Abstract
Bipolar disorder (BD) is a mood psychiatric disorder described by changes between depressive, hypomanic, or manic episodes. The aimed of the present study was evaluated possible changes in the AA pathway in BD through a systematic review of observational studies. A search in the electronic databases was proceeded, on Cochrane Library, MEDLINE, EMBASE, PsycINFO, Google Scholar and the British Library for studies published until August 2020. A search strategy was developed using the terms: “Bipolar Disorder" and “Phospholipase A2” or “Arachidonic Acids” or “Cyclooxygenase 2” or “Prostaglandins E” as text words and Medical Subject Headings (i.e., MeSH and EMTREE). Seven primary studies were included in the systematic review, with a total of 246 BD patients, 20 depression patients, and 425 heathy controls (HC). The studies showed contradictory results in the AA and PLA2, no primary articles with COX and PGE2 assessments were included in this review. According to the Newcastle–Ottawa quality score scale (NOS), our systematic review presented high quality. The investigation of the inflammatory pathway of AA still needs further investigation and evidence, given the growing number of studies suggesting the efficacy of anti-inflammatory drugs as adjunctive therapy in the pharmacological treatment of BD.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Findling RL, Stepanova E, Youngstrom EA, Young AS (2018) Progress in diagnosis and treatment of bipolar disorder among children and adolescents: an international perspective. Evid Based Ment Health 21(4):177–181
Pedersen CB, Mors O, Bertelsen A, Waltoft BL, Agerbo E, McGrath JJ, Mortensen PB, Eaton WW (2014) A comprehensive nationwide study of the incidence rate and lifetime risk for treated mental disorders. JAMA Psychiatr 71(5):573–581
Vieta E, Berk M, Schulze TG, Carvalho AF, Suppes T, Calabrese JR, Gao K, Miskowiak KW, Grande I (2018) Bipolar Disord Nat Rev Dis Primers 4:18008
Subramaniam M, Abdin E, Vaingankar JA, Chong SA (2013) Prevalence, correlates, comorbidity and severity of bipolar disorder: results from the Singapore mental health study. J Affect Disord 146(2):189
McIntyre RS, Konarski JZ, Soczynska JK, Wilkins K, Panjwani G, Bouffard B, Bottas A, Kennedy SH (2006) Medical comorbidity in bipolar disorder: implications for functional outcomes and health service utilization. Psychiatr Serv 57(8):1140
Leboyer M, Soreca I, Scott J, Frye M, Henry C, Tamouza R, Kupfer DJ (2012) Can bipolar disorder be viewed as a multi-system inflammatory disease? J Affect Disord 141(1):1–10
Magalhães PVS, Fries GR, Kapczinski F (2012) Peripheral markers and the pathophysiology of bipolar disorder. Rev Psiquiatr Clín 39(2):60–67
Dantzer R, O’Connor JC, Freund GG, Johnson RW, Kelley KW (2008) From inflammation to sickness and depression: when the immune system subjugates the brain. Nat Rev Neurosci 43(9):46–56
O’Donovan A, Rush G, Hoatam G, Hughes BM, McCrohan A, Kelleher C, O'Farrelly C, Malone KM (2013) Suicidal ideation is associated with elevated inflammation in patients with major depressive disorder. Depress Anxiety 30(4):307–314
Baumeister D, Russell A, Pariante CM, Mondelli V (2014) Inflammatory biomarker profiles of mental disorders and their relation to clinical, social and lifestyle factors. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 49(6):841–849
Hsu CC, Chen SC, Liu CJ, Lu T, Shen CC, Hu YW, Yeh CM, Chen PM, Chen TJ, Hu LY (2014) Rheumatoid arthritis and the risk of bipolar disorder: a nationwide population-based study. PLoS ONE 9(9):e107512
Farhi A, Cohen AD, Shovman O, Comaneshter D, Amital H, Amital D (2016) Bipolar disorder associated with rheumatoid arthritis: a case-control study. J Affect Disord 189:287–289
Rao JS, Lee HJ, Rapoport SI, Bazinet RP (2008) Mode of action of mood stabilizers: is the arachidonic acid cascade a common target? Mol Psychiatry 13(6):585–596
