Abstract
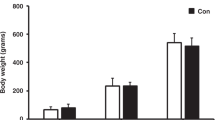
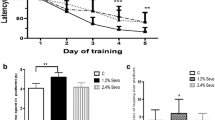
To investigate the effects of sevoflurane on cognitive function in old Sprague–Dawley (SD) rats and the expression of insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) in CA1 region of hippocampus. Forty Sprague–Dawley rats of 12 months old were randomly divided into five groups: the normal control group; 1.5% sevoflurane I group (be tested after received 1.5% sevoflurone for 1 day); 1.5% sevoflurane II group (be tested after received 1.5% sevoflurone for 7 day); 3.0% sevoflurane I group (be tested after received 3.0% sevoflurone for 1 day) and 3.0% sevoflurane II group (be tested after received 3.0% sevoflurone for 7 day). All SD rats were received 1.5 or 3.0% sevoflurone in a special glass anesthesia box for 2 h respectively, except for the normal control group. Y-maze was used to test the ability of learning and memory after being received sevoflurone for 1 or 7 days at the same moment portion. The altered expression level of IGF-1 in the hippocampus was tested to compare its transcripts by RT-PCR analysis. The results showed that 3% sevoflurane induced the decline of cognitive function and significantly deceased the IGF-1 expression at mRNA levels at 1 day in the 3.0% sevoflurone I group when compared with the normal control group. However, there were no significant difference among the other groups when compared with normal control group. Therefore, administration of sevoflurane might temporally affect the ability of cognitive function of rats through suppressing the IGF-1 expression at mRNA levels in hippocampus.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parikh SS, Chung F (1995) Postoperative delirium in the elderly. Anesth Analg 80:1223–1232
Gustafson Y, Brannstrom B, Berggren D et al (1991) A geriatricanesthesiologic program to reduce acute confusional states in elderly patients treated for femoral neck fractures. J Am Geriatr Soc 39:655–662
Williams-Russo P, Urquhart BL, Sharrock NE, Charlson ME (1992) Post-operative delirium: predictors and prognosis in elderly orthopedic patients. J Am Geriatr Soc 40:759–767
Jevtovic-Todorovic V, Hartman RE, Izumi Y, Benshoff ND, Dikranian K, Zorumski CF, Olney JW, Wozniak DF (2003) Early exposure to common anesthetic agents causes widespread neurodegeneration in the developing rat brain and persistent learning deficits. J Neurosci 23:876–882
Eger EI II, Saidman LJ, Brandstater B (1965) Minimum alveolar anesthetic concentration: a standard of anesthetic potency. Anesthesiology 26:756–763
Cook TL, Smith M, Winter PM, Starkweather JA, Eger EI III (1978) Effect of subanesthetic concentration of enflurane and halothane on human behavior. Anesth Analg 57:434–440
Dwyer R, Bennett HL, Eger EI II, Heilbron D (1992) Effects of isoflurane and nitrous oxide in subanesthetic concentrations on memory and responsiveness in volunteers. Anesthesiology 77:888–898
Ghoneim MM, Block RI (1997) Learning and memory during general anesthesia: An update. Anesthesiology 87:387–410
El-Zahaby HM, Ghoneim MM, Johnson GM, Gormezano I (1994) Effects of subanesthetic concentrations of isoflurane and their interactions with epinephrine on acquisition and retention of the rabbit nictitating membrane response. Anesthesiology 81:229–237
Kandel L, Chortkoff BS, Sonner J, Laster MJ, Eger EI II (1996) Nonanesthetics can suppress learning. Anesth Analg 82:321–326
Dutton RC, Maurer AJ, Sonner JM, Fanselow MS, Laster MJ, Eger EI II (2001) The concentration of isoflurane required to suppress learning depends on the type of learning. Anesthesiology 94:514–519
Alkire MT, Gorski LA (2004) Relative amnesic potency of five inhalational anesthetics follows the Meyer-Overton rule. Anesthesiology 101:417–429
McGaugh JL (2000) Memory. a century of consolidation. Science 287:248–251
Veselis RA, Reinsel RA, Feshchenko VA, Wronski M (1997) The comparative amnestic effects of midazolam, propofol, thiopental, and fentanyl at equisedative concentrations. Anesthesiology 87:749–764
Jones JI, Clemmons DR (1995) Insulin like growth factors and their binding proteins: biological actions. Endocr Rev 16:3–34
D’Ercole AJ, Ye P, Calikoglu AS, Gutierrez-Ospina G (1996) The role of the insulin-like growth factors in the central nervous system. Mol Neurobiol 13:227–255
Richard-Parpaillon L, Heligon C, Chesnel F, Boujard D, Philpott A (2002) The IGF pathway regulates head formation by inhibiting Wnt signaling in Xenopus. Dev Biol 244:407–417
