Abstract
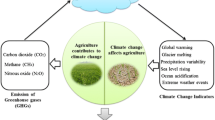
Adopting climate-smart agricultural (CSA) practices is a long-term solution for enhancing agricultural sustainability and food security under the changing climate. However, the penetration rate of CSA practices remains low worldwide. Understanding the key factors driving the adoption of CSA practices is key to increasing its penetration. This study provides a systematic review of the literature comprising 190 studies published between 2013 and 2023. Based on the reviewed literature, we provide comprehensive definitions of CSA practices from broad and narrow perspectives. We also discuss the factors influencing farmers’ decisions to adopt CSA practices from four categories: socio-demographic factors, institutional factors, resource endowment factors, and socio-economic factors. Our literature review reveals that most of the factors (e.g., age, gender, education, risk perception and preference, access to credit, farm size, production conditions, off-farm income, and labor allocation) discussed in the literature have a dual (either positive or negative) impact on CSA practice adoption. The variables such as labor endowment, land tenure security, access to extension services, access to agricultural training, membership in farmers’ organizations, non-governmental organization (NGO) support, climate conditions, and access to information consistently and positively impact CSA practice adoption. These findings provide solid evidence for designing appropriate policy instruments that help accelerate CSA diffusion and transmission. We also find gaps in CSA practice measurements, influencing factor identification, and econometric methods used for empirical analysis, which should be explored by future research.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from Junpeng Li upon request.
References
Abdur Rashid Sarker M, Alam K, Gow J (2013) Assessing the determinants of rice farmers’ adaptation strategies to climate change in Bangladesh. Int J Clim Chang Strateg Manag 5:382–403. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJCCSM-06-2012-0033
Abegunde VO, Sibanda M, Obi A (2020) Determinants of the adoption of climate-smart agricultural practices by small-scale farming households in King Cetshwayo district municipality, South Africa. Sustain 12(1):195. https://doi.org/10.3390/SU12010195
Abeysekara WCSM, Siriwardana M, Meng S (2023) Economic consequences of climate change impacts on the agricultural sector of South Asia: a case study of Sri Lanka. Econ Anal Policy 77:435–450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eap.2022.12.003
Abid M, Schilling J, Scheffran J, Zulfiqar F (2016a) Climate change vulnerability, adaptation and risk perceptions at farm level in Punjab, Pakistan. Sci Total Environ 547:447–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.11.125
Abid M, Schneider UA, Scheffran J (2016b) Adaptation to climate change and its impacts on food productivity and crop income: perspectives of farmers in rural Pakistan. J Rural Stud 47:254–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrurstud.2016.08.005
Abid M, Scheffran J, Schneider UA, Elahi E (2019) Farmer perceptions of climate change, observed trends and adaptation of agriculture in Pakistan. Environ Manage 63:110–123. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-018-1113-7
Adamides G (2020) A review of climate-smart agriculture applications in Cyprus. Atmosphere (Basel) 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/ATMOS11090898
Adhikari U, Nejadhashemi AP, Woznicki SA (2015) Climate change and eastern Africa: a review of impact on major crops. Food Energy Secur 4:110–132. https://doi.org/10.1002/fes3.61
Aftab A, Ahmed A, Scarpa R (2021) Farm households’ perception of weather change and flood adaptations in northern Pakistan. Ecol Econ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2020.106882
Agamile P, Dimova R, Golan J (2021) Crop choice, drought and gender: new insights from smallholders’ response to weather shocks in Rural Uganda. J Agric Econ. https://doi.org/10.1111/1477-9552.12427
Agarwal T, Goel PA, Gartaula H et al (2022) Gendered impacts of climate-smart agriculture on household food security and labor migration: insights from Bihar, India. Int J Clim Chang Strateg Manag 14:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJCCSM-01-2020-0004
Ahmed MH, Tesfaye WM, Gassmann F (2022a) Early growing season weather variation, expectation formation and agricultural land allocation decisions in Ethiopia. J Agric Econ 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1111/1477-9552.12507
Ahmed Z, Shew AM, Mondal MK et al (2022) Climate risk perceptions and perceived yield loss increases agricultural technology adoption in the polder areas of Bangladesh. J Rural Stud 94:274–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrurstud.2022.06.008
Akinlabi Tiamiyu S, Bernadette Ugalahi U, Nwafor Eze J, Adebayo Shittu M (2018) Adoption of climate smart agricultural practices and farmers’ willingness to accept incentives in Nigeria. Res Artic IJAER 4:198–205
Akter S, Rutsaert P, Luis J et al (2017) Women ’ s empowerment and gender equity in agriculture: a different perspective from Southeast Asia. Food Policy 69:270–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodpol.2017.05.003
Alam K (2015) Farmers’ adaptation to water scarcity in drought-prone environments: a case study of Rajshahi District, Bangladesh. Agric Water Manag 148:196–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2014.10.011
Alauddin M, Sarker MAR (2014) Climate change and farm-level adaptation decisions and strategies in drought-prone and groundwater-depleted areas of Bangladesh: an empirical investigation. Ecol Econ 106:204–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2014.07.025
Ali E (2021) Farm households’ adoption of climate-smart practices in subsistence agriculture: evidence from Northern Togo. Environ Manage 67:949–962. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00267-021-01436-3
Amare A, Simane B (2017) Determinants of smallholder farmers’ decision to adopt adaptation options to climate change and variability in the Muger Sub basin of the Upper Blue Nile basin of Ethiopia. Agric Food Secur 6:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40066-017-0144-2
Antwi-Agyei P, Dougill AJ, Stringer LC (2015) Barriers to climate change adaptation: evidence from northeast Ghana in the context of a systematic literature review. Clim Dev 7:297–309. https://doi.org/10.1080/17565529.2014.951013
Antwi-Agyei P, Abalo EM, Dougill AJ, Baffour-Ata F (2021) Motivations, enablers and barriers to the adoption of climate-smart agricultural practices by smallholder farmers: evidence from the transitional and savannah agroecological zones of Ghana. Reg Sustain 2:375–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.regsus.2022.01.005
