Abstract
Yin and Yang 1 gene (YY1; MIM#600,013) is recognized as a dual transcriptional activating and repressing factor, RNA-binding protein, and 3D chromatin regulator, with multi roles in neurodevelopmental and maintenance pathways. YY1 haploinsufficiency caused either by heterozygous sequence variants or deletions involving the whole gene has been recently associated with Gabriele-de Vries syndrome (GADEVS), a rare congenital autosomal dominant condition, leading to intellectual disability (ID) and multiple physical/behavioural abnormalities. Herein, we describe clinical and molecular findings from a Brazilian female harbouring a de novo missense pathogenic variant in YY1 gene (NM_003403.5:c.1106A > G; p.Asn369Ser) found by whole exome sequencing with potential implications for protein structure and function. Undescribed or uncommon clinical features in this patient included non-febrile seizures, severe scoliosis, hearing impairment, and chorioretinitis. Further bioinformatics analyses using YY1-other protein interaction networks reinforced the involvement of YY1 interactors in such phenotypes, in exception of chorioretinitis. Moreover, X-chromosome inactivation (XCI) skewing was evidenced in the patient and attributed to the haploinsufficiency of YY1, which direct and indirectly interacts with numerous XCI key regulators. Besides expanding the mutational and phenotype spectrum of GADEVS, our results highlight the role of YY1 as an essential autosomal regulator of XCI epigenetic process.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The variant described in this study is available at ClinVar repository (accession number SCV002505686).
References
Bronisz E, Kurkowska-Jastrzębska I (2016) Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 in Epilepsy: The Role of Neuroinflammation in Seizure Development. Mediators Inflamm 2016:7369020. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/7369020
Carminho-Rodrigues MT, Steel D, Sousa SB, Brandt G, Guipponi M, Laurent S, Fokstuen S, Moren A, Zacharia A, Dirren E, Oliveira R, Kurian MA, Burkhard PR, Bally JF (2020) Complex movement disorder in a patient with heterozygous YY1 mutation (Gabriele-de Vries syndrome). Am J Med Genet A 182:2129–2132. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.a.61731
Castro VL, Quintana AM (2020) The role of HCFC1 in syndromic and non-syndromic intellectual disability. Med Res Arch 8. https://doi.org/10.18103/mra.v8i6.2122.
Chapman AG, Cotton AM, Kelsey AD, Brown CJ (2014) Differentially methylated CpG island within human XIST mediates alternative P2 transcription and YY1 binding. BMC Genet 15:89. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12863-014-0089-4
Cherik F, Reilly J, Kerkhof J, Levy M, McConkey H, Barat-Houari M, Butler KM, Coubes C, Lee JA, Le Guyader G, Louie RJ, Patterson WG, Tedder ML, Bak M, Hammer TB, Craigen W, Démurger F, Dubourg C, Fradin M, Franciskovich R, Frengen E, Friedman J, Palares NR, Iascone M, Misceo D, Monin P, Odent S, Philippe C, Rouxel F, Saletti V, Strømme P, Thulin PC, Sadikovic B, Genevieve D (2022) DNA methylation episignature in Gabriele-de Vries syndrome. Genet Med S1098–3600(21):05422–05428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gim.2021.12.003
Dixon JR, Selvaraj S, Yue F, Kim A, Li Y, Shen Y, Hu M, Liu JS, Ren B (2012) Topological domains in mammalian genomes identified by analysis of chromatin interactions. Nature 485(7398):376–380. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11082
Donohoe ME, Zhang X, McGinnis L, Biggers J, Li E (1999) Shi Y (1999) Targeted disruption of mouse Yin Yang 1 transcription factor results in peri-implantation lethality. Mol Cell Biol 19(10):7237–7244. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.19.10.7237
El-Gebali S, Mistry J, Bateman A, Eddy SR, Luciani A, Potter SC, Qureshi M, Richardson LJ, Salazar GA, Smart A, Sonnhammer ELL, Hirsh L, Paladin L, Piovesan D, Tosatto SCE, Finn RD (2019) The Pfam protein families database in 2019. Nucl Acids Res 47(D1):D427–D432. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky995
Figiel M, Łakomska J, Dziedzicka-Wasylewska M, Górecki A (2020) The effect of D380Y pathogenic mutation in human Yin Yang 1 on the protein’s structure and function. Acta Biochim Pol 67(1):73–77. https://doi.org/10.18388/abp.2020_2911
