Abstract
Pancreatic cancer is considered as one of the most aggressive tumor types, representing over 45,750 mortality cases annually in the USA solely. The aggressive nature and late identification of pancreatic cancer, combined with the restrictions of existing chemotherapeutics, present the mandatory need for the advancement of novel treatment systems. Ongoing reports have shown an important role of microRNAs (miRNAs) in the initiation, migration, and metastasis of malignancies. Besides, abnormal transcriptional levels of miRNAs have regularly been related with etiopathogenesis of pancreatic malignancy, underlining the conceivable utilization of miRNAs in the management of pancreatic disease patients. In this review article, we give a concise outline of molecular pathways involved in etiopathogenesis of pancreatic cancer patients as well as miRNA implications in pancreatic cancer patients. Ensuing sections describe the involvement of miRNAs in the diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy of pancreatic cancer patients. The involvement of miRNAs in the chemoresistance of pancreatic cancers was also discussed. End area portrays the substance of survey with future headings.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Biancur DE, Kimmelman AC (2018) The plasticity of pancreatic cancer metabolism in tumor progression and therapeutic resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer 1870:67–75
Mattiuzzi C, Lippi G (2020) Cancer statistics: a comparison between world health organization (WHO) and global burden of disease (GBD). Eur J Pub Health 30:1026–1027
Miller KD, Fidler-Benaoudia M, Keegan TH, Hipp HS, Jemal A, Siegel RL (2020) Cancer statistics for adolescents and young adults, 2020. CA: Cancer J Clin 70:443–459
Sener SF, Fremgen A, Menck HR, Winchester DP (1999) Pancreatic cancer: a report of treatment and survival trends for 100,313 patients diagnosed from 1985–1995, using the National Cancer Database. J Am Coll Surg 189:1–7
Costa-Silva B, Aiello NM, Ocean AJ, Singh S, Zhang H, Thakur BK, Becker A, Hoshino A, Mark MT, Molina H (2015) Pancreatic cancer exosomes initiate pre-metastatic niche formation in the liver. Nat Cell Biol 17:816–826
Yachida S, Jones S, Bozic I, Antal T, Leary R, Fu B, Kamiyama M, Hruban RH, Eshleman JR, Nowak MA (2010) Distant metastasis occurs late during the genetic evolution of pancreatic cancer. Nature 467:1114–1117
Evans J, Chapple A, Salisbury H, Corrie P, Ziebland S (2014) “It can’t be very important because it comes and goes”—patients’ accounts of intermittent symptoms preceding a pancreatic cancer diagnosis: a qualitative study. BMJ Open 4:e004215
Acunzo M, Romano G, Wernicke D, Croce CM (2015) MicroRNA and cancer—a brief overview. Adv Biol Regul 57:1–9
Croce CM (2009) Causes and consequences of microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Nat Rev Genet 10:704–714
Gilles M-E, Hao L, Huang L, Rupaimoole R, Lopez-Casas PP, Pulver E, Jeong JC, Muthuswamy SK, Hidalgo M, Bhatia SN (2018) Personalized RNA medicine for pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res 24:1734–1747
Iorio MV, Croce CM (2012) MicroRNA dysregulation in cancer: diagnostics, monitoring and therapeutics. A comprehensive review. EMBO Mol Med 4:143–159
Rozenblum E, Schutte M, Goggins M, Hahn SA, Panzer S, Zahurak M, Goodman SN, Sohn TA, Hruban RH, Yeo CJ (1997) Tumor-suppressive pathways in pancreatic carcinoma. Can Res 57:1731–1734
Hruban RH, Maitra A, Goggins M (2008) Update on pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 1:306
Khan MA, Azim S, Zubair H, Bhardwaj A, Patel GK, Khushman M, Singh S, Singh AP (2017) Molecular drivers of pancreatic cancer pathogenesis: looking inward to move forward. Int J Mol Sci 18:779
Maitra A (2008) H. Hruban R. Pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res 3:1–30
Hingorani SR, Tuveson DA (2003) Ras redux: rethinking how and where Ras acts. Curr Opin Genet Dev 13:6–13
Jonckheere N, Vasseur R, Van Seuningen I (2017) The cornerstone K-RAS mutation in pancreatic adenocarcinoma: from cell signaling network, target genes, biological processes to therapeutic targeting. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 111:7–19
