Abstract
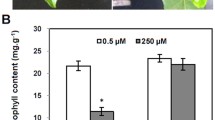
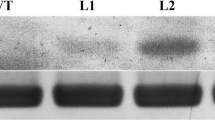
Zinc is essential but toxic in excess. A bacterial metallothionein, SmtA from Synechococcus PCC 7942, has high affinity for Zn2+ and the intracellular exclusively handling of Zn2+. In this study, we report a functional analysis of SmtA in Arabidopsis thaliana and its response to zinc stress. After high zinc stress, the transgenic plants over-expressing SmtA showed higher survival rate than the wild type. We also found that over-expression of SmtA in Arabidopsis increased the activities of SOD and POD, and enhanced the tolerance to zinc stress. Together, our results indicate that SmtA may play an important role in the response to zinc stress in Arabidopsis.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MTs:
-
Metallothioneins
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- POD:
-
Peroxidase
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
References
Krupa Z, Siedlecka A, Maksymiec T (1993) In vivo response of photosynthetic apparatus of Phaseolus vulgaris L. to nickel toxicity. J Plant Physiol 142:664–668
Maksymiec W, Russa R, Urbanik-Sypniewska T (1994) Effect of excess Cu on the photosynthetic apparatus of runner bean leaves treated at two different growth stages. Physiol Plant 91:715–721
Ouzounidou G, Giamparova M, Moustakas M, Karataglis S (1995) Responses of maize (Zea mays L.) plants to copper stress. I. Growth, mineral content and ultrastructure of roots. Environ Exp Bot 35:167–176
Weckx JEJ, Clijsters HMM (1997) Zn phytotoxicity induces oxidative stress in primary leaves of Phaseolus vulgaris. Plant Physiol Biochem 35:405–410
Molas J (2002) Changes of chloroplast ultrastructure and total chlorophyll concentration in cabbage leaves caused by excess of organic Ni(II) complexes. Environ Exp Bot 47:115–126
Sobkowiak R, Deckert J (2003) Cadmium-induced changes in growth and cell cycle gene expression in suspension-culture cells of soybean. Plant Physiol Biochem 41:767–772
Goyer RA (1997) Toxic and essential metal interactions. Annu Rev Nutr 17:37–50
Stohs SJ, Bagchi D (1995) Oxidative mechanisms in the toxicity of metal ions. Free Radic Biol Med 18:321–336
Clemens S (2001) Molecular mechanisms of plant metal tolerance and homeostasis. Planta 212:475–486
Cobbett C, Goldsbrough P (2002) Phytochelatins and metallothioneins: roles in heavy metal detoxification and homeostasis. Annu Rev Plant Biol 53:159–182
Hall JL, Williams LE (2003) Transition metal transporters in plants. J Exp Bot 54:2601–2613
Foyer CH, Lopez-Delgado H, Dat JF, Scott IM (1997) Hydrogen peroxide and glutathione-associated mechanisms of acclamatory stress tolerance and signaling. Physiol Plant 100:241–254
Kaegi JHR, Schaeffer A (1988) Biochemistry of metallothionein. Biochemistry 27:8509–8515
Robinson NJ, Gupta A, Fordham-Skelton AP, Croy RRD (1990) Prokaryotic metallothionein gene characterization and expression: chromosome crawling by ligation-mediated PCR. Proc R Soc Lond B 242:241–247
Huckle JW, Morby AP, Turner JS, Robinson NJ (1993) Isolation of a prokaryotic metallothionein locus and analysis of transcriptional control by trace metal ions. Mol Microbiol 7:177–187
Turner JS, Morby AP, Whitton BA, Gupta A, Robinson NJ (1993) Construction of Zn2+/Cd2+ hypersensitive cyanobacterial mutants lacking a functional metallothionein locus. J Biol Chem 268:4494–4498
Olafson RW, McCubbin WD, Kay CM (1988) Primary-and-secondary-structural analysis of a unique prokaryotic metallothionein from a Synechococcus sp. cyanobacterium. Biochem J 251:691–699
Daniels MJ, Turner-Cavet JS, Selkirk R (1998) Coordination of Zn2+ (and Cd2+) by prokaryotic metallothionein. J Biol Chem 273:22957–22961
Xiong AS, Yao QH, Peng RH, Li X, Fan HQ, Cheng ZM, Li Y (2004) A simple, rapid, high-fidelity and cost-effective PCR-based two-step DNA synthesis method for long gene sequence. Nucleic Acids Res 32:e98
Zhang X, Henriques R, Lin SS (2006) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana using the floral dip method. Nat Protoc 1:641–646
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Lichtenthaler HK (1987) ChlorophyIIs and carotenoids: pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes. Meth Enzymol 48:350–382
