Abstract
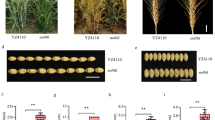
The monogenetic recessive male-sterile gene ms-IR36 is widely used to facilitate the inter-crossing phase of recurrent selection in rice (Oryza sativa), but its segregation within the progeny disturbs other breeding phases. Marker-assisted early identification of msms and Msms seedlings would help overcome this drawback. Using successively bulked segregant analysis and large F2 populations, we mapped the ms-IR36 gene to a 33-kb region on the short arm of chromosome 2 that includes 10 candidate genes. Sequencing of these candidates together with checking rice genome annotations and expression databases allowed the target to be narrowed down to one candidate gene already isolated and characterized as the tapetum degeneration retardation (TDR) gene and reported to be involved in tapetal programmed cell death. Comparison of the sequence of the TDR gene between male-sterile (MS) and male-fertile (MF) IR36 plants detected one non-synonymous nucleotide substitution affecting the active domain of the encoded protein. Perfect co-segregation was observed between polymorphism at this nucleotide (SNP) and the MS/MF phenotype of 946 F2 plants. Spatial modelling of the active domain of the candidate protein reinforced the candidate status of the only SNP identified. Histological characterization of anther development in MS IR36 revealed defects identical to the ones observed in mutants used for the isolation and characterization of the TDR gene: delayed/non-degradation of tapetum tissue and collapse of the haploid microspores. We concluded that ms-IR36 corresponded to the TDR gene with a different mutation from the earlier one described in the same gene. No significant linkage drag was associated with ms-IR36. A SNP-based marker that enables simple early identification of MS plants and MF plants with the Msms genotype was designed.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buffard-Morel J, Verdeil JL, Pannetier C (1992) Embryogenèse somatique du cocotier (Cocos nucifera L.) à partir d’explant foliaire: étude histologique. Can J Bot 70:735–741
Chatel M, Guimaraes EP (1997) Recurrent selection in rice using male-sterility gene. CIAT publication no. 276. ISBN 958-9439-90-X. Cali, Colombia, p 77
Comstock RE, Robinson HF, Harvey PH (1949) A breeding procedure designed to make maximum use of both general and specific combining ability. Agron J 41:360–367
Courtois B, Filloux D, Ahmadi N, Noyer JL, Billot C, Guimaraes EP (2005) Using molecular markers in rice population improvement through recurrent selection. In: Guimaraes EP (ed) Population improvement: a way of exploiting the rice genetic resources of Latin America. FAO, Rome, pp 56–94
da Cunha KS, Pereira MG, Gonçalves LSA, Berilli APCG, de Oliveira ED, Ramos HCC, do Amaral Júnior AD (2012) Full-sib reciprocal recurrent selection in the maize populations Cimmyt and Piranão. Genet Mol Res 11(3):3398–3408
Fisher DB (1968) Protein staining of ribboned epon sections for light microscopy. Histochemie 16:92–96
Fujimaki H (1979) Recurrent selection by using genetic male sterility for rice improvement. JARQ (Tsukuba) 13(3):153–156
Gallais A (1977) Amélioration des populations, méthodes de sélection et création de variétés. I. Synthèse critique sur les problèmes généraux et sur les bases théoriques pour la sélection récurrente intrapopulation. Ann Amélior Plant 27:281–330
Gallais A (1978) Amélioration des populations, méthodes de sélection et de création de variétés. II. Le concept de valeur variétale et ses conséquences pour la sélection récurrente. Ann Amélior Plant 28:269–287
Gallais A (2009) Full-sib reciprocal recurrent selection with the use of doubled haploids. Crop Sci 49:150–152
Gaudet M, Fara A-G, Sabatti M, Kuzminsky E, Mugnozza GS (2007) Single-reaction for SNP Genotyping on Agarose Gelby Allele-specific PCR in Black Poplar (Populus nigra L.) Plant Mol Biol Rep 25(1–2):1–9. doi:10.1007/s11105-007-0003-6
Guimaraes EP (2005) Population improvement: a way of exploiting the rice genetic resources of Latin America. FAO, Rome, pp 56–94
Guo JX, Liu YG (2012) Molecular control of male reproductive development and pollen fertility in rice. J Integr Plant Biol 54(12):967–978
Hallauer AR (1985) Compendium of recurrent selection methods and their application. Crit Rev Plant Sci 3:1–33
Hallauer AR, Carena MJ, Miranda Filho JB (2009) Quantitative genetics in maize breeding. Springer, New York
Hara S (1946) Linkage between factors for sterility and anthocyanin pigmentation in rice plant. Jpn J Genet 21(2):32 (in Japanese)
Hull F (1945) Recurrent selection for specific combining ability in corn. J Am Soc Agron 37:134–145
Khera P, Priyadarshi R, Singh A, Mohan R, Gangashetti MG, Singh BN, Kole C, Shenoy V (2012) Molecular characterization of different cytoplasmic male sterile lines using mitochondrial DNA specific markers in rice. J Biol Sci 12:154–160