Collins MA, Bednar F, Zhang Y, Brisset J-C, Galbán S, Galbán CJ, Rakshit S, Flannagan KS, Adsay NV, di Magliano MP (2012) Oncogenic Kras is required for both the initiation and maintenance of pancreatic cancer in mice. J Clin Investig 122:639–653
Ying H, Kimmelman AC, Lyssiotis CA, Hua S, Chu GC, Fletcher-Sananikone E, Locasale JW, Son J, Zhang H, Coloff JL (2012) Oncogenic Kras maintains pancreatic tumors through regulation of anabolic glucose metabolism. Cell 149:656–670
Singh A, Greninger P, Rhodes D, Koopman L, Violette S, Bardeesy N, Settleman J (2009) A gene expression signature associated with “K-Ras addiction” reveals regulators of EMT and tumor cell survival. Cancer Cell 15:489–500
Weinstein IB (2002) Addiction to oncogenes–the Achilles heal of cancer. Science 297:63–64
Collins MA, Brisset J-C, Zhang Y, Bednar F, Pierre J, Heist KA, Galbán CJ, Galbán S, di Magliano MP (2012) Metastatic pancreatic cancer is dependent on oncogenic Kras in mice. PLoS ONE 7:e49707
Nan X, Tamgüney TM, Collisson EA, Lin L-J, Pitt C, Galeas J, Lewis S, Gray JW, McCormick F, Chu S (2015) Ras-GTP dimers activate the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci 112:7996–8001
Roy SK, Srivastava RK, Shankar S (2010) Inhibition of PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK pathways causes activation of FOXO transcription factor, leading to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in pancreatic cancer. J Mol Signal 5:10
Boucher MJ, Morisset J, Vachon PH, Reed JC, Lainé J, Rivard N (2000) MEK/ERK signaling pathway regulates the expression of Bcl-2, Bcl-XL, and Mcl-1 and promotes survival of human pancreatic cancer cells. J Cell Biochem 79:355–369
Taniuchi K, Furihata M, Hanazaki K, Iwasaki S, Tanaka K, Shimizu T, Saito M, Saibara T (2015) Peroxiredoxin 1 promotes pancreatic cancer cell invasion by modulating p38 MAPK activity. Pancreas 44:331
Handra-Luca A, Lesty C, Hammel P, Sauvanet A, Rebours V, Martin A, Fagard R, Fléjou J-F, Faivre S, Bédossa P (2012) Biological and prognostic relevance of mitogen-activated protein kinases in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Pancreas 41:416–421
Zhong Y, Naito Y, Cope L, Naranjo-Suarez S, Saunders T, Hong S-M, Goggins MG, Herman JM, Wolfgang CL, Iacobuzio-Donahue CA (2014) Functional p38 MAPK identified by biomarker profiling of pancreatic cancer restrains growth through JNK inhibition and correlates with improved survival. Clin Cancer Res 20:6200–6211
Schutte M, Hruban RH, Geradts J, Maynard R, Hilgers W, Rabindran SK, Moskaluk CA, Hahn SA, Schwarte-Waldhoff I, Schmiegel W (1997) Abrogation of the Rb/p16 tumor-suppressive pathway in virtually all pancreatic carcinomas. Can Res 57:3126–3130
Ouelle DE, Zindy F, Ashmun RA, Sherr CJ (1995) Alternative reading frames of the INK4a tumor suppressor gene encode two unrelated proteins capable of inducing cell cycle arrest. Cell 83:993–1000
Bertoli C, Skotheim JM, De Bruin RA (2013) Control of cell cycle transcription during G1 and S phases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 14:518–528
Vogelstein B, Lane D, Levine AJ (2000) Surfing the p53 network. Nature 408:307–310
Makohon-Moore A, Iacobuzio-Donahue CA (2016) Pancreatic cancer biology and genetics from an evolutionary perspective. Nat Rev Cancer 16:553
Cowgill SM, Muscarella P (2003) The genetics of pancreatic cancer. Am J Surg 186:279–286
Marcel V, Catez F, Diaz J (2015) p53, a translational regulator: contribution to its tumour-suppressor activity. Oncogene 34:5513–5523
Siegel PM, Massagué J (2003) Cytostatic and apoptotic actions of TGF-β in homeostasis and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 3:807–820
Macias MJ, Martin-Malpartida P, Massagué J (2015) Structural determinants of Smad function in TGF-β signaling. Trends Biochem Sci 40:296–308
Budi EH, Duan D, Derynck R (2017) Transforming growth factor-β receptors and Smads: regulatory complexity and functional versatility. Trends Cell Biol 27:658–672
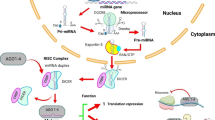
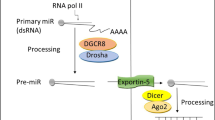
Ha M, Kim VN (2014) Regulation of microRNA biogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 15:509–524
Kim VN (2005) MicroRNA biogenesis: coordinated cropping and dicing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6:376–385
Sarwar A, Wang B, Su Q, Zhang Y (2021) MiRNAs directly targeting the key intermediates of biological pathways in pancreatic cancer. Biochem Pharmacol 189:114357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114357
Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP, Anderson TA (2007) microRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev Biol 302:1–12
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA (2005) MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 435:834–838
Szafranska A, Davison T, John J, Cannon T, Sipos B, Maghnouj A, Labourier E, Hahn S (2007) MicroRNA expression alterations are linked to tumorigenesis and non-neoplastic processes in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncogene 26:4442–4452
Moody L, He H, Pan Y-X, Chen H (2017) Methods and novel technology for microRNA quantification in colorectal cancer screening. Clin Epigenet 9:119
Yonemori K, Seki N, Idichi T, Kurahara H, Osako Y, Koshizuka K, Arai T, Okato A, Kita Y, Arigami T (2017) The microRNA expression signature of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by RNA sequencing: anti-tumour functions of the microRNA-216 cluster. Oncotarget 8:70097
Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Fritz BR, Wyman SK, Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, Peterson A, Noteboom J, O’Briant KC, Allen A (2008) Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105:10513–10518
Wang H, Peng R, Wang J, Qin Z, Xue L (2018) Circulating microRNAs as potential cancer biomarkers: the advantage and disadvantage. Clin Epigenet 10:1–10
Rawlings-Goss RA, Campbell MC, Tishkoff SA (2014) Global population-specific variation in miRNA associated with cancer risk and clinical biomarkers. BMC Med Genom 7:1–14
Humeau M, Torrisani J, Cordelier P (2013) miRNA in clinical practice: pancreatic cancer. Clin Biochem 46:933–936
Słotwiński R, Lech G, Słotwińska SM (2018) MicroRNAs in pancreatic cancer diagnosis and therapy. Cent Eur J Immunol 43:314
Abue M, Yokoyama M, Shibuya R, Tamai K, Yamaguchi K, Sato I, Tanaka N, Hamada S, Shimosegawa T, Sugamura K (2015) Circulating miR-483-3p and miR-21 is highly expressed in plasma of pancreatic cancer. Int J Oncol 46:539–547
Cao R, Wang K, Long M, Guo M, Sheng L, Zhan M, Yang R, Wang H, Yang L (2020) miR-3613-5p enhances the metastasis of pancreatic cancer by targeting CDK6. Cell Cycle 19:3086–3095. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2020.1831254
Wray CJ, Ahmad SA, Matthews JB, Lowy AM (2005) Surgery for pancreatic cancer: recent controversies and current practice. Gastroenterology 128:1626–1641
Hong TH, Park IY (2014) MicroRNA expression profiling of diagnostic needle aspirates from surgical pancreatic cancer specimens. Ann Surg Treat Res 87:290–297
Ballehaninna UK, Chamberlain RS (2011) Serum CA 19–9 as a biomarker for pancreatic cancer—a comprehensive review. Indian J Surg Oncol 2:88–100
Winter JM, Yeo CJ, Brody JR (2013) Diagnostic, prognostic, and predictive biomarkers in pancreatic cancer. J Surg Oncol 107:15–22
Saito Y, Jones PM (2006) Epigenetic activation of tumor suppressor microRNAs in human cancer cells. Cell Cycle 5:2220–2222
Yu Y, Tong Y, Zhong A, Wang Y, Lu R, Guo L (2020) Identification of Serum microRNA-25 as a novel biomarker for pancreatic cancer. Medicine 99:e23863. https://doi.org/10.1097/md.0000000000023863
Li Y, Sarkar FH (2016) MicroRNA targeted therapeutic approach for pancreatic cancer. Int J Biol Sci 12:326
Yu J, Ohuchida K, Mizumoto K, Sato N, Kayashima T, Fujita H, Nakata K, Tanaka M (2010) MicroRNA, hsa-miR-200c, is an independent prognostic factor in pancreatic cancer and its upregulation inhibits pancreatic cancer invasion but increases cell proliferation. Mol Cancer 9:169
Lee EJ, Gusev Y, Jiang J, Nuovo GJ, Lerner MR, Frankel WL, Morgan DL, Postier RG, Brackett DJ, Schmittgen TD (2007) Expression profiling identifies microRNA signature in pancreatic cancer. Int J Cancer 120:1046–1054
Guz M, Jeleniewicz W, Cybulski M, Kozicka J, Kurzepa J, Mądro A (2021) Serum miR-210-3p can be used to differentiate between patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and chronic pancreatitis. Biomed Rep 14:10. https://doi.org/10.3892/br.2020.1386
Habbe N, Koorstra J-BM, Mendell JT, Offerhaus GJ, Ryu JK, Feldmann G, Mullendore ME, Goggins MG, Hong S-M, Maitra A (2009) MicroRNA miR-155 is a biomarker of early pancreatic neoplasia. Cancer Biol Ther 8:340–346
Zhang Y, Li M, Wang H, