126/science.1060928
Belin T, Epron F (2005) Characterization methods of carbon nanotubes: a review. Mater Sci Eng B Solid State Mater Adv Technol 119:105–118. doi:10.1016/j.mseb.2005.02.046
Boncel S, Koziol KKK (2014) Enhanced graphitization of c-CVD grown multi-wall carbon nanotube arrays assisted by removal of encapsulated iron-based phases under thermal treatment in argon. Appl Surf Sci 301:488–491. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.02.108
Bougrine A, Dupont-Pavlovsky N, Naji A et al (2001) Influence of high temperature treatments on single-walled carbon nanotubes structure, morphology and surface properties. Carbon 39:685–695. doi:10.1016/S0008-6223(00)00165-2
Brown DM, Kinloch IA, Bangert U et al (2007) An in vitro study of the potential of carbon nanotubes and nanofibres to induce inflammatory mediators and frustrated phagocytosis. Carbon 45:1743–1756. doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2007.05.011
Bussy C, Pinault M, Cambedouzou J et al (2012) Critical role of surface chemical modifications induced by length shortening on multi-walled carbon nanotubes-induced toxicity. Part Fibre Toxicol 9:46. doi:10.1186/1743-8977-9-46
Cai X, Ramalingam R, Wong HS et al (2013) Characterization of carbon nanotube protein corona by using quantitative proteomics. Nanomed Nanotechnol Biol Med 9:583–593. doi:10.1016/j.nano.2012.09.004
Casey A, Herzog E, Davoren M et al (2007) Spectroscopic analysis confirms the interactions between single walled carbon nanotubes and various dyes commonly used to assess cytotoxicity. Carbon 45:1425–1432. doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2007.03.033
Chen J, Shan JY, Tsukada T et al (2007) The structural evolution of thin multi-walled carbon nanotubes during isothermal annealing. Carbon 45:274–280. doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2006.09.028
Cheng C, Müller KH, Koziol KKK et al (2009) Toxicity and imaging of multi-walled carbon nanotubes in human macrophage cells. Biomaterials 30:4152–4160. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2009.04.019
De Volder MFL, Tawfick SH, Baughman RH, Hart AJ (2013) Carbon nanotubes: present and future commercial applications. Science 339:535–539. doi:10.1126/science.1222453
Dutta D, Sundaram SK, Teeguarden JG et al (2007) Adsorbed proteins influence the biological activity and molecular targeting of nanomaterials. Toxicol Sci 100:303–315. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfm217
Ebbesen TW, Takada T (1995) Topological and sp3 defect structures in nanotubes. Carbon 33:973–978. doi:10.1016/0008-6223(95)00025-9
Exley C (2004) The pro-oxidant activity of aluminum. Free Radic Biol Med 36:380–387. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2003.11.017
Fenoglio I, Tomatis M, Lison D et al (2006) Reactivity of carbon nanotubes: free radical generation or scavenging activity? Free Radic Biol Med 40:1227–1233. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2005.11.010
Fenoglio I, Greco G, Tornatis M et al (2008) Structural defects play a major role in the acute lung toxicity of multiwall carbon nanotubes: physicochemical aspects. Chem Res Toxicol 21:1690–1697. doi:10.1021/tx800100s
Figarol A, Pourchez J, Boudard D et al (2014) Biological response to purification and acid functionalization of carbon nanotubes. J Nanoparticle Res 16:1–12. doi:10.1007/s11051-014-2507-y
Fiorito S, Monthioux M, Psaila R et al (2009) Evidence for electro-chemical interactions between multi-walled carbon nanotubes and human macrophages. Carbon 47:2789–2804. doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2009.06.023
Forest V, Figarol A, BOUDARD D et al (2015) Adsorption of lactate dehydrogenase enzyme on carbon nanotubes: how to get accurate results about the cytotoxicity of these nanomaterials. Langmuir. doi:10.1021/acs.langmuir.5b00631
Fröhlich E, Meindl C, Höfler A, et al (2012) Combination of small size and carboxyl functionalisation causes cytotoxicity of short carbon nanotubes. Nanotoxicology 1–14. doi: 10.3109/17435390.2012.729274