Pera EM, Wessely O, Li SY, De Robertis EM (2001) Neural and head induction by insulin-like growth factor signals. Dev Cell 1:655–665
Cheng CM, Cohen M, Tseng V, Bondy CA (2001) Endogenous IGF-1 enhances cell survival in the postnatal dentate gyrus. J Neurosci Res 64:341–347
Bondy CA, Cheng CM (2002) Insulin-like growth factor-1 promotes neuronal glucose utilization during brain development and repair processes. Int Rev Neurobiol 51:189–217
Bondy CA, Cheng CM (2004) Signaling by insulin-like growth factor 1 in brain. Eur J Pharmacol 490:25–31
Smith A, Wang J, Cheng CM, Zhou J, Weickert CS, Bondy CA (2004) High-level expression of Dok-1 in neurons of the primate prefrontal cortex and hippocampus. J Neurosci Res 75:218–224
Cheng CM, Mervis RF, Niu SL, Salem N Jr, Witters LA, Tseng V, Reinhardt R, Bondy CA (2003) Insulin-like growth factor 1 is essential for normal dendritic growth. J Neurosci Res 73:1–9
Varela-Nieto I, Morales-Garcia JA, Vigil P, Diaz-Casares A, Gorospe I, Sanchez-Galiano S, Canon S, Camarero G, Contreras J, Cediel R, Leon Y (2004) Trophic effects of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) in the inner ear. Hear Res 196:19–25
Sun LY, Evans MS, Hsieh J, Panici J, Bartke A (2005) Increased neurogenesis in dentate gyrus of long-lived Ames dwarf mice. Endocrinology 146:1138–1144
Guan J, Thomas GB, Lin H, Mathai S, Bachelor DC, George S, Gluckman PD (2004) Neuroprotective effects of the N-terminal tripeptide of insulin-like growth factor-1, glycine-proline-glutamate (GPE) following intravenous infusion in hypoxic-ischemic adult rats. Neuropharmacology 47:892–903
Cheng B, Mattson MP (1992) IGF-I and IGF-II protect cultured hippocampal and septal neurons against calcium-mediated hypoglycemic damage. J Neurosci 12:1558–1566
Gluckman PD, Guan J, Williams CE, Scheepens A, Zhang R, Bennet L, Gunn AJ (1998) Asphyxial brain injury—the role of the IGF system. Mol Cell Endocrinol 140:95–99
McLay RN, Freeman SM, Harlan RE, Ide CF, Kastin AJ, Zadina JE (1997) Aging in the hippocampus: interrelated actions of neurotrophins and glucocorticoids. Neurosci Behav Rev 21:615–629
Peng S, Zhang Y, Zhang J, Wang H, Ren B (2009) Effect of ketamine on ERK expression in hippocampal neural cell and the ability of learning behavior in minor rats. Mol Biol Rep. [Epub ahead of print]
Ma YL, Peng JY, Liu WJ, Zhang P, Huang L, Gao BB, Shen TY, Zhou YK, Chen HQ, Chu ZX et al (2009) Proteomics identification of desmin as a potential oncofetal diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in colorectal Cancer. Mol Cell Proteomics 8(8):1878–1890
Lenoir D, Honegger P (1983) Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF I) stimulates DNA synthesis in fetal rat brain cell cultures. Brain Res 283:205–213
Recio-Pinto E, Rechler MM, Ishii DN (1986) Effects of insulin, insulin-like growth factor-II, and nerve growth factor on neurite formation and survival in cultured sympathetic and sensory neurons. J Neurosci 6:1211–1219
Vicario-Abejon C, Yusta-Boyo MJ, Fernandez-Moreno C, de Pablo F (2003) Locally born olfactory bulb stem cells proliferate in response to insulin-related factors and require endogenous insulin-like growth factor-I for differentiation into neurons and glia. J Neurosci 23:895–906
Wilkins A, Chandran S, Compston A (2001) A role for oligodendrocytederived IGF-1 in trophic support of cortical neurons. Glia 36:48–57
Markowska AL, Mooney M, Sonntag WE (1998) Insulin-like growth factor-1 ameliorates age-related behavioral deficits. Neuroscience 87:559–569
Lee KH, Calikoglu AS, Ye P, D’Ercole AJ (1999) Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-1) ameliorates and IGF binding protein-1 (IGFBP-1) exacerbates the effects of undernutrition on brain growth during early postnatal life: studies in IGF-1 and IGFBP-1 transgenic mice. Pediatr Res 45:331–336
Cheng CM, Mervis RF, Niu SL, Salem N, Witters LA, Tseng V et al (2003) Insulin-like growth factor 1 is essential for normal dendritic growth. J Neurosci Res 37:1–9
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by Medical Science Research Foundation of Jiangsu Province, China (Grant No. H200645) and Science Foundation of the Health Bureau of Wuxi City, China (Grant No. XM0805).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, S., Zhang, Y., Sun, DP. et al. The effect of sevoflurane anesthesia on cognitive function and the expression of Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 in CA1 region of hippocampus in old rats. Mol Biol Rep 38, 1195–1199 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0217-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0217-9