Arbuckle JG, Morton LW, Hobbs J (2013) Farmer beliefs and concerns about climate change and attitudes toward adaptation and mitigation: evidence from Iowa. Clim Change 118:551–563. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-013-0700-0
Ariani M, Hervani A, Setyanto P (2018) Climate smart agriculture to increase productivity and reduce greenhouse gas emission-a preliminary study. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci 200. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/200/1/012024
Ariom TO, Dimon E, Nambeye E et al (2022) Climate-smart agriculture in African countries: a review of strategies and impacts on smallholder farmers. Sustain 14:1–32. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141811370
Arslan A, Mccarthy N, Lipper L et al (2015) Climate smart agriculture? Assessing the adaptation implications in Zambia. J Agric Econ 66:753–780. https://doi.org/10.1111/1477-9552.12107
Arunrat N, Wang C, Pumijumnong N et al (2017) Farmers’ intention and decision to adapt to climate change: a case study in the Yom and Nan basins, Phichit province of Thailand. J Clean Prod 143:672–685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.12.058
Aryal JP, Farnworth CR, Khurana R et al (2014) Gender dimensions of climate change adaptation through climate smart agricultural practices in India. Innovation in Indian Agriculture: Ways Forward. New Delhi: Institute of Economic Growth (IEG), New Delhi, and International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI), Washington, DC
Aryal JP, Jat ML, Sapkota TB et al (2018a) Adoption of multiple climate-smart agricultural practices in the Gangetic plains of Bihar, India. Int J Clim Chang Strateg Manag 10:407–427. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJCCSM-02-2017-0025
Aryal JP, Rahut DB, Maharjan S, Erenstein O (2018b) Factors affecting the adoption of multiple climate-smart agricultural practices in the Indo-Gangetic Plains of India. Nat Resour Forum 42:141–158. https://doi.org/10.1111/1477-8947.12152
Aryal JP, Farnworth CR, Khurana R et al (2020a) Does women’s participation in agricultural technology adoption decisions affect the adoption of climate-smart agriculture? Insights from Indo-Gangetic Plains of India. Rev Dev Econ 24:973–990. https://doi.org/10.1111/rode.12670
Aryal JP, Sapkota TB, Khurana R et al (2020b) Climate change and agriculture in South Asia: adaptation options in smallholder production systems. Springer, Netherlands
Aryal JP, Sapkota TB, Rahut DB et al (2020c) Major climate risks and adaptation strategies of smallholder farmers in Coastal Bangladesh. Environ Manage 66:105–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-020-01291-8
Aryal JP, Sapkota TB, Rahut DB et al (2022) Gender and climate change adaptation: a case of Ethiopian farmers. Nat Resour Forum 46:263–288. https://doi.org/10.1111/1477-8947.12259
Asfaw S, McCarthy N, Lipper L et al (2016) What determines farmers’ adaptive capacity? Empirical evidence from Malawi. Food Secur 8:643–664. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12571-016-0571-0
Asfawa S, Di Battista F, Lipper L (2016) Agricultural technology adoption under climate change in the Sahel: micro-evidence from Niger. J Afr Econ 25:637–669. https://doi.org/10.1093/jae/ejw005
Ashraf M, Routray JK, Saeed M (2014) Determinants of farmers’ choice of coping and adaptation measures to the drought hazard in northwest Balochistan, Pakistan. Nat Hazards 73:1451–1473. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-014-1149-9
Autio A, Johansson T, Motaroki L et al (2021) Constraints for adopting climate-smart agricultural practices among smallholder farmers in Southeast Kenya. Agric Syst 194:103284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agsy.2021.103284
Azadi Y, Yazdanpanah M, Mahmoudi H (2019) Understanding smallholder farmers’ adaptation behaviors through climate change beliefs, risk perception, trust, and psychological distance: evidence from wheat growers in Iran. J Environ Manage 250:109456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109456
Bardsley DK, Palazzo E, Pütz M (2018) Regional path dependence and climate change adaptation: a case study from the McLaren Vale, South Australia. J Rural Stud 63:24–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrurstud.2018.08.015
Bate BG, Kimengsi JN, Amawa SG (2019) Determinants and policy implications of farmers’ climate adaptation choices in rural Cameroon. Sustain 11:1–14. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11071921
Belay A, Mirzabaev A, Recha JW (2023) Does climate‑smart agriculture improve household income and food security ? Evidence from Southern Ethiopia. Environ Dev Sustain. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-023-03307-9
Benitez-Altuna F, Trienekens J, Materia VC, Bijman J (2021) Factors affecting the adoption of ecological intensification practices: a case study in vegetable production in Chile. Agric Syst 194:103283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agsy.2021.103283
Benson T, Ayiga N (2022) Classifying the involvement of men and women in climate smart agricultural practices in Kayonza Sub-county, Kanungu District Uganda. Int J Energy Environ Sci 7(1):7. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ijees.20220701.12
Bernier Q, Meinzen-Dick R, Kristjanson P et al (2015) Gender and institutional aspects of climate-smart agricultural practices: evidence from Kenya. CCAFS Working Paper. https://hdl.handle.net/10568/65680
Brar HS, Vashist KK (2020) Drip irrigation and nitrogen fertilization alter phenological development and yield of spring maize (Zea mays L.) under semi-arid conditions. J Plant Nutr 43:1757–1767. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2020.1744648
Brüssow K, Faße A, Grote U (2017) Implications of climate-smart strategy adoption by farm households for food security in Tanzania. Food Secur 9:1203–1218. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12571-017-0694-y
Bryan E, Ringler C, Okoba B et al (2013) Adapting agriculture to climate change in Kenya: household strategies and determinants. J Environ Manage 114:26–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2012.10.036
Castaing P (2021) Joint liability and adaptation to climate change: evidence from Burkinabe cooperatives. Eur Rev Agric Econ 48:502–537. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurrag/jbaa020
Cavanagh CJ, Chemarum AK, Vedeld PO, Petursson JG (2017) Old wine, new bottles? Investigating the differential adoption of ‘climate-smart’ agricultural practices in western Kenya. J Rural Stud 56:114–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrurstud.2017.09.010
Ceci P, Monforte L, Perelli C, et al (2021) Smallholder farmers’ perception of climate change and drivers of adaptation in agriculture: a case study in Guinea. Rev Dev Econ 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1111/rode.12815
