Abstract
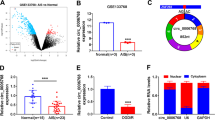
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) can induce vascular endothelial injury. Circular RNAs (circRNAs) have been verified to regulate different cellular processes in various diseases. This study intended to explore the potential role and mechanism of circ_0057583 in brain microvascular endothelial cell injury. Human brain microvascular endothelial cells (hBMECs) were exposed to different doses of LPS to induce cell damage. The levels of circ_0057583, microRNA-204-5p (miR-204-5p) and nuclear receptor 4A1 (NR4A1) were detected by quantitative real-time PCR or Western blot assays. Cell viability, apoptosis, inflammation and angiogenesis were assessed by Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8), flow cytometry, enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and tube formation assays. The targeting relationship between miR-204-5p and circ_0057583 or NR4A1 was verified by dual-luciferase reporter assay and RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) assay. LPS treatment elevated the expression of circ_0057583 and NR4A1, but decreased the expression of miR-204-5p in LPS-induced hBMECs. Downregulation of circ_0057583 abated LPS-induced hBMEC injury by inducing cell proliferation and angiogenesis, as well as inhibiting cell apoptosis, autophagy and inflammation. Circ_0057583 aggravated LPS-evoked hBMEC injury by regulating miR-204-5p. Also, miR-204-5p suppressed LPS-evoked hBMEC damage via targeting NR4A1. Moreover, circ_0057583 sponged miR-204-5p to up-regulate NR4A1 level. Depletion of circ_0057583 alleviated LPS-triggered brain microvascular endothelial endothelial cell injury through modulating miR-204-5p/NR4A1 axis.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Bai Y, Zhang Y, Han B, Yang L, Chen X, Huang R et al (2018) Circular RNA DLGAP4 ameliorates ischemic stroke outcomes by targeting miR-143 to regulate endothelial-mesenchymal transition associated with blood-brain barrier integrity. J Neurosci 38(1):32–50
Bannerman DD, Goldblum SE (2003) Mechanisms of bacterial lipopolysaccharide-induced endothelial apoptosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 284(6):L899-914
Bernstein DL, Zuluaga-Ramirez V, Gajghate S, Reichenbach NL, Polyak B, Persidsky Y et al (2020) miR-98 reduces endothelial dysfunction by protecting blood-brain barrier (BBB) and improves neurological outcomes in mouse ischemia/reperfusion stroke model. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 40(10):1953–1965
Chen L, Fan F, Wu L, Zhao Y (2020) The nuclear receptor 4A family members: mediators in human disease and autophagy. Cell Mol Biol Lett 25(1):48
Chen X, Song D (2020) LPS promotes the progression of sepsis by activation of lncRNA HULC/miR-204-5p/TRPM7 network in HUVECs. Biosci Rep 40(6):BSR20200740
Cui X, Wang J, Guo Z, Li M, Li M, Liu S et al (2018) Emerging function and potential diagnostic value of circular RNAs in cancer. Mol Cancer 17(1):123
Deng W, Fan C, Shen R, Wu Y, Du R, Teng J (2020) Long noncoding MIAT acting as a ceRNA to sponge microRNA-204-5p to participate in cerebral microvascular endothelial cell injury after cerebral ischemia through regulating HMGB1. J Cell Physiol 235(5):4571–4586
Dong Y, Fan X, Wang Z, Zhang L, Guo S (2020) Circ_HECW2 functions as a miR-30e-5p sponge to regulate LPS-induced endothelial-mesenchymal transition by mediating NEGR1 expression. Brain Res 1748:147114
Hanan M, Soreq H, Kadener S (2017) CircRNAs in the brain. RNA Biol 14(8):1028–1034
Jackson S, Meeks C, Vezina A, Robey RW, Tanner K, Gottesman MM (2019) Model systems for studying the blood-brain barrier: applications and challenges. Biomaterials 214:119217
Liu L, Wang J, Khanabdali R, Kalionis B, Tai X, Xia S (2017) Circular RNAs: isolation, characterization and their potential role in diseases. RNA Biol 14(12):1715–1721
Liu X, Wang Y, Lu H, Li J, Yan X, Xiao M et al (2019) Genome-wide analysis identifies NR4A1 as a key mediator of T cell dysfunction. Nature 567(7749):525–529
Lopez-Ramirez MA, Reijerkerk A, de Vries HE, Romero IA (2016) Regulation of brain endothelial barrier function by microRNAs in health and neuroinflammation. FASEB J 30(8):2662–2672
Lu S, Yang X, Wang C, Chen S, Lu S, Yan W et al (2019) Current status and potential role of circular RNAs in neurological disorders. J Neurochem 150(3):237–248
