Abstract
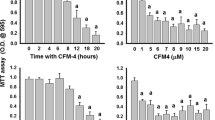
The study aimed to correlate cell proliferation inhibition with oxidative stress and p53 protein expression in cancerous cells. Hydroxyapatite (HAP) (Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2) is the essential component of inorganic composition in human bone. It has been found to have obvious inhibitory function on growth of many kinds of tumor cells and its nanoparticle has stronger anti-cancerous effect than macromolecule microparticles. Human breast cancer cells (MCF-7) were cultured and treated with HAP nanoparticles at various concentrations. Cells viability was detected with MTT colorimetric assay. The morphology of the cancerous cells was performed by transmission electron microscopy and the expression of a cell apoptosis related gene (p53) was determined by ELISA assay and flow cytometry (FCM). The intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) level in HAP exposed cells was measured by H2DCFDA staining. DNA damage was measured by single-cell gel electrophoresis assay. The statistical analysis was done by one way ANOVA. The cellular proliferation inhibition rate was significantly (p < 0.05) increasing in a dose-dependent manner of HAP nanoparticles. Cell apoptotic characters were observed after MCF-7 cells were treated by HAP nanoparticles for 48 h. Moreover, ELISA assay and FCM shows a dose-dependent activation of p53 in MCF-7 cells treated with nanoHAP. These causative factors of the above results may be justified by an overproduction of ROS. In this study, a significant (p < 0.05) increase in the level of intracellular ROS in HAP-treated cells was observed. This study shows that HAP inhibits the growth of human breast cancer MCF-7 cells as well as induces cell apoptosis. This study shows that HAP NPs Induce the production of intracellular reactive oxygen species and activate p53, which may be responsible for DNA damage and cell apoptosis.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balasundaram G, Sato M, Webster TJ (2006) Using hydroxyapatite nanoparticles and decreased crystallinity to promote osteoblast adhesion similar to functionalizing with RGD. Biomaterials 27:2798–2805
Bensaad K, Tsuruta A, Selak MA et al (2006) Tigar, a p-53 inducible regulator of glycolysis and apoptosis. Cell 126:107–120
Bootman MD, Collins TJ, Peppiatt CM, Prothero LS, MacKenzie L, De SP (2001) Calcium signalling: an overview. Semin Cell Develop Biol 12:3–10
Cao XY (2003) Effect on the hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and cell cycle treated with hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. China J Prev Treat 10:256–258
Cao XY, Qi ZT, Dai HI (2003) Cytogenic mechanism of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles on human hepatoma cell lines. J Wuhan Univ Technol Mater Sci Ed 18:66–68
Cardaci S, Filomeni G, Rotilio G, Ciriolo MR (2008) Reactive oxygen species mediate p53 activation and apoptosis induced by sodium nitroprusside in SHSY5Y cells. Mol Pharmacol 74:1234–1245
Chen P, Dai H, Han YC, Yin M, Li S (2008) Effect of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles on K562 cells in vitro. J Wuhan Univ Technol Mater Sci Ed 23:222–224
Chowdhury R, Chowdhury S, Roychoudhury P, Mandal C, Chaudhuri K (2009) Arsenic induced apoptosis in malignant melanoma cells is enhanced by menadione through ROS generation, p38 signaling and p53 activation. Apoptosis 14:108–123
Christensen KA, Myers JT, Swanson JA (2002) pH-dependent regulation of lysosomal calcium in macrophages. J Cell Sci 115:599–607
Elbekai RH, El-Kadi AOS (2005) The role of oxidative stress in the modulation of aryl hydrocarbon receptor-regulated genes by As3+, Cd2+, and Cr6+. Free Radic Biol Med 39:1499–1511
Elliot JC, Mackie PE, Young RA (1973) Monoclinic hydroxyapatite. Science 180:1055
Fotakis G, Cemeli E, Anderson D, Timbrell JA (2005) Cadmium chloride-induced DNA and lysosomal damage in a hepatoma cell line. Toxicol In Vitro 19:481–489
Fu Q, Zhou N, Huang W, Wang D, Zhang L, Li H (2005) Effects of nano HAP on biological and structural properties of glass bone cement. J Biomed Mater Res A 2:156–163
Gogvadze V, Orrenius S (2006) Mitochondrial regulation of apoptotic cell death. Chem Biol Interact 163(1–2):4–14
Guo D, Wu C, Li X, Jiang H, Wang X, Chen B (2008) In vitro cellular uptake and cytotoxic effect of functionalized nickel nanoparticles on leukemia cancer cells. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 8:2301–2307
Hepler PK (1996) The role of calcium in cell division. Cell Calcium 16:322–330
Hu S, Li S, Yan Y, Wang Y, Cao XY (2005) Apoptosis of cancer cells induced by HAP nanoparticles. J Wuhan Univ Technol Mater Sci Ed 20:13–15
Kerr JF (2002) History of the events leading to the formulation of the apoptosis concept. Toxicology 181:471–474
Kyprianou N, English HF, Isaacs JT (1988) Activation of Ca2+, Mg2+ dependent endonuclease an early event in castration induced prostatic cell death. Prostate 13:103–107
Lai H, Singh NP (1996) Single and double strand breaks in rat’s brain cells after acute exposure to radio frequency electromagnetic radiation. Int J Radiat Biol 69:513–521
Li N, Sioutas C, Cho A, Schmitz D, Misra C, Sempf J, Wang M, Oberley T, Froines J, Nel A (2003) Ultrafine particulate pollutants induce oxidative stress and mitochondrial damage. Environ Health Perspect 111(4):455–460
Li J, Yin Y, Yao F, Zhang L, Yao K (2008) Effect of nano and micro-hydroxyapatite/chitosan–gelatin network film on human gastric cancer cells. Mater Lett 62:3220–3223
Liu ZS, Tang SL, Ai ZL (2003) Effects of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles on proliferation and apoptosis of human hepatoma BEL-7402 cells. World J Gastroenterol 9:1968–1971
Liu X, Qin D, Cui Y, Chen L, Li H, Chen Z, Gao L, Li Y, Liu J (2010) The effect of calcium phosphate nanoparticles on hormone production and apoptosis in human granulose cells. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 8:32–40
Magrez A, Kasas S, Salicio V (2006) Cellular toxicity of carbon based nanomaterials. Nano Lett 6:1121–1125
Maitra A (2005) Calcium phosphate nanoparticles: second generation non viral vectors in gene therapy. Expert Rev Mol Diagn 5:893–905
Moroni A, Pegreffi F, Cadossi M, Hoang-Kim A, Lio V, Giannini S (2005) Hydroxyapatite-coated external fixation pins. Expert Rev Med Devices 2:465–471
Mroz RM, Schins RP, Li H, Jimenez LA, Drost EM, Holownia A, MacNee W, Donaldson K (2008) Nanoparticle-driven DNA damage mimics irradiation related carcinogenesis pathways. Eur Respir J 31:241–251
Nicotera P, Zhivotovsky B, Orrenius S (1994) Nuclear calcium transport and the role of calcium in apoptosis. Cell Calcium 16:279–288
Orrenius S, McCabe MJ, Nicotera P (1992) Ca2+ dependent mechanism of cytotoxicity and programmed cell death. Toxicol Lett 64:357–364
Ostrakhovitch EA, Cherian MG (2005) Role of p53 and reactive oxygen species in apoptotic response to copper and zinc in epithelial breast cancer cells. Apoptosis 10:111–121
Pathi SP, Lin DDW, Dorvee JR, Estroff LA, Fischbach C (2011) Hydroxyapatite nanoparticle-containing scaffolds for the study of breast cancer bone metastasis. Biomaterials 32:5112–5122
Paulraj R, Behari J (2006) Single strand DNA breaks in rat brain cells exposed to microwave radiation. Mutat Res 596:76–80
Queiroz AC, Santos JD (2005) Development of a system to adsorb drugs onto calcium phosphate materials. J Mater Sci Mater Med 16:641–646
Shi Z, Huang X, Cai Y, Tang R, Yang D (2009) Size effect of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles on proliferation and apoptosis of osteoblast-like cells. Acta Biomater 5:338–345
Shiraishi T, Pankratova S, Nielsen PE (2005) Calcium ions effectively enhance the effect of antisense peptide nucleic acids conjugated to cationic tat and oligo arginine peptides. Chem Biol 12:923–929
Stoeckel D, Pelton A, Duerig T (2004) Self-expanding nitinol stents: material and design considerations. Eur Radiol 14:292–301
Sundarsanan K, Young RA (1989) Significant precision in crystal structural details: Holly Springs hydroxyapatite. Acta Crystallogr B 25:1534–1543
Tian Q, Streuli M, Saito H, Schlossman SF, Paul A (1991) A polyadenylate binding protein localized to the granules of cytolytic lymphocytes induces DNA fragmentation in target cells. Cell 67:629–639
Tice RR, Agurell E, Anderson E et al (2000) Single cell gel/comet assay: guidelines for in vitro and in vivo genetic toxicology testing. Environ Mol Mutagen 35:206–221
Wahl DA, Czernuszka JT (2006) Collagen–hydroxyapatite composites for hard tissue repair. Eur Cell Mater 11:43–56
Welzel T, Radtke I, Meyer-Zaika W, Heumann R, Epple M (2004) Transfection of cells with custom-made calcium phosphate nanoparticles coated with DNA. J Mater Chem 14:2213–2217
Wilson RM, Elliott JC, Dowkor SEP (1999) Riveted refinement of the crystallographic structure of human dental enamel apatite. Am Minerals 84:1406–1414
Yuan Y, Liu C, Qian J, Wang J, Zhang Y (2010) Size-mediated cytotoxicity and apoptosis of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles in human hepatoma HepG2 cells. Biomaterials 31:730–740
Zhang AP, Yan P (2004) Sun Photocatalytic killing effect of TiO2 nanoparticles on Ls-174-t human colon carcinoma cells. World J Gastroenterol 10:3191–3193
Zhang H, Li S, Yan Y (2001) Dissolution behaviour of hydroxyapatite powder in hydrothermal solution. Ceram Int 27:451–454
Zhu WH, Loh TT (1995) Role of calcium in the regulation of apoptosis in HL-60 promyelocytic leukemia cells. Life Sci 57:2091–2099
Acknowledgments
Authors are thankful to Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) New Delhi, for the financial assistance. Authors are also thankful to Advance Instrumentation Research Facility (AIRF), JNU, New Delhi for their continuous support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meena, R., Kesari, K.K., Rani, M. et al. Effects of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles on proliferation and apoptosis of human breast cancer cells (MCF-7). J Nanopart Res 14, 712 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-011-0712-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-011-0712-5