Chamberlin J, Ricker-Gilbert J (2016) Participation in rural land rental markets in sub-Saharan Africa: who benefits and by how much? Evidence from Malawi and Zambia. Am J Agric Econ 98:1507–1528. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.5524
Chandra A, Dargusch P, McNamara KE et al (2017a) A study of climate-smart farming practices and climate-resiliency field schools in Mindanao, the Philippines. World Dev 98:214–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.worlddev.2017.04.028
Chandra A, McNamara KE, Dargusch P (2017b) The relevance of political ecology perspectives for smallholder climate-smart agriculture: a review. J Polit Ecol 24:821–842. https://doi.org/10.2458/v24i1.20969
Chicas SD, Nielsen JØ, Robinson GM, et al (2023) The adoption of climate-smart agriculture to address wildfires in the Maya Golden Landscape of Belize: smallholder farmers’ perceptions. J Environ Manage 345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.118562
Cui X (2020) Climate change and adaptation in agriculture: evidence from US cropping patterns. J Environ Econ Manage 101:102306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeem.2020.102306
de Sousa K, Casanoves F, Sellare J et al (2018) How climate awareness influences farmers’ adaptation decisions in Central America? J Rural Stud 64:11–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrurstud.2018.09.018
Di Falco S (2014) Adaptation to climate change in sub-Saharan agriculture: assessing the evidence and rethinking the drivers. Eur Rev Agric Econ 41:405–430. https://doi.org/10.1093/erae/jbu014
Di Falco S, Sharma S (2018) Investing in climate change adaptation: motivations and green incentives in the Fiji Islands. Ecol Econ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2018.08.015
Dietz KJ, Zörb C, Geilfus CM (2021) Drought and crop yield. Plant Biol 23:881–893. https://doi.org/10.1111/plb.13304
Diro S, Tesfaye A, Erko B (2022) Determinants of adoption of climate-smart agricultural technologies and practices in the coffee-based farming system of Ethiopia. Agric Food Secur 11:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40066-022-00385-2
Djido A, Zougmoré RB, Houessionon P, et al (2021) To what extent do weather and climate information services drive the adoption of climate-smart agriculture practices in Ghana? Clim Risk Manag 32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crm.2021.100309
Do H-L, Ho TQ (2022) Climate change adaptation strategies and shrimp aquaculture: empirical evidence from the Mekong Delta of Vietnam. Ecol Econ 196:107411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2022.107411
Egeru A, Bbosa MM, Siya A et al (2022) Micro-level analysis of climate-smart agriculture adoption and effect on household food security in semi-arid Nakasongola District in Uganda. Environ Res Clim 1:025003. https://doi.org/10.1088/2752-5295/ac875d
Eigenbrode SD, Adhikari S (2023) Climate change and managing insect pests and beneficials in agricultural systems. Agron J 115:2194–2215. https://doi.org/10.1002/agj2.21399
Eitzinger A, Binder CR, Meyer MA (2018) Risk perception and decision-making: do farmers consider risks from climate change? Clim Change 151:507–524. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-018-2320-1
ELD Initiative (2015) Report for policy and decision makers: reaping economic and environmental benefits from sustainable land management. Available from www.eld-initiative.org
Elum ZA, Modise DM, Marr A (2017) Farmer’s perception of climate change and responsive strategies in three selected provinces of South Africa. Clim Risk Manag 16:246–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crm.2016.11.001
Engel S, Muller A (2016) Payments for environmental services to promote “climate-smart agriculture”? Potential and challenges. Agric Econ (united Kingdom) 47:173–184. https://doi.org/10.1111/agec.12307
Engels A (2018) Understanding how China is championing climate change mitigation. Palgrave Commun 4. https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-018-0150-4
Everest B (2021) Farmers’ adaptation to climate-smart agriculture (CSA) in NW Turkey. Environ Dev Sustain 23:4215–4235. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-020-00767-1
Di FS, Adinolfi F, Bozzola M, Capitanio F (2014) Crop insurance as a strategy for adapting to climate change. J Agric Econ 65:485–504. https://doi.org/10.1111/1477-9552.12053
Feleke FB, Berhe M, Gebru G, Hoag D (2016) Determinants of adaptation choices to climate change by sheep and goat farmers in Northern Ethiopia: the case of Southern and Central Tigray, Ethiopia. Springerplus 5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-016-3042-3
Feola G, Lerner AM, Jain M et al (2015) Researching farmer behaviour in climate change adaptation and sustainable agriculture: lessons learned from five case studies. J Rural Stud 39:74–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrurstud.2015.03.009
Fisher M, Abate T, Lunduka RW et al (2015) Drought tolerant maize for farmer adaptation to drought in sub-Saharan Africa: determinants of adoption in eastern and southern Africa. Clim Change 133:283–299. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-015-1459-2
Gashure S, Wana D (2022) Smallholders’ adoption of climate-smart practices in Konso, Ethiopia. Int J Environ Stud 00:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207233.2022.2043115
Ghimire R, Khatri-Chhetri A, Chhetri N (2022) Institutional innovations for climate smart agriculture: assessment of climate-smart village approach in Nepal. Front Sustain Food Syst 6. https://doi.org/10.3389/fsufs.2022.734319
Ghosh M (2019) Climate-smart agriculture, productivity and food security in India. J Dev Policy Pract 4:166–187. https://doi.org/10.1177/2455133319862404
Ginbo T, Hansson H (2023) Intra-household risk perceptions and climate change adaptation in sub-Saharan Africa. Eur Rev Agric Econ 50:1039–1063. https://doi.org/10.1093/erae/jbad011
Girard J, Delacote P, Leblois A (2021) Agricultural households’ adaptation to weather shocks in sub-Saharan Africa: implications for land-use change and deforestation. Environ Dev Econ 26:538–560. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1355770X2000056X
Gruda N, Bisbis M, Tanny J (2019) Impacts of protected vegetable cultivation on climate change and adaptation strategies for cleaner production – a review. J Clean Prod 225:324–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.03.295
Gwambene B, Saria JA, Jiwaji NT et al (2015) Smallholder farmers’ practices and understanding of climate change and climate smart agriculture in the southern highlands of Tanzania. J Resour Dev Manag 13:37–47
Haldar T, Damodaran A (2022) Can cooperatives influence farmer’s decision to adopt organic farming? Agri-decision making under price volatility. Environ Dev Sustain 24:5718–5742. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01679-4