Bavaresco DV, Colonetti T, Grande AJ, Colom F, Valvassori SS, Quevedo J, da Rosa MI (2019) Efficacy of celecoxib adjunct treatment on Bipolar disorder: systematic review and meta-analysis. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 18(1):19–28
Nery FG, Monkul ES, Hatch JP, Fonseca M, Zunta-Soares GB, Frey BN, Bowden CL, Soares JC (2008) Celecoxib as an adjunct in the treatment of depressive or mixed episodes of bipolar disorder: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Hum Psychopharmacol 23(2):87–94
Mendes RT, Stanczyk CP, Sordi R, Otuki MF, dos Santos FA, Fernandes D (2012) Inibição seletiva da ciclo-oxigenase-2: riscos e benefícios. Rev Bras Reumatol 52(5):767–782
Fitzpatrick FA (2004) Cyclooxygenase enzymes: regulation and function. Curr Pharm Des 10(6):577–588
Carvalho WA, Carvalho RDS, Rios-Santos F (2004) Analgésicos inibidores específicos da ciclooxigenase-2: avanços terapêuticos. Rev Bras Anestesiol 54(3):448–464
Legler DF, Krause P, Scandella E, Singer E, Groettrup M (2006) Prostaglandin E2 is generally required for human dendritic cell migration and exerts its effect via EP2 and EP4 receptors. J Immunol 176(2):966–973
Schmidley JW, Dadson J, Iyer RS, Salomon RG (1992) Brain tissue injury and blood-brain barrier opening induced by injection of LGE2 or PGE2. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 47(2):105–110
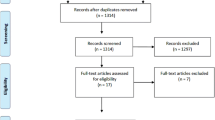
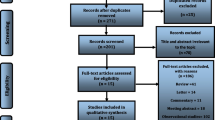
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gøtzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, Clarke M, Devereaux PJ, Kleijnen J, Moher D (2009) The Prisma statement for reporting systematic review and meta-analysis of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration. BMJ 339:b2700
Ross BM, Hughes B, Kish SJ, Warsh JJ (2006) Serum calcium-independent phospholipase A2 activity in bipolar affective disorder. Bipolar Disord 8(3):265–270
Ikenaga EH, Talib LL, Ferreira AS, Machado-Vieira R, Forlenza OV, Gattaz WF (2015) Reduced Activities of Phospholipases A2 in platelets of drug-naïve Bipolar disorder patients. Bipolar Disord 17(1):97–101
McNamara RK, Jandacek R, Rider T, Tso P, Dwivedi Y, Pandey GN (2010) Selective deficits in erythrocyte docosahexaenoic acid composition in adult patients with Bipolar disorder and major depressive disorder. J Affect Disord 126(1–2):303–311
Pomponi M, Janiri L, La Torre G, Di Stasio E, Di Nicola M, Mazza M, Martinotti G, Bria P, Lippa S, Natili R, Pomponi MF (2013) Plasma levels of n-3 fatty acids in bipolar patients: deficit restricted to DHA. J Psychiatr Res 47(3):337–342
Koga N, Ogura J, Yoshida F, Hattori K, Hori H, Aizawa E, Ishida I, Kunugi H (2019) Altered polyunsaturated fatty acid levels in relation to proinflammatory cytokines, fatty acid desaturase genotype, and diet in bipolar disorder. Transl Psychiatry 9(1):208
Bavaresco DV, da Rosa MI, Uggioni MLR, Ferraz SD, Pacheco TR, Toé HCZD, da Silveira AP, Quadros LFA, de Souza TD, Varela RB, Vieira AAS, Pizzol FD, Valvassori SS, Quevedo J (2020) Increased inflammatory biomarkers and changes in biological rhythms in bipolar disorder: A case-control study. J Affect Disord 271:115–122
Saunders EF, Reider A, Singh G, Gelenberg AJ, Rapoport SI (2015) Low unesterified: esterified eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) plasma concentration ratio is associated with bipolar disorder episodes, and omega-3 plasma concentrations are altered by treatment. Bipolar Disord 17(7):729–742
Law MH, Cotton RG, Berger GE (2006) The role of phospholipases A2 in schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 11(6):547–556
Ross BM, Hudson CJ, Erlich J, Warsh JJ, Kish SJ (1997) Increased phospholipid breakdown in schizophrenia. Evidence for the involvement of a calcium-independent phospholipase A2. Arch Gen Psychiatr 54:487–494
