Abstract
Background
Thyroid hormones play a vital function in the maturation in the course of mind development. Regarding the well-known effects of choline on brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), the study examined the effects of choline on hippocampal BDNF gene expression in maternal hypothyroidism rats.
Methods and results
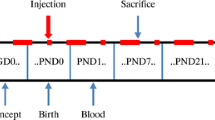
To induce the hypothyroidism, 6-propyl-2-thiouracil was introduced to the ingesting water from the sixth day of gestation to twenty-first postnatal day (PND). Choline-treatment started twice a day on the first day of gestation until PND 21. On PND28, pups were sacrificed. The expression of BDNF gene was evaluated after the hippocampus was harvested. Our results demonstrated that both male and female pre-pubertal offspring rats’ BDNF gene expression was decreased by developmental hypothyroidism. Choline increases the ratio of relative gene expression of BDNF in the hippocampus of males and females in the control/hypothyroidism group, especially in males.
Conclusions
It can be concluded that maternal choline supplementation on the first day of gestation until PND 21 improves brain development and cognitive function in pre-pubertal offspring rats regarding control/hypothyroidism groups.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chiovato L, Magri F, Carlé A (2019) Hypothyroidism in context: where we’ve been and where we’re going. Adv Ther 36(Suppl 2):47–58
Turkal R, Turan CA, Elbasan O et al (2022) Accurate interpretation of thyroid dysfunction during pregnancy: should we continue to use published guidelines instead of population-based gestation-specific reference intervals for the thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)? BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 22:271
Salazar P, Villaseca P, Cisternas P, Inestrosa NC (2021) Neurodevelopmental impact of the offspring by thyroid hormone system-disrupting environmental chemicals during pregnancy. Environ Res 200:111345
Päkkilä F, Männistö T, Hartikainen AL et al (2015) Maternal and child’s thyroid function and child’s intellect and scholastic performance. Thyroid 25(12):1363–1374
Anifantaki F, Pervanidou P, Lambrinoudaki I, Panoulis K, Vlahos N, Eleftheriades M (2021) Maternal prenatal stress, thyroid function and neurodevelopment of the offspring: a mini review of the literature. Front Neurosci 15:692446
Cooke GE, Mullally S, Correia N, O’Mara SM, Gibney J (2014) Hippocampal volume is decreased in adults with hypothyroidism. Thyroid 24(3):433–440
Karin O, Raz M, Tendler A, Bar A, Korem Kohanim Y, Milo T, Alon U (2020) A new model for the HPA axis explains dysregulation of stress hormones on the timescale of weeks. Mol Syst Biol 16(7):e9510
Walsh K, McCormack CA, Webster R et al (2019) Maternal prenatal stress phenotypes associate with fetal neurodevelopment and birth outcomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116(48):23996–24005
Ali MA, Nasir M, Pasha TN et al (2020) Preventive therapy of antioxidant vitamins against the blood choline levels in cardiovascular patients. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 66(4):184–190
Ali MA, Nasir M, Pasha TN et al (2020) Association of life style and dietary habits with blood choline and cardiovascular outcome. Cell Mol Biol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 66(4):178–183
Brailoiu E, Chakraborty S, Brailoiu GC et al (2019) Choline is an intracellular messenger linking extracellular stimuli to IP3-Evoked Ca2+ signals through sigma-1 receptors. Cell Rep 26(2):330-337.e4
Halder N, Lal G (2021) Cholinergic system and its therapeutic importance in inflammation and autoimmunity. Front Immunol 12:660342
Derbyshire E, Obeid R (2020) Choline, neurological development and brain function: a systematic review focusing on the first 1000 days. Nutrients 12(6):1731
Poly C, Massaro JM, Seshadri S et al (2011) The relation of dietary choline to cognitive performance and white-matter hyperintensity in the Framingham Offspring Cohort. Am J Clin Nutr 94(6):1584–1591
Caudill MA, Strupp BJ, Muscalu L, Nevins JEH, Canfield RL (2018) Maternal choline supplementation during the third trimester of pregnancy improves infant information processing speed: a randomized, double-blind, controlled feeding study. FASEB J 32(4):2172–2180
Miranda M, Morici JF, Zanoni MB, Bekinschtein P (2019) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor: a key molecule for memory in the healthy and the pathological brain. Front Cell Neurosci 13:363
Rashidy-Pour A, Derafshpour L, Vafaei AA et al (2020) Effects of treadmill exercise and sex hormones on learning, memory and hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels in transient congenital hypothyroid rats. Behav Pharmacol 31(7):641–651