Haq-ul S, Boz I, Shahbaz P (2021) Adoption of climate-smart agriculture practices and differentiated nutritional outcome among rural households: a case of Punjab province, Pakistan. Food Secur 13:913–931. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12571-021-01161-z
Hasan MK, Kumar L (2019) Comparison between meteorological data and farmer perceptions of climate change and vulnerability in relation to adaptation. J Environ Manage 237:54–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.02.028
He X, Yan J, Yang LE et al (2022) The role of government interventions in household climate adaptation on the Tibetan Plateau. J Rural Stud 95:544–559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrurstud.2022.10.003
Heeb L, Jenner E (2004) Cock MJW (2019) Climate-smart pest management: building resilience of farms and landscapes to changing pest threats. J Pest Sci 92:951–969. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-019-01083-y
Hu M, Xiang G, Zhong S (2021) The burden of social connectedness: do escalating gift expenditures make you happy? J Happiness Stud 22:3479–3497. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-020-00341-6
Iglesias A, Garrote L, Bardají I, et al (2021) Looking into individual choices and local realities to define adaptation options to drought and climate change. J Environ Manage 293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112861
Iqbal MH, Aziz A (2022) Crop selection as climate change adaptation: a study on Koyra Upazila of Bangladesh. Ecol Econ 199:107488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2022.107488
Issahaku G, Abdul-Rahaman A (2019) Sustainable land management practices, off-farm work participation and vulnerability among farmers in Ghana: is there a nexus? Int Soil Water Conserv Res 7:18–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iswcr.2018.10.002
Issahaku G, Abdul-Rahaman A, Amikuzuno J (2021) Climate change adaptation strategies, farm performance and poverty reduction among smallholder farming households in Ghana. Clim Dev 13:736–747. https://doi.org/10.1080/17565529.2020.1860884
Jellason NP, Conway JS, Baines RN (2020) Understanding impacts and barriers to adoption of climate-smart agriculture (CSA) practices in North-Western Nigerian drylands. J Agric Educ Ext 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1080/1389224X.2020.1793787
Jin J, Gao Y, Wang X, Nam PK (2015) Farmers’ risk preferences and their climate change adaptation strategies in the Yongqiao District, China. Land Use Policy 47:365–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2015.04.028
Jude Nwafor E, Umar A, Muhammad A, Oloruntoba O (2014) Building resilience for adaptation to climate change among downstream communities in Nigeria through climate smart agriculture. Int J Agric Innov Res 3:2319–1473
Kalema EP, Akpo E, Muricho G et al (2022) Mapping out market drivers of improved variety seed use: the case of sorghum in Tanzania. Heliyon 8:e08715. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e08715
Kane AM, Lagat JK, Fane T et al (2019) Economic viability of alternative small-scale irrigation systems used in vegetables production in Koulikoro and Mopti regions, Mali. Handb Clim Chang Resilience 1–4(2):1051–1082. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-93336-8_101
Kangogo D, Dentoni D, Bijman J (2021) Adoption of climate‐smart agriculture among smallholder farmers: Does farmer entrepreneurship matter? Land use policy 109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2021.105666
Kaptymer BL, Abdulkerim Ute J, Negeso Hule M (2019) Climate smart agriculture and its implementation challenges in Africa. Curr J Appl Sci Technol 38:1–13. https://doi.org/10.9734/cjast/2019/v38i430371
Karume K, Mondo JM, Chuma GB, et al (2022) Current practices and prospects of climate-smart agriculture in Democratic Republic of Congo: a review. Land 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11101850
Keovilignavong O, Suhardiman D (2020) Linking land tenure security with food security: unpacking farm households’ perceptions and strategies in the rural uplands of Laos. Land Use Policy 90:104260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2019.104260
Key N (2019) Farm size and productivity growth in the United States Corn Belt. Food Policy 84:186–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodpol.2018.03.017
Khan I, Lei H, Shah IA et al (2020) Farm households’ risk perception, attitude and adaptation strategies in dealing with climate change: promise and perils from rural Pakistan. Land Use Policy 91:104395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2019.104395
Khan NA, Gong Z, Shah AA et al (2021) Farm-level autonomous adaptation to climate change and its impact on crop productivity: evidence from Pakistan. Environ Dev Sustain. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01978-w
Khanal U, Wilson C, Hoang VN, Lee B (2018) Farmers’ adaptation to climate change, its determinants and impacts on rice yield in Nepal. Ecol Econ 144:139–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2017.08.006
Khanal U, Wilson C, Hoang VN, Lee B (2019) Impact of community-based organizations on climate change adaptation in agriculture: empirical evidence from Nepal. Environ Dev Sustain 21:621–635. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-017-0050-6
Khatri-Chhetri A, Pant A, Aggarwal PK et al (2019) Stakeholders prioritization of climate-smart agriculture interventions: evaluation of a framework. Agric Syst 174:23–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agsy.2019.03.002
Khoza S, de Beer LT, van Niekerk D, Nemakonde L (2021) A gender-differentiated analysis of climate-smart agriculture adoption by smallholder farmers: application of the extended technology acceptance model. Gend Technol Dev 25:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/09718524.2020.1830338
Kifle T, Ayal DY, Mulugeta M (2022) Factors influencing farmers adoption of climate smart agriculture to respond climate variability in Siyadebrina Wayu District Central Highland of Ethiopia. Clim Serv 26:100290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cliser.2022.100290
Kousar R, Abdulai A (2016) Off-farm work, land tenancy contracts and investment in soil conservation measures in rural Pakistan. Aust J Agric Resour Econ 60:307–325
Kpadonou RAB, Owiyo T, Barbier B et al (2017) Advancing climate-smart-agriculture in developing drylands: joint analysis of the adoption of multiple on-farm soil and water conservation technologies in West African Sahel. Land Use Policy 61:196–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2016.10.050
Kreft C, Huber R, Wuepper D, Finger R (2021) The role of non-cognitive skills in farmers’ adoption of climate change mitigation measures. Ecol Econ 189:107169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2021.107169
Kumar N, Nath CP (2019) Impact of zero-till residue management and crop diversification with legumes on soil aggregation and carbon sequestration. Soil Tillage Res 189:158–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2019.02.001
Kumar KNR, Reddy MJM, Reddy KV, et al (2023) Determinants of climate change adaptation strategies in South India: empirical evidence. Front Sustain Food Syst 7. https://doi.org/10.3389/fsufs.2023.1010527
Kumasi TC, Antwi-Agyei P, Obiri-Danso K (2019) Small-holder farmers’ climate change adaptation practices in the Upper East Region of Ghana. Environ Dev Sustain 21:745–762. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-017-0062-2
Kurgat BK, Lamanna C, Kimaro A, et al (2020) Adoption of climate-smart agriculture technologies in Tanzania. Front Sustain Food Syst 4. https://doi.org/10.3389/fsufs.2020.00055
Läderach P, Ramirez-Villegas J, Navarro-Racines C et al (2017) Climate change adaptation of coffee production in space and time. Clim Change 141:47–62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-016-1788-9
Lan L, Sain G, Czaplicki S et al (2018) Farm-level and community aggregate economic impacts of adopting climate smart agricultural practices in three mega environments. PLoS ONE 13:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0207700
Lawson ET, Alare RS, Salifu ARZ, Thompson-Hall M (2020) Dealing with climate change in semi-arid Ghana: understanding intersectional perceptions and adaptation strategies of women farmers. GeoJournal 85:439–452. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10708-019-09974-4
Lee J (2017) Farmer participation in a climate-smart future: evidence from the Kenya agricultural carbon market project. Land Use Policy 68:72–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2017.07.020
Lefebvre M, Midler E, Bontems P (2020) Adoption of environment-friendly agricultural practices with background risk: experimental evidence. Environ Resour Econ 76:405–428. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10640-020-00431-2
Li J, Ma W (2023) Sharing energy poverty: the nexus between social interaction-oriented gift expenditure and energy poverty in rural China. Energy Res Soc Sci 101:103131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.erss.2023.103131
Li H, Liu Y, Zhao X et al (2021) Estimating effects of cooperative membership on farmers’ safe production behaviors: evidence from the rice sector in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:25400–25418. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-12337-z
Li J, Ma W, Botero-R JC, Quoc Luu P (2023a) Mechanization in land preparation and irrigation water productivity: insights from rice production. Int J Water Resour Dev 00:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1080/07900627.2023.2197080
Li J, Ma W, Gong B (2023b) Market participation and subjective well-being of maize farmers. Econ Anal Policy 80:941–960. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eap.2023.09.037
Li J, Ma W, Wang P, Meng X (2023c) Farmers’ willingness to transform untreated livestock manure into organic fertilizer: does information technology adoption make a difference? Environ Dev Sustain. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-023-02920-y
Li J, Vatsa P, Ma W (2023d) Small acts with big impacts: does garbage classification improve subjective well-being in rural China? Appl Res Qual Life. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11482-022-10142-z
Li L, Jin J, He R et al (2023e) Effects of social capital on farmers’ choices of climate change adaptation behavior in Dazu District, China. Clim Dev 15:110–121. https://doi.org/10.1080/17565529.2022.2061403
Liu R, Gao Z, Nayga RM, et al (2020) Can “green food” certification achieve both sustainable practices and economic benefits in a transitional economy? The case of kiwifruit growers in Henan Province, China. Agribusiness 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1002/agr.21641
Liu J, Jain V, Sharma P et al (2022) The role of Sustainable Development Goals to eradicate the multidimensional energy poverty and improve social Wellbeing’s. Energy Strateg Rev 42:100885. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esr.2022.100885
Liverpool-Tasie LSO, Parkhi CM (2021) Climate risk and technology adoption in the midstream of crop value chains: evidence from Nigerian maize traders. J Agric Econ 72:158–179. https://doi.org/10.1111/1477-9552.12394
Lorite IJ, Gabaldón-Leal C, Ruiz-Ramos M et al (2018) Evaluation of olive response and adaptation strategies to climate change under semi-arid conditions. Agric Water Manag 204:247–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2018.04.008
Lu Z, Bandara JS, Paramati SR (2020) Impact of sanitation, safe drinking water and health expenditure on infant mortality rate in developing economies. Aust Econ Pap 59:13–33. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8454.12167
Ma W, Ma C, Su Y, Nie Z (2017) Organic farming: does acquisition of the farming information influence Chinese apple farmers’ willingness to adopt? China Agric Econ Rev 9:211–224. https://doi.org/10.1108/CAER-05-2016-0070
Ma W, Abdulai A, Goetz R (2018) Agricultural cooperatives and investment in organic soil amendments and chemical fertilizer in China. Am J Agric Econ 100:502–520. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajae/aax079
Mailumo SS, Onuwa GC, Oyewole S (2021) Adoption of climate smart agriculture among food crop farmers in Birnin-Kudu Local Government Area, Jigawa State, Nigeria. Russ J Agric Socio-Economic Sci 110:169–176. https://doi.org/10.18551/rjoas.2021-02.20
Makate C (2019) Effective scaling of climate smart agriculture innovations in African smallholder agriculture: a review of approaches, policy and institutional strategy needs. Environ Sci Policy 96:37–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsci.2019.01.014
Makate C, Makate M, Mango N, Siziba S (2019a) Increasing resilience of smallholder farmers to climate change through multiple adoption of proven climate-smart agriculture innovations. Lessons from Southern Africa. J Environ Manage 231:858–868. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.10.069
Makate C, Makate M, Mutenje M et al (2019b) Synergistic impacts of agricultural credit and extension on adoption of climate-smart agricultural technologies in southern Africa. Environ Dev 32:100458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envdev.2019.100458
Mallawaarachchi T, Nauges C, Sanders O, Quiggin J (2017) State-contingent analysis of farmers’ response to weather variability: irrigated dairy farming in the Murray Valley, Australia. Aust J Agric Resour Econ 61:36–55. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8489.12193
Mango N, Makate C, Tamene L et al (2018) Adoption of small-scale irrigation farming as a climate-smart agriculture practice and its influence on household income in the Chinyanja Triangle, Southern Africa. Land 7:1–19. https://doi.org/10.3390/land7020049