Heath RL, Packer L (1968) Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplast. I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch Biochem Biophys 125:180–198
Beyer WF, Fridovich Y (1987) Assaying for superoxide dismutase activity: some large consequences of minor changes in conditions. Anal Biochem 161:559–566
MacAdam JW, Nelson CJ, Sharp RE (1992) Peroxidase activity in the leaf elongation zone of tall fescue. Plant Physiol 99:872–878
Xiong AS, Yao QH, Peng RH, Duan H, Li X, Fan HQ, Cheng ZM, Li Y (2006) PCR-based accurate synthesis of long DNA sequences. Nat Protoc 1:791–797
Esterbauer H, Schauer RJ, Zollner H (1991) Chemistry and biochemistry of 4-hydroxynonenal, malonaldehyde and related aldehydes. Free Radical Bio Med 11:81–128
Smirnoff N (1995) Antioxidant systems and plant response to the environment. In: Smirnoff N (ed) Environment and plant metabolism: flexibility and acclimation. Bios Scientific Publishers, Oxford, UK, pp 217–243
Monk LS, Fagerstedt KV, Crawford RMM (1989) Oxygen toxicity and superoxide dismutase as an antioxidant in physiological stress. Plant Physiol 76:456–459
Chaoui A, Mazhoudi S, Ghorbal MN, Ferjani EE (1997) Cadmium and zinc induction of lipid peroxidation and effects on antioxidant enzymes activities in bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Plant Sci 127:139–147
Samarkoon AB, Rauser WE (1979) Carbohydrate level and photoassimilate export from leaves of Phaseolus vulgaris exposed to excess cobalt, nickel and zinc. Plant Physiol 63:1165–1169
Somashekaraiah BV, Padmaja K, Prasad ARK (1992) Phytotoxicity of cadmium ions on germinating seedlings of mung bean (Phaseolus vulgaris): involvement of lipid peroxides in chlorophyll degradation. Physiol Plant 85:85–89
Fang W, Kao CH (2000) Enhanced peroxidase activity in rice leaves in responses to excess iron, copper and zinc. Plant Sci 158:71–76
Tewari RK, Kumar P, Sharma PN, Bisht SS (2002) Modulation of oxidative stress responsive enzymes by excess cobalt. Plant Sci 162:381–388
Kampfenkel K, Montagu MV, Inze D (1995) Effect of iron excess on Nicotiana plumbaginifolia plants: implication to oxidative stress. Plant Physiol 107:725–735
Becana M, Moran JF, Iturbe-Ormaetxe I (1998) Iron-dependent oxygen free radical generation in plants subjected to environmental stress: toxicity and antioxidant protection. Plant Soil 201:137–147
Gupta M, Cuypers A, Vangronsveld J, Clijsters H (1999) Copper affects the enzymes of ascorbate–glutathione cycle and its related metabolites in the roots of Phaseolus vulgaris. Physiol Plant 106:262–267
Teisseire H, Guy V (2000) Copper-induced changes in antioxidant enzymes activities in fronds of duckweed (Lemna minor). Plant Sci 153:65–72
Prasad KVSK, Saradhi PP, Sharmila P (1999) Concerted action of antioxidant enzymes and curtailed growth under zinc toxicity in Brassica juncea. Environ Exp Bot 42:1–10
Madhava Rao KV, Sresty TV (2000) Antioxidative parameters in the seedlings of pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan (L.) Millspaugh) in response to Zn and Ni stresses. Plant Sci 157:113–128
Baccouch S, Chaoui A, Ferjani EE (1998) Nickel-induced oxidative damage and antioxidant responses in Zea mays shoot. Plant Physiol Biochem 36:689–694
Gonzalez A, Steffen KL, Lynch JP (1998) Light and excess manganese: Implications for oxidative stress in common bean. Plant Physiol 118:493–504
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Shanghai and National Natural Science Foundation (30670179, 08ZR1417200); 863 Program (2006AA10Z117, 2006AA06Z358, 2008AA10Z401); Shanghai Project for ISTC (08540706500); The Key Project Fund of the Shanghai Municipal Committee of Agriculture (No. 2008-7-5) and Shanghai Rising-Star Program (08QH14021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
J. Xu and Y.-S. Tian are contributed equally to the article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, J., Tian, YS., Peng, RH. et al. Cyanobacteria MT gene SmtA enhance zinc tolerance in Arabidopsis . Mol Biol Rep 37, 1105–1110 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-009-9867-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-009-9867-x