Miner JJ, Diamond MS (2016) Mechanisms of restriction of viral neuroinvasion at the blood-brain barrier. Curr Opin Immunol 38:18–23
Su Q, Lv X (2020) Revealing new landscape of cardiovascular disease through circular RNA-miRNA-mRNA axis. Genomics 112(2):1680–1685
Sweeney MD, Sagare AP, Zlokovic BV (2018) Blood-brain barrier breakdown in Alzheimer disease and other neurodegenerative disorders. Nat Rev Neurol 14(3):133–150
Sweeney MD, Zhao Z, Montagne A, Nelson AR, Zlokovic BV (2019) Blood-brain barrier: from physiology to disease and back. Physiol Rev 99(1):21–78
Takeshita Y, Ransohoff RM (2012) Inflammatory cell trafficking across the blood-brain barrier: chemokine regulation and in vitro models. Immunol Rev 248(1):228–239
To SK, Zeng JZ, Wong AS (2012) Nur77: a potential therapeutic target in cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets 16(6):573–585
Wa Q, Huang S, Pan J, Tang Y, He S, Fu X et al (2019) miR-204-5p represses bone metastasis via inactivating NF-kappaB signaling in prostate cancer. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 18:567–579
Wan Y, Jin HJ, Zhu YY, Fang Z, Mao L, He Q et al (2018) MicroRNA-149-5p regulates blood-brain barrier permeability after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats by targeting S1PR2 of pericytes. FASEB J 32(6):3133–3148
Wei Z, Ran H, Yang C (2020) CircRSF1 contributes to endothelial cell growth, migration and tube formation under ox-LDL stress through regulating miR-758/CCND2 axis. Life Sci 259:118241
Wu L, Xu H, Zhang W, Chen Z, Li W, Ke W (2020) Circular RNA circCCDC9 alleviates ischaemic stroke ischaemia/reperfusion injury via the Notch pathway. J Cell Mol Med 24(24):14152–14159
Yang L, Han B, Zhang Y, Bai Y, Chao J, Hu G et al (2018) Engagement of circular RNA HECW2 in the nonautophagic role of ATG5 implicated in the endothelial-mesenchymal transition. Autophagy 14(3):404–418
Yang R, Chen J, Xu B, Yang B, Fu J, Xiao S et al (2020) circ_2858 helps blood-brain barrier disruption by increasing VEGFA via sponging miR-93-5p during Escherichia coli Meningitis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 22:708–721
Yang R, Huang F, Fu J, Dou B, Xu B, Miao L et al (2016) Differential transcription profiles of long non-coding RNAs in primary human brain microvascular endothelial cells in response to meningitic Escherichia coli. Sci Rep 6:38903
Yin D, Xu F, Lu M, Li X (2021) Long non-coding RNA RMST promotes oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced injury in brain microvascular endothelial cells by regulating miR-204–5p/VCAM1 axis. Life Sci 16:119244
Zhang J, Xing L, Xu H, Wang K, She J, Shi F et al (2020a) miR-204-5p suppress lymph node metastasis via regulating CXCL12 and CXCR4 in gastric cancer. J Cancer 11(11):3199–3206
Zhang P, Hou Q, Yue Q (2020b) MiR-204-5p/TFAP2A feedback loop positively regulates the proliferation, migration, invasion and EMT process in cervical cancer. Cancer Biomark 28(3):381–390
Zhang YJ, Song JR, Zhao MJ (2019) NR4A1 regulates cerebral ischemia-induced brain injury by regulating neuroinflammation through interaction with NF-kappaB/p65. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 518(1):59–65
Zhang Z, Yang T, Xiao J (2018) Circular RNAs: promising biomarkers for human diseases. EBioMedicine 34:267–274
Zhong Y, Du Y, Yang X, Mo Y, Fan C, Xiong F et al (2018) Circular RNAs function as ceRNAs to regulate and control human cancer progression. Mol Cancer 17(1):79
Zlokovic BV (2008) The blood-brain barrier in health and chronic neurodegenerative disorders. Neuron 57(2):178–201
Funding
This study was funded by Medical Science and Technology Research Project of Henan Province (No. LHGJ20190809). Scientific and Technological Talents Overseas Training Project (No.2018151).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Tao Li designed and supervised the study. Xiaoyu Wang and Lili Liu conducted the experiments and drafted the manuscript. Lei Zhang collected and analyzed the data. Jing Guo contributed the methodology and analyzed the data. Lixia Yu edited the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Liu, L., Zhang, L. et al. Circ_0057583 facilitates brain microvascular endothelial cell injury through modulating miR-204-5p/NR4A1 axis. Metab Brain Dis 37, 501–511 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-021-00866-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-021-00866-6