Martey E, Etwire PM, Mockshell J (2021) Climate-smart cowpea adoption and welfare effects of comprehensive agricultural training programs. Technol Soc 64:101468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2020.101468
Mashi SA, Inkani A, oghenejbabor obaro (2022) Determinants of awareness levels of climate smart agricultural technologies and practices of urban farmers in Kuje, Abuja, Nigeria. SSRN Electron J. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4061509
Masud MM, Azam MN, Mohiuddin M et al (2017) Adaptation barriers and strategies towards climate change: challenges in the agricultural sector. J Clean Prod 156:698–706. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.04.060
Mazhar R, Ghafoor A, Xuehao B, Wei Z (2021) Fostering sustainable agriculture: do institutional factors impact the adoption of multiple climate-smart agricultural practices among new entry organic farmers in Pakistan? J Clean Prod 283:124620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124620
Mi Z, Sun X (2021) Provinces with transitions in industrial structure and energy mix performed best in climate change mitigation in China. Commun Earth Environ 2:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43247-021-00258-9
Mirón IJ, Linares C, Díaz J (2023) The influence of climate change on food production and food safety. Environ Res 216:114674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.114674
Mizik T (2021) Climate-smart agriculture on small-scale farms: a systematic literature review. Agronomy 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11061096
Mthethwa KN, Ngidi MSC, Ojo TO, Hlatshwayo SI (2022) The determinants of adoption and intensity of climate-smart agricultural practices among smallholder maize farmers. Sustain 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142416926
Mujeyi A, Mudhara M, Mutenje MJ (2020) Adoption determinants of multiple climate smart agricultural technologies in Zimbabwe: considerations for scaling-up and out. African J Sci Technol Innov Dev 12:735–746. https://doi.org/10.1080/20421338.2019.1694780
Mujeyi A, Mudhara M, Mutenje MJ (2022) Adoption patterns of climate-smart agriculture in integrated crop-livestock smallholder farming systems of Zimbabwe. Clim Dev 14:399–408. https://doi.org/10.1080/17565529.2021.1930507
Munang R, Thiaw I, Alverson K et al (2013) The role of ecosystem services in climate change adaptation and disaster risk reduction. Curr Opin Environ Sustain 5:47–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cosust.2013.02.002
Muneer S, Bakhsh K, Ali R et al (2023) Farm households’ perception and adaptation to climate change in relation of food crop productivity in Pakistan. Environ Dev Sustain. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-023-03333-7
Murage AW, Midega CAO, Pittchar JO et al (2015) Determinants of adoption of climate-smart push-pull technology for enhanced food security through integrated pest management in eastern Africa. Food Secur 7:709–724. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12571-015-0454-9
Murray U, Gebremedhin Z, Brychkova G, Spillane C (2016) Smallholder farmers and climate smart agriculture: technology and labor-productivity constraints amongst women smallholders in Malawi. Gend Technol Dev 20:117–148. https://doi.org/10.1177/0971852416640639
Musafiri CM, Kiboi M, Macharia J, et al (2022) Adoption of climate-smart agricultural practices among smallholder farmers in Western Kenya: do socioeconomic, institutional, and biophysical factors matter? Heliyon 8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e08677
Musyoki ME, Busienei JR, Gathiaka JK, Karuku GN (2022) Linking farmers’ risk attitudes, livelihood diversification and adoption of climate smart agriculture technologies in the Nyando basin. South-Western Kenya Heliyon 8:e09305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09305
Mutenje MJ, Farnworth CR, Stirling C et al (2019) A cost-benefit analysis of climate-smart agriculture options in Southern Africa: balancing gender and technology. Ecol Econ 163:126–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2019.05.013
Mutombo P, Musarandega H (2023) Unpacking the determinants of climate-smart agriculture adoption by smallholder farmers in Ward 10, Zvimba District, Zimbabwe. Eur J Dev Stud 3:74–84. https://doi.org/10.24018/ejdevelop.2023.3.1.198
Ngigi MW, Müller U, Birner R (2018) Farmers’ intrinsic values for adopting climate-smart practices in Kenya: empirical evidence from a means-end chain analysis. Clim Dev 10:614–624. https://doi.org/10.1080/17565529.2018.1442786
Nguyen Chau T, Scrimgeour F (2023) Will climate change jeopardize the Vietnamese target of maintaining farmland for food security? A fractional multinomial logit analysis of land use choice. Agric Econ 570–587. https://doi.org/10.1111/agec.12787
Niles MT, Lubell M, Brown M (2015) How limiting factors drive agricultural adaptation to climate change. Agric Ecosyst Environ 200:178–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2014.11.010
Nyang’au JO, Mohamed JH, Mango N et al (2021) Smallholder farmers’ perception of climate change and adoption of climate smart agriculture practices in Masaba South Sub-county, Kisii Kenya. Heliyon 7:e06789. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06789
Nyanga A, Kessler A, Tenge A (2016) Key socio-economic factors influencing sustainable land management investments in the West Usambara Highlands, Tanzania. Land Use Policy 51:260–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2015.11.020
Nyasimi M, Kimeli P, Sayula G et al (2017) Adoption and dissemination pathways for climate-smart agriculture technologies and practices for climate-resilient livelihoods in Lushoto. Northeast Tanzania Clim 5:63
Ochieng J, Kirimi L, Makau J (2017) Adapting to climate variability and change in rural Kenya: farmer perceptions, strategies and climate trends. Nat Resour Forum 41:195–208. https://doi.org/10.1111/1477-8947.12111
Ojo TO, Baiyegunhi LJS (2020) Determinants of climate change adaptation strategies and its impact on the net farm income of rice farmers in south-west Nigeria. Land Use Policy 95:103946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2019.04.007
Ojo TO, Ogundeji AA, Belle JA (2021) Climate change perception and impact of on-farm demonstration on intensity of adoption of adaptation strategies among smallholder farmers in South Africa. Technol Forecast Soc Change 172:121031. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2021.121031
Okello D, Mayega RW, Muhumuza C et al (2018) ender and innovation for climate-smart agriculture: assessment of gender-responsiveness of RAN’s agricultural-focused innovations. CCAFS Working Paper no. 260. CGIAR Research Program on Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security (CCAFS), Wageningen, the Netherlands. Available online at: www.ccafs.cgiar.org