Fischer FP, Kasture AS, Hummel T, Sucic S (2022) Molecular and Clinical Repercussions of GABA Transporter 1 Variants Gone Amiss: Links to Epilepsy and Developmental Spectrum Disorders. Front Mol Biosci 9:834498. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2022.834498
Forlani G, Giarda E, Ala U, Di Cunto F, Salani M, Tupler R, Kilstrup-Nielsen C, Landsberger N (2010) The MeCP2/YY1 interaction regulates ANT1 expression at 4q35: novel hints for Rett syndrome pathogenesis. Hum Mol Genet 19(16):3114–3123. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddq214
Gabriele M, Vulto-van Silfhout AT, Germain PL, Vitriolo A, Kumar R, Douglas E, Haan E, Kosaki K, Takenouchi T, Rauch A, Steindl K, Frengen E, Misceo D, Pedurupillay CRJ, Stromme P, Rosenfeld JA, Shao Y, Craigen WJ, Schaaf CP, Rodriguez-Buritica D, Farach L, Friedman J, Thulin P, McLean SD, Nugent KM, Morton J, Nicholl J, Andrieux J, Stray-Pedersen A, Chambon P, Patrier S, Lynch SA, Kjaergaard S, Tørring PM, Brasch-Andersen C, Ronan A, van Haeringen A, Anderson PJ, Powis Z, Brunner HG, Pfundt R, Schuurs-Hoeijmakers JHM, van Bon BWM, Lelieveld S, Gilissen C, Nillesen WM, Vissers LELM, Gecz J, Koolen DA, Testa G, de Vries BBA (2017) YY1 Haploinsufficiency Causes an Intellectual Disability Syndrome Featuring Transcriptional and Chromatin Dysfunction. Am J Hum Genet 100(6):907–925. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2017.05.006
Gordon S, Akopyan G, Garban H, Bonavida B (2006) Transcription factor YY1: structure, function, and therapeutic implications in cancer biology. Oncogene 25(8):1125–1142. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209080
Guo XQ, Cao YL, Hao F, Yan ZR, Wang ML, Liu XW (2017) Tangeretin alters neuronal apoptosis and ameliorates the severity of seizures in experimental epilepsy-induced rats by modulating apoptotic protein expressions, regulating matrix metalloproteinases, and activating the PI3K/Akt cell survival pathway. Adv Med Sci 62(2):246–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advms.2016.11.011
Huang Q, Liu J, Shi Z, Zhu X (2020) Correlation of MMP-9 and HMGB1 expression with the cognitive function in patients with epilepsy and factors affecting the prognosis. Cell Mol Biol 66(3):39–47
Khachigian LM (2018) The Yin and Yang of YY1 in tumor growth and suppression. Int J Cancer 143(3):460–465. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.31255
Khamirani HJ, Zoghi S, Namdar ZM, Kamal N, Dianatpour M, Tabei SMB, Mohammadi S, Dehghanian F, Farbod Z, Dastgheib SA (2022) Clinical features of patients with Yin Yang 1 deficiency causing Gabriele-de Vries syndrome: A new case and review of the literature. Ann Hum Genet 86(1):52–62. https://doi.org/10.1111/ahg.12448
Kriaucionis S, Paterson A, Curtis J, Guy J, Macleod N, Bird A (2006) Gene expression analysis exposes mitochondrial abnormalities in a mouse model of Rett syndrome. Mol Cell Biol 26(13):5033–5042. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.01665-05
Lee JS, Galvin KM, See RH, Eckner R, Livingston D, Moran E, Shi Y (1995) Relief of YY1 transcriptional repression by adenovirus E1A is mediated by E1A-associated protein p300. Genes Dev 9(10):1188–1198. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.9.10.1188
Liu W, Xie Y, Ma J, Luo X, Nie P, Zuo Z, Lahrmann U, Zhao Q, Zheng Y, Zhao Y, Xue Y, Ren J (2015) IBS: an illustrator for the presentation and visualization of biological sequences. Bioinformatics 31(20):3359–3361. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btv362
Morales-Rosado JA, Kaiwar C, Smith BE, Klee EW, Dhamija R (2018) A case of YY1-associated syndromic learning disability or Gabriele-de Vries syndrome with myasthenia gravis. Am J Med Genet A 176(12):2846–2849. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.a.40626
Morgan MJ, Woltering JM, In der Rieden PM, Durston AJ, Thiery JP (2004) YY1 regulates the neural crest-associated slug gene in Xenopus laevis. J Biol Chem 279(45):46826–46834. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M406140200
Nabais Sá MJ, Gabriele M, Testa G, de Vries BBA. Gabriele-de Vries Syndrome (2019) In: Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Bean LJH, Gripp KW, Mirzaa GM, Amemiya A (eds) GeneReviews®. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; pp 1993–2022
Pabian-Jewuła S, Bragiel-Pieczonka A, Rylski M (2022) Ying Yang 1 engagement in brain pathology. J Neurochem. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.15594
