Abstract
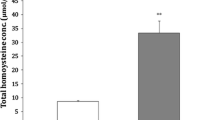
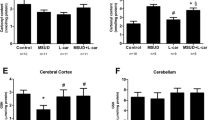
In the present study we investigate the effect of homocysteine (Hcy) administration, the main metabolite accumulating in homocystinuria, on butyrylcholinesterase (BuChE) activity in serum of rats. For the acute treatment, 29-day-old Wistar rats received one subcutaneous injection of Hcy (0.6 μmol/g) or saline (control) and were killed 1 h later. For the chronic treatment, Hcy was administered subcutaneously to rats from the 6th to the 28th day of life. Control rats received saline. The rats were killed 12 h after the last injection. In another set of experiments, rats were pretreated for one week with vitamins E and C or saline and 12 h after the last injection received one single injection of Hcy or saline, being killed 1 h later. Serum was used to determine BuChE activity. Our results showed that acute and chronic administration of Hcy significantly decreased BuChE activity. Furthermore, vitamins E and C per se did not alter BuChE activity, but prevented the reduction of this enzyme activity caused by acute administration of Hcy. The data suggest that the inhibitory effect of Hcy on BuChE activity is probably mediated by free radicals, since vitamins E and C administration prevented such effect.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcantara, V.M., Chautard-Freire-Maia, E.A., Scartezini, M., Cerci, M.S., Braun-Prado, K., and Picheth, G. (2002). Butyrylcholinesterase activity and risk factors for coronary artery disease. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest. 62:399–404.
Allen, I.C., Grieve, A., and Griffiths, R. (1986). Differential changes in the content of amino acid neurotransmitters in discrete regions of the rat brain prior to the onset and during the course of homocysteine-induced seizures. J. Neurochem. 46:1582–1592.
Arpagaus, M., Knott, M., Vatsis, K.P., Bartels, C.F., LaDu, B.N., and Lockridge, O. (1990). Structure of the gene for human butyrylcholinesterase: Evidence for a single copy. Biochemistry 29:124–131.
Bradford, M.M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-die-binding. Anal. Biochem. 72:248–254.
De Franchis, R., Sperandeo, M.P., Sebastio, G., and Andria, G. (1998). Clinical aspects of cystathionine β-synthase: How wide is the spectrum? Eur. J. Pediatr. 157(Suppl 2):S67–S70.
Ellman, G.L., Courtney, K.D., Andres, V., and Featherstone, R.M. (1961). A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 7:88–95.
Everitt, B.J., and Robbins, T.W. (1997). Central cholinergic systems and cognition. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 48:649–684.
Kim, W.-K., and Pae, Y.-S. (1996). Involvement of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor and free radical in homocysteine-mediated toxicity on rat cerebellar granule cells in culture. Neurosci. Lett. 216:117–120.
Kraus, J.P. (1998). Biochemistry and molecular genetics of cystathionine β-synthase deficiency. Eur. J. Pediatr. 157(Suppl 2):S50–S53.
Kuhn, W., Roebroek, R., Blom, H., Van Oppenraaij, D., Przuntek, H., Kretschmer, A., Buttner, T., Woitalla, D., and Muller, T. (1998). Elevated plasma levels of homocysteine in Parkinson’s disease. Eur. Neurol. 40:225–227.
Leblhuber, F., Walli, J., Artner-Dworzak, E., Vrecko, K., Widner, B., Reibnegger, G., and Fuchs, D. (2000). Hyperhomocysteinemia in dementia. J. Neural. Transm. 107:343–353.
Mack, A., and Robitzki, A. (2000). The key role of butyrylcholinesterase during neurogenesis and neural disorders: An antisense-5′-butyrylcholinesterase-DNA study. Prog. Neurobiol. 60:607–628.
Malinow, M.R. (1990). Hyperhomocyst(e)inemia. A common and easily reversible risk factor for occlusive atherosclerosis. Circulation 81:2004–2006.
Matté, C., Monteiro, S.C., Calcagnotto, T., Bavaresco, C.S., Netto, C.A., and Wyse, A.T.S. (2004). In vivo and in vitro effects of homocysteine on Na+,K+-ATPase activity in parietal, prefrontal and cingulate cortex of young rats. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 22:185–190.
Matthias, D., Becker, C.H., Riezler, R., and Kindling, P.H. (1996). Homocysteine induced arteriosclerosis-like alterations of the aorta in normotensive and hypertensive rats following application of high doses of methionine. Atherosclerosis 122:201–216.
McCully, K.S. (1996). Homocysteine and vascular disease. Nat. Med. 2:386–389.
Mudd, S.H., Levy, H.L., and Skovby, F. (2001). Disorders of transsulfuration. In: C.R. Scriver, A.L. Beaudet, W.S. Sly, and D. Valle (eds.) The Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease, Vol. 2, McGraw-Hill, New York, pp. 1279–1327.
