Abstract
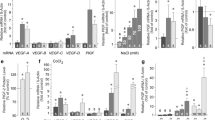
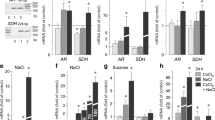
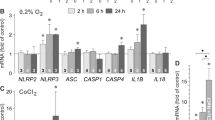
The expression of aquaporin (AQP) water channels may influence the development of retinal edema. We investigated the transcriptional regulation of AQP3 in cultured human retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells. As shown by RT-PCR and immunocytochemistry, cultured RPE cells express AQP3 mRNA and protein. The AQP3 mRNA level in RPE cells was elevated under the following conditions: chemical hypoxia induced by CoCl2, hyperosmolarity induced by 100 mM NaCl, and upon stimulation of the cultures with PDGF, arachidonic acid, prostaglandin E2, and blood serum, respectively. Chemical hypoxia increased AQP3 gene expression through MEK/ERK and JNK activation. The hyperosmolarity-, PDGF-, and serum-induced upregulation of AQP3 was prevented by inhibition of the phospholipase A2, but not by inhibition of the cyclooxygenase. Triamcinolone acetonide prevented the upregulation of AQP3 induced by arachidonic acid and prostaglandin E2, but not by the other factors tested. It is concluded that AQP3 is transcriptionally activated in RPE cells by various pathogenic factors involved in the development of retinal edema in situ. Activation of phospholipase A2 is a critical factor which induces AQP3 in RPE cells.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bresnick GH (1983) Diabetic maculopathy. A critical review highlighting diffuse macular edema. Ophthalmology 90:1301–1317
Bressler NM, Bressler SB, Fine SL (2001) Neovascular (exudative) age-related macular degeneration. In: Schachat AP (ed) Retina. Mosby, St Louis, pp 1100–1135
Strauss O (2005) The retinal pigment epithelium in visual function. Physiol Rev 85:845–881
Bringmann A, Pannicke T, Grosche J, Francke M, Wiedemann P, Skatchkov SN, Osborne NN, Reichenbach A (2006) Müller cells in the healthy and diseased retina. Prog Retin Eye Res 25:397–424
Stamer WD, Bok D, Hu J, Jaffe GJ, McKay BS (2003) Aquaporin-1 channels in human retinal pigment epithelium: role in transepithelial water movement. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 44:2803–2808
Nagelhus EA, Mathiisen TM, Ottersen OP (2004) Aquaporin-4 in the central nervous system: cellular and subcellular distribution and coexpression with Kir4.1. Neuroscience 129:905–913
Bringmann A, Reichenbach A, Wiedemann P (2004) Pathomechanisms of cystoid macular edema. Ophthalmic Res 36:241–249
Aiello LP, Bursell SE, Clermont A, Duh E, Ishii H, Takagi C, Mori F, Ciulla TA, Ways K, Jirousek M, Smith LE, King GL (1997) Vascular endothelial growth factor-induced retinal permeability is mediated by protein kinase C in vivo and suppressed by an orally effective beta-isoform-selective inhibitor. Diabetes 46:1473–1480
Claudio L, Martiney JA, Brosnan CF (1994) Ultrastructural studies of the blood-retina barrier after exposure to interleukin-1ß or tumor necrosis factor-α. Lab Invest 70:850–861
Luna JD, Chan CC, Derevjanik NL, Mahlow J, Chiu C, Peng B, Tobe T, Campochiaro PA, Vinores SA (1997) Blood-retinal barrier (BRB) breakdown in experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis: comparison with vascular endothelial growth factor, tumor necrosis factor-α, and interleukin-1ß-mediated breakdown. J Neurosci Res 49:268–280
Derevjanik NL, Vinores SA, Xiao WH, Mori K, Turon T, Hudish T, Dong S, Campochiaro PA (2002) Quantitative assessment of the integrity of the blood-retinal barrier in mice. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 43:2462–2467
Hollborn M, Petto C, Steffen A, Trettner S, Bendig A, Wiedemann P, Bringmann A, Kohen L (2009) Effects of thrombin on RPE cells are mediated by transactivation of growth factor receptors. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 50:4452–4459
Sakamoto T, Sakamoto H, Sheu SJ, Gabrielian K, Ryan SJ, Hinton DR (1994) Intercellular gap formation induced by thrombin in confluent cultured bovine retinal pigment epithelial cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 35:720–729
Bian ZM, Elner SG, Elner VM (2007) Thrombin-induced VEGF expression in human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 48:2738–2746
Agre P, King LS, Yasui M, Guggino WB, Ottersen OP, Fujiyoshi Y, Engel A, Nielsen S (2002) Aquaporin water channels—from atomic structure to clinical medicine. J Physiol 542:3–16
Ishibashi K (2006) Aquaporin subfamily with unusual NPA boxes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1758:989–993
Ishibashi K, Sasaki S, Fushimi K, Uchida S, Kuwahara M, Saito H, Furukawa T, Nakajima K, Yamaguchi Y, Gojobori T, Marumo F (1994) Molecular cloning and expression of a member of the aquaporin family with permeability to glycerol and urea in addition to water expressed at the basolateral membrane of kidney collecting duct cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:6269–6273
Echevarria M, Windhager EE, Frindt G (1996) Selectivity of the renal collecting duct water channel aquaporin-3. J Biol Chem 271:25079–25082
Kuriyama H, Kawamoto S, Ishida N, Ohno I, Mita S, Matsuzawa Y, Matsubara K, Okubo K (1997) Molecular cloning and expression of a novel human aquaporin from adipose tissue with glycerol permeability. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 241:53–58