Pan X, Papasani M, Hao Y, Calamito M, Wei F, Quinn Iii WJ, Basu A, Wang J, Hodawadekar S, Zaprazna K, Liu H, Shi Y, Allman D, Cancro M, Atchison ML (2013) YY1 controls Igκ repertoire and B-cell development, and localizes with condensin on the Igκ locus. EMBO J 32(8):1168–1182. https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2013.66
Park K, Atchison ML (1991) Isolation of a candidate repressor/activator, NF-E1 (YY-1, delta), that binds to the immunoglobulin kappa 3’ enhancer and the immunoglobulin heavy-chain mu E1 site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 88(21):9804–9808. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.88.21.9804
Richards S, Aziz N, Bale S, Bick D, Das S, Gastier-Foster J, Grody WW, Hegde M, Lyon E, Spector E, Voelkerding K, Rehm HL, Laboratory Quality Assurance Committee ACMG (2015) Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet Med 17(5):405–424. https://doi.org/10.1038/gim.2015.30
Santos-Rebouças CB (2022) Chapter 23: Epigenetics of X-Chromosome Inactivation. Handbook of Epigenetics, Third edition, edited Trygve Tollefsbol, Elsevier, Amsterdam, Holland, in press
Shah R, Sharma A, Kelkar A, Sengupta K, Galande S (2021) A novel cis Regulatory Element Regulates Human XIST in a CTCF-Dependent Manner. Mol Cell Biol 41(8):e0038220. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.00382-20
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS, Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B, Ideker T (2003) Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res 13(11):2498–2504. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.1239303
Shi Y, Seto E, Chang LS, Shenk T (1991) Transcriptional repression by YY1, a human GLI-Krüppel-related protein, and relief of repression by adenovirus E1A protein. Cell 67(2):377–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(91)90189-6
Stawarski M, Stefaniuk M, Wlodarczyk J (2014) Matrix metalloproteinase-9 involvement in the structural plasticity of dendritic spines. Front Neuroanat 8:68. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnana.2014.00068
Tan L, Li Y, Liu F, Huang Y, Luo S, Zhao P, Gu W, Lin J, Zhou A, He X (2021) A 9-month-old Chinese patient with Gabriele-de Vries syndrome due to novel germline mutation in the YY1 gene. Mol Genet Genomic Med 9(2):e1582. https://doi.org/10.1002/mgg3.1582
Verheul TCJ, van Hijfte L, Perenthaler E, Barakat TS (2020) The Why of YY1: Mechanisms of Transcriptional Regulation by Yin Yang 1. Front Cell Dev Biol 8:592164. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2020.592164
Vianna EQ, Piergiorge RM, Gonçalves AP, Dos Santos JM, Calassara V, Rosenberg C, Krepischi ACV, Boy da Silva RT, Dos Santos SR, Ribeiro MG, Machado FB, Medina-Acosta E, Pimentel MMG, Santos-Rebouças CB (2020) Understanding the Landscape of X-linked Variants Causing Intellectual Disability in Females Through Extreme X Chromosome Inactivation Skewing. Mol Neurobiol 57(9):3671–3684. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-020-01981-8
Vissers LE, de Ligt J, Gilissen C, Janssen I, Steehouwer M, de Vries P, van Lier B, Arts P, Wieskamp N, del Rosario M, van Bon BW, Hoischen A, de Vries BB, Brunner HG, Veltman JA (2010) A de novo paradigm for mental retardation. Nat Genet 42(12):1109–1112. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.712
Weintraub AS, Li CH, Zamudio AV, Sigova AA, Hannett NM, Day DS, Abraham BJ, Cohen MA, Nabet B, Buckley DL, Guo YE, Hnisz D, Jaenisch R, Bradner JE, Gray NS, Young RA (2017) YY1 Is a Structural Regulator of Enhancer-Promoter Loops. Cell 171(7):1573-1588.e28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.11.008
Wilkinson FH, Park K, Atchison ML (2006) Polycomb recruitment to DNA in vivo by the YY1 REPO domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103(51):19296–19301. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0603564103
Xu D, Zhang Y (2011) Improving the physical realism and structural accuracy of protein models by a two-step atomic-level energy minimization. Biophys J 101(10):2525–2534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2011.10.024
Yang WM, Yao YL, Sun JM, Davie JR, Seto E (1997) Isolation and characterization of cDNAs corresponding to an additional member of the human histone deacetylase gene family. J Biol Chem 272(44):28001–28007. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.272.44.28001