Fubini B, Zanetti G, Altilia S et al (1999) Relationship between surface properties and cellular responses to crystalline silica: studies with heat-treated cristobalite. Chem Res Toxicol 12:737–745. doi:10.1021/tx980261a
Galano A, Francisco-Marquez M, Martinez A (2010) Influence of point defects on the free-radical scavenging capability of single-walled carbon nanotubes. J Phys Chem C 114:8302–8308. doi:10.1021/jp101544u
Ge C, Li Y, Yin J-J et al (2012) The contributions of metal impurities and tube structure to the toxicity of carbon nanotube materials. NPG Asia Mater 4:e32. doi:10.1038/am.2012.60
Hirano S, Kanno S, Furuyama A (2008) Multi-walled carbon nanotubes injure the plasma membrane of macrophages. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 232:244–251. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2008.06.016
Iijima S (1991) Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Nature 354:56–58. doi:10.1038/354056a0
Jiang J, Oberdorster G, Biswas P (2009) Characterization of size, surface charge, and agglomeration state of nanoparticle dispersions for toxicological studies. J Nanoparticle Res 11:77–89. doi:10.1007/s11051-008-9446-4
Kagan VE, Tyurina YY, Tyurin VA et al (2006) Direct and indirect effects of single walled carbon nanotubes on RAW 264.7 macrophages: role of iron. Toxicol Lett 165:88–100. doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2006.02.001
Kapralov AA, Feng WH, Amoscato AA et al (2012) Adsorption of surfactant lipids by single-walled carbon nanotubes in mouse lung upon pharyngeal aspiration. ACS Nano 6:4147–4156. doi:10.1021/nn300626q
Kayat J, Gajbhiye V, Tekade RK, Jain NK (2011) Pulmonary toxicity of carbon nanotubes: a systematic report. Nanomed Nanotechnol Biol Med 7:40–49. doi:10.1016/j.nano.2010.06.008
Lanone S, Andujar P, Kermanizadeh A, Boczkowski J (2013) Determinants of carbon nanotube toxicity. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 65:2063–2069. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2013.07.019
Leshuai W, Zhang LZ (2007) Biological interactions of functionalized single-wall carbon nanotubes in human epidermal keratinocytes. Int J Toxicol 26:103–113. doi:10.1080/10915810701225133
Liu X, Sen S, Liu J et al (2011) antioxidant deactivation on graphenic nanocarbon surfaces. Small 7:2775–2785. doi:10.1002/smll.201100651
Lynch I, Dawson KA (2008) Protein–nanoparticle interactions. Nano Today 3:40–47. doi:10.1016/S1748-0132(08)70014-8
Mahdi AA, Tripathi S, Neerja J, Hasan M (2010) Aluminium mediated oxidative stress: possible relationship to cognitive impairment of Alzheimer’s type. Ann Neurosci 13:18–24. doi:10.5214/112
Mao H, Chen W, Laurent S et al (2013) Hard corona composition and cellular toxicities of the graphene sheets. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 109:212–218. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2013.03.049
Muller J, Huaux F, Moreau N et al (2005) Respiratory toxicity of multi-wall carbon nanotubes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 207:221–231. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2005.01.008
Muller J, Huaux F, Fonseca A et al (2008) Structural defects play a major role in the acute lung toxicity of multiwall carbon nanotubes: toxicological aspects. Chem Res Toxicol 21:1698–1705. doi:10.1021/tx800101p
Nagai H, Okazaki Y, Chew SH et al (2011) Diameter and rigidity of multiwalled carbon nanotubes are critical factors in mesothelial injury and carcinogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:E1330–E1338. doi:10.1073/pnas.1110013108
Peigney A, Laurent C, Flahaut E et al (2001) Specific surface area of carbon nanotubes and bundles of carbon nanotubes. Carbon 39:507–514. doi:10.1016/S0008-6223(00)00155-X
Pinault M, Mayne-L’Hermite M, Reynaud C et al (2004) Carbon nanotubes produced by aerosol pyrolysis: growth mechanisms and post-annealing effects. Diam Relat Mater 13:1266–1269. doi:10.1016/j.diamond.2003.12.015