Tsukaguchi H, Weremowicz S, Morton CC, Hediger MA (1999) Functional and molecular characterization of the human neutral solute channel aquaporin-9. Am J Physiol 277:F685–F696
Miller EW, Dickinson BC, Chang CJ (2010) Aquaporin-3 mediates hydrogen peroxide uptake to regulate downstream intracellular signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:15681–15686
Hollborn M, Rehak M, Iandiev I, Pannicke T, Ulbricht E, Reichenbach A, Wiedemann P, Bringmann A, Kohen L (2012) Transcriptional regulation of aquaporins in the ischemic rat retina: upregulation of aquaporin-9. Curr Eye Res (in press)
Hollborn M, Dukic-Stefanovic S, Pannicke T, Ulbricht E, Reichenbach A, Wiedemann P, Bringmann A, Kohen L (2011) Expression of aquaporins in the retina of diabetic rats. Curr Eye Res 36:850–856
Fraser-Bell S, Kaines A, Hykin PG (2008) Update on treatments for diabetic macular edema. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 19:185–189
Silva PS, Sun JK, Aiello LP (2009) Role of steroids in the management of diabetic macular edema and proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Semin Ophthalmol 24:93–99
Orgül S, Reuter U, Kain HL (1993) Osmotic stress in an in vitro model of the outer blood-retinal barrier. Ger J Ophthalmol 2:436–443
Miyake K, Ibaraki N (2002) Prostaglandins and cystoid macular edema. Surv Ophthalmol 47:S203–S218
Guex-Crosier Y (1999) The pathogenesis and clinical presentation of macular edema in inflammatory diseases. Doc Ophthalmol 97:297–309
Ishibashi K, Sasaki S, Saito F, Ikeuchi T, Marumo F (1995) Structure and chromosomal localization of a human water channel (AQP3) gene. Genomics 27:352–354
Matsuzaki T, Suzuki T, Koyama H, Tanaka S, Takata K (1999) Water channel protein AQP3 is present in epithelia exposed to the environment of possible water loss. J Histochem Cytochem 47:1275–1286
Hara-Chikuma M, Verkman AS (2008) Roles of aquaporin-3 in the epidermis. J Invest Dermatol 128:2145–2151
Levin MH, Verkman AS (2006) Aquaporin-3-dependent cell migration and proliferation during corneal re-epithelialization. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 47:4365–4372
Hara-Chikuma M, Verkman AS (2008) Prevention of skin tumorigenesis and impairment of epidermal cell proliferation by targeted aquaporin-3 gene disruption. Mol Cell Biol 28:326–332
Cao C, Wan S, Jiang Q, Amaral A, Lu S, Hu G, Bi Z, Kouttab N, Chu W, Wan Y (2008) All-trans retinoic acid attenuates ultraviolet radiation-induced down-regulation of aquaporin-3 and water permeability in human keratinocytes. J Cell Physiol 215:506–516
Boury-Jamot M, Daraspe J, Bonté F, Perrier E, Schnebert S, Dumas M, Verbavatz JM (2009) Skin aquaporins: function in hydration, wound healing, and skin epidermis homeostasis. Handb Exp Pharmacol 190:205–217
Huang Y, Zhu Z, Sun M, Wang J, Guo R, Shen L, Wu W (2010) Critical role of aquaporin-3 in the human epidermal growth factor-induced migration and proliferation in the human gastric adenocarcinoma cells. Cancer Biol Ther 9:1000–1007
Joussen AM, Poulaki V, Le ML, Koizumi K, Esser C, Janicki H, Schraermeyer U, Kociok N, Fauser S, Kirchhof B, Kern TS, Adamis AP (2004) A central role for inflammation in the pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy. FASEB J 18:1450–1452
Ji C, Yang Y, Yang B, Xia J, Sun W, Su Z, Yu L, Shan S, He S, Cheng L, Wan Y, Bi Z (2010) Trans-Zeatin attenuates ultraviolet induced down-regulation of aquaporin-3 in cultured human skin keratinocytes. Int J Mol Med 26:257–263
Song X, Xu A, Pan W, Wallin B, Kivlin R, Lu S, Cao C, Bi Z, Wan Y (2008) Nicotinamide attenuates aquaporin 3 overexpression induced by retinoic acid through inhibition of EGFR/ERK in cultured human skin keratinocytes. Int J Mol Med 22:229–236
Cao C, Sun Y, Healey S, Bi Z, Hu G, Wan S, Kouttab N, Chu W, Wan Y (2006) EGFR-mediated expression of aquaporin-3 is involved in human skin fibroblast migration. Biochem J 400:225–234
Matsuzaki T, Suzuki T, Takata K (2001) Hypertonicity-induced expression of aquaporin 3 in MDCK cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 281:C55–C63
Sugiyama Y, Ota Y, Hara M, Inoue S (2001) Osmotic stress up-regulates aquaporin-3 gene expression in cultured human keratinocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1522:82–88
Lambert IH, Pedersen SF, Poulsen KA (2006) Activation of PLA2 isoforms by cell swelling and ischaemia/hypoxia. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 187:75–85
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Franziska Rickers for excellent technical assistance. This study was supported by grants from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (KO 1547/6-1) and the Geschwister Freter Stiftung (Hannover, Germany).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hollborn, M., Ulbricht, E., Reichenbach, A. et al. Transcriptional regulation of aquaporin-3 in human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Mol Biol Rep 39, 7949–7956 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-1640-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-1640-x