Yao YL, Yang WM, Seto E (2001) Regulation of transcription factor YY1 by acetylation and deacetylation. Mol Cell Biol 21(17):5979–5991. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.21.17.5979-5991.2001
Zorzi G, Keller Sarmiento IJ, Danti FR, Bustos BI, Invernizzi F, Panteghini C, Reale C, Garavaglia B, Chiapparini L, Lubbe SJ, Nardocci N, Mencacci NE (2021) YY1-Related Dystonia: Clinical Aspects and Long-Term Response to Deep Brain Stimulation. Mov Disord 36(6):1461–1462. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.28547
Zurkirchen L, Varum S, Giger S, Klug A, Häusel J, Bossart R, Zemke M, Cantù C, Atak ZK, Zamboni N, Basler K, Sommer L (2019) Yin Yang 1 sustains biosynthetic demands during brain development in a stage-specific manner. Nat Commun 10(1):2192. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09823-5
Żylicz JJ, Bousard A, Žumer K, Dossin F, Mohammad E, da Rocha ST, Schwalb B, Syx L, Dingli F, Loew D, Cramer P, Heard E (2019) The Implication of Early Chromatin Changes in X Chromosome Inactivation. Cell 176(1–2):182-197.e23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.11.041
Web Resources
The URLs for data presented herein are as follows:
ClinVar (2022) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/clinvar/variation/VCV001321254.1. Accessed 24 March 2022
DisGeNET (2022) https://www.disgenet.org/
Enrichr (2022) https://maayanlab.cloud/Enrichr/
GeneCards (2022) https://www.genecards.org/
Mutation Taster (2021) http://www.mutationtaster.org
OMIM (2022) http://www.omim.org/
Pfam 32.0 platform (2022) http://pfam.sanger.ac.uk/
Variant Effect Predictor (VEP) Ensembl Genome Browser (2022) http://www.ensembl.org/info/docs/tools/vep/script/vep_plugins.html
Varsome (2022) https://varsome.com/
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the family members for their kind cooperation. This work was supported by Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq/Brazil; 302263/2019-5), Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro (FAPERJ/Brazil; E-26/010.001888/2019), Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES/BRAZIL; Finance Code 001) and Centro de Produção da Universidade do Estado do Rio de Janeiro (CEPUERJ).
Funding
This work was supported by Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq/Brazil; 302263/2019–5), Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro (FAPERJ/Brazil; E-26/010.001888/2019), Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES/BRAZIL; Finance Code 001), Departamento de Inovação (InovUerj/UERJ/Brazil), and Centro de Produção da Universidade do Estado do Rio de Janeiro (CEPUERJ/Brazil).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Cíntia Barros Santos-Rebouças contributed to the study conception and design. Data collection were performed by Cíntia Barros Santos-Rebouças, Suely Rodrigues dos Santos, Rafael Mina Piergiorge, Jady Rocha, Bianca Barbosa Abdala, Andressa Pereira Gonçalves, and Márcia Mattos Gonçalves Pimentel. Clinical evaluation was done by Suely Rodrigues dos Santos. Analysis and interpretation of data were performed by Cíntia Barros Santos-Rebouças, Suely Rodrigues dos Santos, and Rafael Mina Piergiorge. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Cíntia Barros Santos-Rebouças, Suely Rodrigues dos Santos, and Rafael Mina Piergiorge. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Funding was obtained by Cíntia Barros Santos-Rebouças.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This study was performed in line with the principles of The Institutional Ethics Committee from the State University of Rio de Janeiro (CAAE 46769315.5.0000.5259).
Brazil does not take part from the Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent to publish
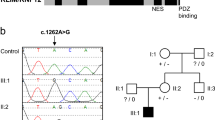
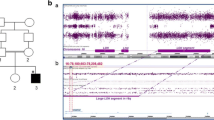
The authors affirm that human research participants provided informed consent for publication of the images in Fig. 1.
Competing interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Suely Rodrigues dos Santos and Rafael Mina Piergiorge contributed equally to this work.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
dos Santos, S.R., Piergiorge, R.M., Rocha, J. et al. A de novo YY1 missense variant expanding the Gabriele-de Vries syndrome phenotype and affecting X-chromosome inactivation. Metab Brain Dis 37, 2431–2440 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-01024-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-01024-2