Kinoshita T (1995) Report of committee on gene symbolization, nomenclature and linkage groups. Rice Genet Newsl 12:9–153
Ko T, Yamagata H (1987) Gene analysis of male-sterility induced in rice. Studies on the utility of artificial mutations in plant breeding. XVI. Jpn J Breed 37:192–198 (in Japanese with English summary)
Ko T, Yamagata H (1989) Studies on the induction of male-sterile strains in rice. Linkage groups of few male-sterility genes. Jpn J Breed 39(Suppl. 1):234–235. (in Japanese)
Lee S, Jung KH, An GH, Chung YY (2004) Isolation and characterization of a rice cysteine protease gene, OSCP1, using T-DNA gene-trap system. Plant Mol Biol 54:755–765
Li N, Zhang D, Liu HS, Yin CS, Li XX, Liang W, Yuan Z, Xu B, Chu HW, Wang J, Wen TQ, Huang H, Luo D, Ma H, Zhang DB (2006a) The rice tapetum degeneration retardation gene is required for tapetum degradation and anther development. Plant Cell 18:2999–3014
Li X, Duan X, Jiang H, Sun Y, Tang Y, Yuan Z, Guo J, Liang W, Chen L, Wang J, Ma H, Yin J, Zhang D (2006b) Genome-wide analysis of basic/helix-loop-helix transcription factor family in rice and Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 141:1167–1184
Li S, Yang D, Zhu Y (2007) Characterization and use of male sterility in hybrid rice breeding. J Integr Plant Biol 49(6):791–804
Liu HS, Chu H, Li H, Wang H, Wei J, Li N, Ding S, Huang H, Ma H, Huang C, Luo D, Yuang Z, Liu J, Zhang D (2005) Genetic analysis and mapping of rice (Oryza sativa L.) male-sterile (OsMS-L) mutant. Chin Sci Bull 50:38–41
Long Y, Zhao L, Niu B, Su J, Wu H, Chen Y, Zhang Q, Guo J, Zhuang C, Mei M, Xia J, Wang L, Wu H, Liu YG (2009) Hybrid male sterility in rice controlled by interaction between divergent alleles of two adjacent genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(48):18871–18876
Ma H (2005) Molecular genetic analyses of microsporogenesis and microgametogenesis in flowering plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 56:393–434
Michelmore RW, Paran I, Kesseli RV (1991) Identification of markers linked to disease-resistance genes by bulked segregant analysis: a rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions by using segregating populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:9828–9832
Oka HI (1983) The indica-japonica differentiation of rice cultivars. A review. In: Proceedings of the 4th international SABRAO congress. 4–8 May 1981, Kuala Lumpur, pp 117–128
Pons JL, Labesse G (2009) @TOME-2: a new pipeline for comparative modeling of protein–ligand complexes. Nucleic Acids Res: 1–7. doi:10.1093/nar/gkp368
Risterucci AM, Grivet L, N’Goran JAK, Pieretti I, Flament MH, Lanaud C (2000) A high-density linkage map of Theobroma cacao L. Theor Appl Genet 101:948–955
Rutger JN, Shinio (1980) Male sterility in rice and its potential use in breeding. In: Proceedings of the international rice research conference. Innovative approach to rice breeding. IRRI. Los Banos, The Philippines, pp 53–66
Schwendiman J, Pannetier C, Michaux-Ferriere N (1988) Histology of somatic embryogenesis from leaf explants of the oil palm Elaeis guineensis. Ann Bot 62:43–52
Singh RJ, Ikehashi H (1981) Monogenic male-sterility in rice: introduction, identification and inheritance. Crop Sci 21:286–289
Suneson CA (1956) An evolutionary plant breeding method. Agron J 48:188–191
Taillebois JE (2006) CIRAD hybrid rice program: lower breeding costs and sustainability. In: 2nd international rice research congress, 9–13 October 2006, New Delhi, India. CIRAD, Montpellier, France
Tan HX, Liang WQ, Hu JP, Zhang DB (2012) MICROSPORE AND TAPETUM REGULATOR 1 encodes a secretory fasciclin glycoprotein required for male reproductive development in rice. Dev Cell 22:1127–1137
Van Ooijen JW (2006) JoinMap ® 4, Software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps in experimental population. Kyazma B.V, Wagningen
Zhang H, Liang WQ, Yang XJ, Luo X, Jiang N, Ma H, Zhang DB (2010) Carbon starved anther encodes a MYB domain protein that regulates sugar partitioning required for rice pollen development. Plant Cell 22:672–689
Zhang D, Luo X, Zhu L (2011) Cytological analysis and genetic control of rice anther development. J Genet Genomics 38:379–390
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11032_2013_9972_MOESM2_ESM.pdf
Supplementary figure SF1: Pattern of expression of the seven candidate genes selected based on map data. Expression data were retrieved from RiceXPro database (http://ricexpro.dna.affrc.go.jp/GGEP/index.html) (PDF 443 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Frouin, J., Filloux, D., Taillebois, J. et al. Positional cloning of the rice male sterility gene ms-IR36, widely used in the inter-crossing phase of recurrent selection schemes. Mol Breeding 33, 555–567 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-013-9972-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-013-9972-3