Abstract
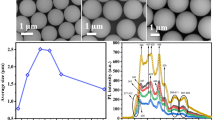
An experimental study of the molecular O2 diffusion process in high purity non-porous silica nanoparticles having 50 m2/g BET specific surface and 20 nm average radius was carried out in the temperature range from 127 to 177 °C at O2 pressure in the range from 0.2 to 66 bar. The study was performed by measuring the volume average interstitial O2 concentration by a Raman and photoluminescence technique using a 1,064 nm excitation laser to detect the singlet to triplet emission at 1,272 nm of the molecular oxygen in silica. A dependence of the diffusion kinetics on the O2 absolute pressure, in addition to temperature dependence, was found. The kinetics can be fit by the solution of Fick’s diffusion equation using an effective diffusion coefficient related to temperature and O2 external pressure. The fit results have evidenced that the temperature and pressure dependencies can be disentangled and that the pressure effects are more pronounced at lower temperatures. An Arrhenius temperature law is determined for the effective diffusion coefficient and the activation energy and pre-exponential factor are found in the explored experimental range. The reported findings have not been evidenced previously in the studies in bulk silica and could probably be originated by the reduced spatial extension of the considered system.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agnello S, Cannas M, Vaccaro L, Vaccaro G, Gelardi FM, Leone M, Militello V, Boscaino R (2011) Near-infrared emission of O2 embedded in amorphous SiO2 nanoparticles. J Phys Chem C 115:12831–12835. doi:10.1021/jp2035554. Accessed 2013
Burns A, Ow H, Weisner U (2006) Fluorescent core–shell silica nanoparticles: towards “labs on a particle” architectures for nanobiotechnology. Chem Soc Rev 35:1028–1042
Buscarino G, Ardizzone V, Vaccaro G, Agnello S, Gelardi FM (2010) Atomic force microscopy and raman investigation on the synthesis process of amorphous SiO2 nanoparticles. J Appl Phys 108:074314 1–9
Correa-Duarte MA, Giersig M, Liz-Marzán LM (1998) Stabilization of CdS semiconductor nanoparticles against photodegradation by a silica coating procedure. Chem Phys Lett 286:497–501
Crank J (1979) The mathematics of diffusion: second edition. Clarendon, Oxford
Deal BE, Grove AS (1965) General relationship for the thermal oxidation of silicon. J Appl Phys 36:3770–3776
Doremus RH (ed) (2002) Diffusion of reactive molecules in solids and melts. Wiley, New York
Degussa (2001) Basic characteristics of aerosil, 4th edn. Degussa, Frankfurt
Evonik AG (2010) Evonik industries online catalog. http://www.aerosil.com/product/aerosil/en/products/hydrophilic-fumed-silica/pages/default.aspx. Accessed 2013
Galeener FL (1982) Planar rings in glasses. Solid State Commun 44:1037–1040
Geissberger AE, Galeener FL (1983) Raman studies of vitreous SiO2 versus fictive temperature. Phys Rev B 28:3266–3271
Iovino G, Agnello S, Gelardi FM, Boscaino R (2012) O2 diffusion in amorphous SiO2 nanoparticles probed by outgassing. J Phys Chem 116:11351–11356
Kajihara K, Kamioka H, Hirano M, Miura T, Skuja L, Hosono H (2005) Interstitial oxygen molecules in amorphous SiO2. iii. Measurements of dissolution kinetics, diffusion coefficient, and solubility by infrared photoluminescence. J Appl Phys 98:0135291–0135297
Kajihara K, Miura T, Kamioka H, Aiba A, Uramoto M, Morimoto Y, Hirano M, Skuja L, Hosono H (2008) Diffusion and reactions of interstitial oxygen species in amorphous SiO2: A review. J Non-Cryst Sol 354:224–232
Kajihara K, Miura T, Kamioka H, Hirano M, Skuja L, Hosono H (2009) Oxygen exchange at the internal surface of amorphous SiO2 studied by photoluminescence of isotopically labeled oxygen molecules. Phys Rev Lett 102:175502 1–4
Kajihara K, Miura T, Kamioka H, Hirano M, Skuja L, Hosono H (2011) Exchange between interstitial oxygen molecules and network oxygen atoms in amorphous SiO2 studied by 18O isotope labeling and infrared photoluminescence spectroscopy. Phys Rev B 83:064202–064212
Lu Y, Yin Y, Li ZY, Xia Y (2002) Synthesis and self-assembly ofau@SiO2 core–shell colloids. Nanoletters 2:785–788
Nalwa HS (ed) (2001) Silicon based materials and devices. Academic Press, San Diego
Noginov MA, Zhu G, Belgrave AM, Bakker R, Shalaev VM, Narimanov EE, Stout S, Herz E, Suteewong T, Wiesner U (2009) Demonstration of a spaser-based nanolaser. Nature 460:1110–1113
Norton F (1961) Permeation of gaseous oxygen through vitreous silica. Nature 191:701
Ohta H, Watanabe T, Ohdomari I (2008) Potential energy landscape of an interstitial O2 molecule in a SiO2 film near the SiO2/Si(001) interface. Phys Rev B 78:155326 1–7
Orlandini S, Meloni S, Ippolito M, Colombo L (2010) Mechanism of self-diffusion in stoichiometric and substoichiometric amorphous silicon dioxide. Phys Rev B 81:014203 1–8
Pacchioni G, Skuja L, Griscom DL (eds) (2000) Defects in SiO2 and related dielectrics: science and technology. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht
Skuja L, Guttler B (1996) Detection of interstitial oxygen molecules in SiO2 glass by a direct photoexcitation of the infrared luminescence of singlet O2. Phys Rev Lett 77:2093–2096
Skuja L, Guttler B, Schiel D, Silin AR (1998) Quantitative analysis of the concentration of interstitial O2 molecules in SiO2 glass using luminescence and raman spectroscopy. J Appl Phys 83:6106–6110
Syutkin V, Korolev VV (2011) Heterogeneity length scale for oxygen diffusion in glassy squalane. J Non-Cryst Sol 357:3781–3784
Watanabe T, Tatsumura K, Ohdomari I (2006) New linear-parabolic rate equation for thermal oxidation of silicon. Phys Rev Lett 96:196102 1–4
Yang Y, Jing L, Yu X, Yan D, Gao M (2007) Coating aqueous quantum dots with silica via reverse microemulsion method: toward size-controllable and robust fluorescent nanoparticles. Chem Mat 19:4123–4128
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the people of the LAMP group (http://www.fisica.unipa.it/amorphous/) for useful discussions and partial financial support by University of Palermo project FFR 2012/2013. Technical assistance by G. Napoli and G. Tricomi is acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Special Issue Editors: Juan Manuel Rojo, Vasileios Koutsos
This article is part of the topical collection on Nanostructured Materials 2012
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iovino, G., Agnello, S. & Gelardi, F.M. Dependence of O2 diffusion dynamics on pressure and temperature in silica nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res 15, 1876 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-1876-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-1876-y