Olorunfemi TO, Olorunfemi OD, Oladele OI (2020) Determinants of the involvement of extension agents in disseminating climate smart agricultural initiatives: implication for scaling up. J Saudi Soc Agric Sci 19:285–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssas.2019.03.003
Olutumise AI (2023) Impact of credit on the climate adaptation utilization among food crop farmers in Southwest, Nigeria: application of endogenous treatment Poisson regression model. Agric Food Econ 11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40100-023-00251-0
Onyeneke RU, Igberi CO, Uwadoka CO, Aligbe JO (2018) Status of climate-smart agriculture in southeast Nigeria. GeoJournal 83:333–346. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10708-017-9773-z
Onyeneke RU, Igberi CO, Aligbe JO et al (2020) Climate change adaptation actions by fish farmers: evidence from the Niger Delta Region of Nigeria. Aust J Agric Resour Econ 64:347–375. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8489.12359
Ouédraogo M, Houessionon P, Zougmoré RB, Partey ST (2019) Uptake of climate-smart agricultural technologies and practices: actual and potential adoption rates in the climate-smart village site of Mali. Sustain 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11174710
Oyawole FP, Shittu A, Kehinde M et al (2021) Women empowerment and adoption of climate-smart agricultural practices in Nigeria. African J Econ Manag Stud 12:105–119. https://doi.org/10.1108/AJEMS-04-2020-0137
Pakmehr S, Yazdanpanah M, Baradaran M (2020) How collective efficacy makes a difference in responses to water shortage due to climate change in southwest Iran. Land Use Policy 99:104798. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2020.104798
Pakmehr S, Yazdanpanah M, Baradaran M (2021) Explaining farmers’ response to climate change-induced water stress through cognitive theory of stress: an Iranian perspective. Environ Dev Sustain 23:5776–5793. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-020-00846-3
Pan D, Tang J, Zhang L et al (2021) The impact of farm scale and technology characteristics on the adoption of sustainable manure management technologies: evidence from hog production in China. J Clean Prod 280:124340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124340
Perino G, Schwickert H (2023) Animal welfare is a stronger determinant of public support for meat taxation than climate change mitigation in Germany. Nat Food 4:160–169. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43016-023-00696-y
Ponce C (2020) Intra-seasonal climate variability and crop diversification strategies in the Peruvian Andes: a word of caution on the sustainability of adaptation to climate change. World Dev 127:104740. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.worlddev.2019.104740
Roco L, Engler A, Bravo-Ureta B, Jara-Rojas R (2014) Farm level adaptation decisions to face climatic change and variability: evidence from Central Chile. Environ Sci Policy 44:86–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsci.2014.07.008
Salehi M (2022) Global water shortage and potable water safety; Today’s concern and tomorrow’s crisis. Environ Int 158:106936. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2021.106936
Saptutyningsih E, Diswandi D, Jaung W (2020) Does social capital matter in climate change adaptation? A lesson from agricultural sector in Yogyakarta. Indonesia Land Use Policy 95:104189
Sardar A, Kiani AK, Kuslu Y (2021) Does adoption of climate-smart agriculture (CSA) practices improve farmers’ crop income? Assessing the determinants and its impacts in Punjab province, Pakistan. Environ Dev Sustain 23:10119–10140
Sargani GR, Jiang Y, Joyo MA et al (2023) No farmer no food, assessing farmers climate change mitigation, and adaptation behaviors in farm production. J Rural Stud 100:103035. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrurstud.2023.103035
Sattar RS, Mehmood MS, Raza MH et al (2023) Evaluating adoption of climate smart agricultural practices among farmers in the Fujian Province, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:45331–45341. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25480-0
Scognamillo A, Sitko NJ (2021) Leveraging social protection to advance climate-smart agriculture: an empirical analysis of the impacts of Malawi’s Social Action Fund (MASAF) on farmers’ adoption decisions and welfare outcomes. World Dev 146:105618. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.worlddev.2021.105618
Sesmero J, Ricker-Gilbert J, Cook A (2018) How do african farm households respond to changes in current and past weather patterns? A structural panel data analysis from Malawi. Am J Agric Econ 100:115–144. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajae/aax068
Shahzad MF, Abdulai A (2020) Adaptation to extreme weather conditions and farm performance in rural Pakistan. Agric Syst 180:102772. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agsy.2019.102772
Shahzad MF, Abdulai A (2021) The heterogeneous effects of adoption of climate-smart agriculture on household welfare in Pakistan. Appl Econ 53:1013–1038
Shripati Mishra C, Taraputia T, Suchen B (2014) Policy advocacy for climate smart agriculture in millets: an initiative for ensuring food security in tribal communities of Koraput Tract, Odisha, India. Glob Adv Res J Agric Sci 3:179–185
Sitko NJ, Scognamillo A, Malevolti G (2021) Does receiving food aid influence the adoption of climate-adaptive agricultural practices? Evidence from Ethiopia and Malawi. Food Policy 102:102041. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodpol.2021.102041
Smith R, Ehrenberg R (2016) Modern labor economics. Pearson Education Asia LTD
Steinhübel L, Wegmann J, Mußhoff O (2020) Digging deep and running dry—the adoption of borewell technology in the face of climate change and urbanization. Agric Econ (united Kingdom) 51:685–706. https://doi.org/10.1111/agec.12586
Tadesse M, Simane B, Abera W et al (2021) The effect of climate-smart agriculture on soil fertility, crop yield, and soil carbon in southern ethiopia. Sustain 13:1–11. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13084515
Tambet H, Stopnitzky Y (2021) Climate adaptation and conservation agriculture among Peruvian farmers. Am J Agric Econ 103:900–922. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajae.12177
Tambo JA, Abdoulaye T (2013) Smallholder farmers’ perceptions of and adaptations to climate change in the Nigerian savanna. Reg Environ Chang 13:375–388. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10113-012-0351-0
Tankha S, Fernandes D, Narayanan NC (2020) Overcoming barriers to climate smart agriculture in India. Int J Clim Chang Strateg Manag 12:108–127. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJCCSM-10-2018-0072