Porter DW, Hubbs AF, Mercer RR et al (2010) Mouse pulmonary dose- and time course-responses induced by exposure to multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Toxicology 269:136–147. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2009.10.017
Rakotomalala R (2005) TANAGRA: un logiciel gratuit pour l’enseignement et la recherche. RNTI-E-3, pp 697–702
Ruipérez F, Mujika JI, Ugalde JM et al (2012) Pro-oxidant activity of aluminum: promoting the Fenton reaction by reducing Fe(III) to Fe(II). J Inorg Biochem 117:118–123. doi:10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2012.09.008
Schinwald A, Murphy FA, Prina-Mello A et al (2012) The threshold length for fiber-induced acute pleural inflammation: shedding light on the early events in asbestos-induced mesothelioma. Toxicol Sci 128:461–470. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfs171
Schrurs F, Lison D (2012) Focusing the research effort. Nat Nanotechnol 7:546–548
Shvedova AA, Kisin E, Murray AR et al (2008) Inhalation vs. aspiration of single-walled carbon nanotubes in C57BL/6 mice: inflammation, fibrosis, oxidative stress, and mutagenesis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 295:L552–L565. doi:10.1152/ajplung.90287.2008
Shvedova AA, Kisin ER, Porter D et al (2009) Mechanisms of pulmonary toxicity and medical applications of carbon nanotubes: two faces of Janus? Pharmacol Ther 121:192–204. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2008.10.009
Shvedova AA, Pietroiusti A, Fadeel B, Kagan VE (2012) Mechanisms of carbon nanotube-induced toxicity: focus on oxidative stress. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 261:121–133. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2012.03.023
Simon-Deckers A, Gouget B, Mayne-L’Hermite M et al (2008) In vitro investigation of oxide nanoparticle and carbon nanotube toxicity and intracellular accumulation in A549 human pneumocytes. Toxicology 253:137–146. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2008.09.007
Tsukahara T, Haniu H (2011) Cellular cytotoxic response induced by highly purified multi-wall carbon nanotube in human lung cells. Mol Cell Biochem 352:57–63. doi:10.1007/s11010-011-0739-z
Vietti G, Ibouraadaten S, Palmai-Pallag M et al (2013) Towards predicting the lung fibrogenic activity of nanomaterials: experimental validation of an in vitro fibroblast proliferation assay. Part Fibre Toxicol 10:52
Wörle-Knirsch JM, Pulskamp K, Krug HF (2006) Oops they did it again! Carbon nanotubes hoax scientists in viability assays. Nano Lett 6:1261–1268. doi:10.1021/nl060177c
Xia W, Wang Y, Bergsträßer R et al (2007) Surface characterization of oxygen-functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes by high-resolution X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and temperature-programmed desorption. Appl Surf Sci 254:247–250. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2007.07.120
Yamamoto G, Shirasu K, Nozaka Y et al (2013) Structure–property relationships in thermally-annealed multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Carbon. doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2013.08.061
Zhang X, Zhu Y, Li J et al (2011) Tuning the cellular uptake and cytotoxicity of carbon nanotubes by surface hydroxylation. J Nanoparticle Res 13:6941–6952. doi:10.1007/s11051-011-0603-9
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dominique Goeuriot and Christophe Meunier from the center of structures and materials sciences (EMSE, St-Etienne) for their help regarding the annealing treatment.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Figarol, A., Pourchez, J., Boudard, D. et al. Thermal annealing of carbon nanotubes reveals a toxicological impact of the structural defects. J Nanopart Res 17, 194 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-015-2999-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-015-2999-0