Nelson, T.C., and Burritt, M.F. (1986). Pesticide poisoning, succinylcholine induced apnea, and pseudocholinesterase. Mayo Clin. Proc. 61:750–755.
Nihei, S., Tasaki, H., Yamashita, K., Ozumi, K., Morishita, T., Tsutsui, M., Okazaki, M., Nakashima, Y., and Adachi, T. (2004). Hyperhomocysteinemia is associated with human coronary atherosclerosis through the reduction of the ratio of endothelium-bound to basal extracellular superoxide dismutase. Circ. J. 68:822–828.
Prody, C.A., Zevin-Sonkin, D., Gnatt, A., Golberg, O., and Soreq, H. (1987). Isolation and characterization of full-length cDNA clones coding for cholinesterase from fetal human tissues. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84:3555–3559.
Pullin, C.H., Bonham, J.R., McDowell, I.F., Lee, P.J., Powers, H.J., Wilson, J.F., Lewis, M.J., and Moat, S.J. (2002). Vitamins C therapy ameliorates vascular endothelial dysfunction in treated patients with homocystinuria. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 25:107–118.
Reis, E.A., Zugno, A.I., Franzon, R., Tagliari, B., Matté, C., Lamers, M.L., Netto, C.A., and Wyse, A.T.S. (2002). Pretreatment with vitamins E and C prevent the impairment of memory caused by homocysteine administration in rats. Metab. Brain Dis. 17:211–217.
Romerio, S.C., Linder, L., Nyfeler, J., Wenk, M., Litynsky, P., Asmis, R., and Haefeli, W.E. (2004). Acute hyperhomocysteinemia decreases NO bioavailability in healthy adults. Atherosclerosis 176:337–344.
Seshadri, S., Beiser, A., Selhub, J., Jacques, P.F., Rosemberg, I.H., D’Agostino, R.B., Wilson, P.W.F., and Wolf, P.A. (2002). Plasma homocysteine as a risk for dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. New Engl. J. Med. 346:476–483.
Stefanello, F.M., Zugno, A.I., Wannmacher, C.M.D., Wajner, M., and Wyse, A.T.S. (2003a). Homocysteine inhibits butyrylcholinesterase activity in rat serum. Metab. Brain Dis. 18:187–194.
Stefanello, F.M., Franzon, R., Wannmacher, C.M.D., Wajner, M., and Wyse, A.T.S. (2003b). In vitro homocysteine inhibits platelet Na+,K+-ATPase and serum butyrylcholinesterase activities of young rats. Metab. Brain Dis. 18:273–280.
Streck, E.L., Matté, C., Vieira, P.S., Rombaldi, F., Wannmacher, C.M.D., Wajner, M., and Wyse, A.T.S. (2002). Reduction of Na+,K+-ATPase activity in hippocampus of rats subjected to chemically induced hyperhomocysteinemia. Neurochem. Res. 27:1593–1598.
Streck, E.L., Delwing, D., Tagliari, B., Matté, C., Wannmacher, C.M.D., Wajner, M., and Wyse, A.T.S. (2003a). Brain energy metabolism is compromised by the metabolites accumulating in homocystinuria. Neurochem. Int. 43:597–602.
Streck, E.L., Vieira, P.S., Wannmacher, C.M.D., Dutra-Filho, C.S., Wajner, M., and Wyse, A.T.S. (2003b). In vitro effect of homocysteine on some parameters of oxidative stress in rat hippocampus. Metab. Brain Dis. 18:147–154.
Streck, E.L., Bavaresco, C.S., Netto, C.A., and Wyse, A.I.S. (2004). Chronic hyperhomocysteinemia provokes a memory deficit in rats in the Morris water maze task. Behav. Brain Res. 153:377–381.
Whetherell, J.R., and French, M.C. (1986). The hydrolysis of succinyldithiocholine and related thiocholine esters by human plasma and purified cholinesterase. Biochem. Pharmacol. 35:939–945.
Wyse, A.T.S., Zugno, A.I., Streck, E.L., Matte, C., Calcagnotto, T., Wannmacher, C.M.D., and Wajner, M. (2002). Inhibition of Na+,K+-ATPase activity in hippocampus of rats subjected to acute administration of homocysteine is prevented by vitamins E and C treatment. Neurochem. Res. 27:1677–1681.
Wyse, A.T.S., Stefanello, F.M., Chiaranl, F., Delwing, D., Wannmacher, C.M.D., and Wajner, M. (2004). Arginine administration decreases cerebral cortex acetylchollnesterase and serum butyrylcholinesterase probably by oxidative stress induction. Neurochem. Res. 29:385–389.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stefanello, F.M., Franzon, R., Tagliari, B. et al. Reduction of Butyrylcholinesterase Activity in Rat Serum Subjected to Hyperhomocysteinemia. Metab Brain Dis 20, 97–103 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-005-4147-5
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-005-4147-5