Cattaneo A, Cattane N, Begni V, Pariante CM, Riva MA (2016) The human BDNF gene: peripheral gene expression and protein levels as biomarkers for psychiatric disorders. Transl Psychiatry 6(11):e958
Urbina-Varela R, Soto-Espinoza MI, Vargas R, Quiñones L, Del Campo A (2020) Influence of BDNF genetic polymorphisms in the pathophysiology of aging-related diseases. Aging Dis 11(6):1513–1526
Bathina S, Das UN (2015) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and its clinical implications. Arch Med Sci 11(6):1164–1178
Coskunoglu A, Orenay-Boyacioglu S, Deveci A et al (2017) Evidence of associations between brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) serum levels and gene polymorphisms with tinnitus. Noise Health 19(88):140–148
Pruunsild P, Kazantseva A, Aid T, Palm K, Timmusk T (2007) Dissecting the human BDNF locus: bidirectional transcription, complex splicing, and multiple promoters. Genomics 90(3):397–406
Adachi N, Numakawa T, Richards M, Nakajima S, Kunugi H (2014) New insight in expression, transport, and secretion of brain-derived neurotrophic factor: Implications in brain-related diseases. World J Biol Chem 5(4):409–428
Xie X, Shang K, Li X (2020) Tuling Wendan Decoction combined with flunarizine in the treatment of migraine patients and the effect of intervention on serum cyclooxygenase-2, endothelin-1 and nitric oxide. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 66(6):34–40
Li M, Xie Y, Niu K, Li K (2020) Electroacupuncture ameliorates post-traumatic stress disorder in rats via a mechanism involving the BDNF-TrkB signaling pathway. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 66(3):165–170
Timmusk T, Palm K, Metsis M, Reintam T, Paalme V, Saarma M, Persson H (1993) Multiple promoters direct tissue-specific expression of the rat BDNF gene. Neuron 10(3):475–489
Aid T, Kazantseva A, Piirsoo M, Palm K, Timmusk T (2007) Mouse and rat BDNF gene structure and expression revisited. J Neurosci Res 85(3):525–535
Amirahmadi S, Hosseini M, Ahmadabady S, Akbarian M, Abrari K, Vafaee F, Rajabian A (2021) Folic acid attenuated learning and memory impairment via inhibition of oxidative damage and acetylcholinesterase activity in hypothyroid rats. Metab Brain Dis 36(8):2393–2403
Strupp BJ, Powers BE, Velazquez R et al (2016) Maternal choline supplementation: a potential prenatal treatment for down syndrome and Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Alzheimer Res 13(1):97–106
Rashidi Molaei R, Kazemi A, Rahmati M (2016) The effect of a 6-week endurance training on BDNF and TrKB gene expression in the soleus of rats with diabetic neuropathy. J Kerman Univ Med Sci 23(6):741–753
Gil-Ibáñez P, Bernal J, Morte B (2014) Thyroid hormone regulation of gene expression in primary cerebrocortical cells: role of thyroid hormone receptor subtypes and interactions with retinoic acid and glucocorticoids. PLoS ONE 9(3):e91692
Herwig A, Campbell G, Mayer CD et al (2014) A thyroid hormone challenge in hypothyroid rats identifies T3 regulated genes in the hypothalamus and in models with altered energy balance and glucose homeostasis. Thyroid 24(11):1575–1593
Tiffon C (2018) The impact of nutrition and environmental epigenetics on human health and disease. Int J Mol Sci 19(11):3425
Liu D, Teng W, Shan Z et al (2010) The effect of maternal subclinical hypothyroidism during pregnancy on brain development in rat offspring. Thyroid 20(8):909–915
Marrocco J, McEwen BS (2016) Sex in the brain: hormones and sex differences. Dialogues Clin Neurosci 18(4):373–383
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to all staff of Cellular and Molecular Medicine Institute, Urmia University of Medical Sciences, Urmia, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SSH, LD, HS, ES, and MB contributed in study design, data analysis and interpretation, and drafting of manuscript; SSH, LD, and MB contributed in interpretation of results and critical revision of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have not disclosed any competing interests.
Ethical approval and informed consent
Ethics committee of Urmia Medical Sciences University approved all stages of the study (IR.UMSU.REC.1397.449).
Data availability
Data available on request from the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sheikhi, S., Derafshpour, L., Aghazadeh, R. et al. Effects of choline supplementation in mothers with hypothyroidism on the brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene expression changes in pre-pubertal offspring rats. Mol Biol Rep 50, 2351–2356 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-08014-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-08014-8