Tesfahunegn GB, Mekonen K, Tekle A (2016) Farmers’ perception on causes, indicators and determinants of climate change in northern Ethiopia: implication for developing adaptation strategies. Appl Geogr 73:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2016.05.009
Thoai TQ, Rañola RF, Camacho LD, Simelton E (2018) Determinants of farmers’ adaptation to climate change in agricultural production in the central region of Vietnam. Land Use Policy 70:224–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2017.10.023
Tran H, Simelton E, Quinn C (2017) Roles of social learning for the adoption of climate-smart agriculture innovations: case study from My Loi Climate-Smart Village, Vietnam. CCAFS Working Paper 31
Tran NLD, Rañola RF, Ole Sander B et al (2020) Determinants of adoption of climate-smart agriculture technologies in rice production in Vietnam. Int J Clim Chang Strateg Manag 12:238–256. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJCCSM-01-2019-0003
UN (2017) World population prospects: the 2017 revision, key findings and advance tables. Working Paper No. ESA/P/WP/248
van Valkengoed AM, Steg L (2019) Meta-analyses of factors motivating climate change adaptation behaviour. Nat Clim Chang 9:158–163. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41558-018-0371-y
Venus TE, Bilgram S, Sauer J, Khatri-Chettri A (2022) Livelihood vulnerability and climate change: a comparative analysis of smallholders in the Indo-Gangetic plains. Environ Dev Sustain 24:1981–2009. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01516-8
Verhagen J, Vellinga T, Neijenhuis F et al (2014) Climate-smart agriculture: scientists’ perspectives. CGIAR Research Program on Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security (CCAFS), Copenhagen
Waaswa A, Oywaya Nkurumwa A, Mwangi Kibe A, Ngeno Kipkemoi J (2022) Climate-Smart agriculture and potato production in Kenya: review of the determinants of practice. Clim Dev 14:75–90. https://doi.org/10.1080/17565529.2021.1885336
Wang Y, Huang J, Wang J, Findlay C (2018) Mitigating rice production risks from drought through improving irrigation infrastructure and management in China. Aust J Agric Resour Econ 62:161–176. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8489.12241
Wang W, Zhao X, Li H, Zhang Q (2021) Will social capital affect farmers’ choices of climate change adaptation strategies? Evidences from rural households in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. J Rural Stud 83:127–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrurstud.2021.02.006
Weniga AS, Gordon C, Boon E, Musah-Issah Surugu J (2019) Determinants of climate smart agriculture (CSA) adoption among smallholder food crop farmers in the Techiman Municipality, Ghana. Ghana J Geogr 11:124–139
Westermann O, Thornton P, Förch W (2015) Reaching more farmers: innovative approaches to scaling up climate-smart agriculture. CCAFS Working Paper
Wheeler S, Zuo A, Bjornlund H (2013) Farmers’ climate change beliefs and adaptation strategies for a water scarce future in Australia. Glob Environ Chang 23:537–547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2012.11.008
Wouterse F, Andrijevic M, Schaeffer M (2022) The microeconomics of adaptation: evidence from smallholders in Ethiopia and Niger. World Dev 154:105884. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.worlddev.2022.105884
Xu Y, Findlay C (2019) Farmers’ constraints, governmental support and climate change adaptation: evidence from Guangdong Province, China. Aust J Agric Resour Econ 63:866–880. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8489.12321
Yegbemey RN, Yabi JA, Tovignan SD et al (2013) Farmers’ decisions to adapt to climate change under various property rights: a case study of maize farming in northern Benin (West Africa). Land Use Policy 34:168–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2013.03.001
Zakaria A, Alhassan SI, Kuwornu JKM et al (2020a) Factors influencing the adoption of climate-smart agricultural technologies among rice farmers in northern Ghana. Earth Syst Environ 4:257–271
Zakaria A, Azumah SB, Appiah-Twumasi M, Dagunga G (2020b) Adoption of climate-smart agricultural practices among farm households in Ghana: the role of farmer participation in training programmes. Technol Soc 63:101338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2020.101338
Zeleke T, Beyene F, Deressa T, et al (2022) Smallholder farmers’ perception of climate change and choice of adaptation strategies in East Hararghe Zone, Eastern Ethiopia. Int J Clim Chang Strateg Manag. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJCCSM-01-2022-0014
Zhai SY, Song GX, Qin YC et al (2018) Climate change and Chinese farmers: perceptions and determinants of adaptive strategies. J Integr Agric 17:949–963. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(17)61753-2
Zheng H, Ma W, Li G (2021a) Learning from neighboring farmers: does spatial dependence affect adoption of drought-tolerant wheat varieties in China? Can J Agric Econ Can D’agroeconomie 69:519–537. https://doi.org/10.1111/cjag.12294
Zheng H, Ma W, Li G (2021b) Adoption of organic soil amendments and its impact on farm performance: evidence from wheat farmers in China*. Aust J Agric Resour Econ 65:367–390. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8489.12406
Zheng Y, Tang J, Huang F (2023) The impact of industrial structure adjustment on the spatial industrial linkage of carbon emission: from the perspective of climate change mitigation. J Environ Manage 345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.118620
Zhou X, Ma W, Zheng H, et al (2023) Promoting banana farmers’ adoption of climate-smart agricultural practices: the role of agricultural cooperatives. Clim Dev 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1080/17565529.2023.2218333
Zizinga A, Mwanjalolo J-GM, Tietjen B et al (2022) Climate change and maize productivity in Uganda: simulating the impacts and alleviation with climate smart agriculture practices. Agric Syst 199:103407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agsy.2022.103407
Zorom M, Barbier B, Mertz O, Servat E (2013) Diversification and adaptation strategies to climate variability: a farm typology for the Sahel. Agric Syst 116:7–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agsy.2012.11.004
Funding
Junpeng Li received the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project No.: 72103075), National Statistical Science Research Project (2023LY033), and the Jiangsu Provincial Department of Education (Project No.: 2020SJA1763).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Ma, W. & Zhu, H. A systematic literature review of factors influencing the adoption of climate-smart agricultural practices. Mitig Adapt Strateg Glob Change 29, 2 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11027-023-10098-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11027-023-10098-x