Kim HW, Rapoport SI, Rao JS (2011) Altered arachidonic acid cascade enzymes in postmortem brain from bipolar disorder patients. Mol Psychiatry 16(4):419–428
Gałecki P, Gałecka E, Maes M, Chamielec M, Orzechowska A, Bobińska K, Lewiński A, Szemraj J (2012) The expression of genes encoding for COX-2, MPO, iNOS, and sPLA2-IIA in patients with recurrent depressive disorder. J Affect Disord 138(3):360–366
Hanna VS, Hafez EAA (2018) Synopsis of arachidonic acid metabolism: a review. J Adv Res 11:23–32
Norris PC, Gosselin D, Reichart D, Glass CK, Dennis EA (2014) Phospholipase A2 regulates eicosanoid class switching during inflammasome activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111(35):12746–12751
Hamazaki K, Hamazaki T, Inadera H (2012) Fatty acid composition in the postmortem amygdala of patients with schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and major depressive disorder. J Psychiatr Res 46(8):1024–1028
Giridharan VV, Sayana P, Pinjari OF, Ahmad N, da Rosa MI, Quevedo J, Barichello T (2020) Postmortem evidence of brain inflammatory markers in bipolar disorder: a systematic review. Mol Psychiatr 25(1):94–113
Sayana P, Colpo GD, Simoes LR, Giridharan VV, Teixeira AL, Quevedo J, Barichello T (2017) A systematic review of evidence for the role of inflammatory biomarkers in bipolar patients. J Psychiatr Res 92:160–182
Silverman MN, Pearce BD, Biron CA, Miller AH (2005) Immune modulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis during viral infection. Viral Immunol 18(1):41–78
Pape K, Tamouza R, Leboyer M, Zipp F (2019) Immunoneuropsychiatry-novel perspectives on brain disorders. Nat Rev Neurol 15(6):317–328
Ozdemircan A, Dasdemir S, Kucukali CI, Bireller ES, Ozturk H, Cakmakoglu B (2015) COX-2 gene variants in bipolar disorder-I. Psychiatr Danub 27(4):385–389
Maida ME, Hurley SD, Daeschner JA, Moore AH, O'Banion MK (2006) Cytosolic prostaglandin E2 synthase (cPGES) expression is decreased in discrete cortical regions in psychiatric disease. Brain Res 1103(1):164–172
Gurvich A, Begemann M, Dahm L, Sargin D, Miskowiak K, Ehrenreich H (2014) A role for prostaglandins in rapid cycling suggested by episode-specific gene expression shifts in peripheral blood mononuclear cells: a preliminary report. Bipolar Disord 16(8):881–888
Krause DL, Riedel M, Müller N, Weidinger E, Schwarz MJ, Myint AM (2012) Effects of antidepressants and cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor on cytokines and kynurenines in stimulated in vitro blood culture from depressed patients. Inflammopharmacology 20(3):169–176
Faridhosseini F, Sadeghi R, Farid L, Pourgholami M (2014) Celecoxib: a new augmentation strategy for depressive mood episodes. A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials. Hum Psychopharmacol 29:216–223
Eyre HA, Air T, Proctor S, Rositano S, Baune BT (2015) A critical review of the efficacy of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in depression. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 57:11–16
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the generous funding University of Southern Santa Catarina (UNESC).
Funding
This article does not contain any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DVB, JQ, and MIR designed the study and wrote the protocol. DVB, MLRU, TC, and MIR managed the literature searches and screening. DVB, DVB, SDF, MVBC, and CSS contributed to analyses interpretation. MIR, TC and DVB wrote the first draft of the manuscript. All authors contributed and have approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The review protocol was registered at PROSPERO (CRD42020158464).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bavaresco, D.V., Uggioni, M.L.R., Simon, C.S. et al. Evaluation of the arachidonic acid pathway in bipolar disorder: a systematic review. Mol Biol Rep 47, 8209–8217 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-020-05785-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-020-05785-w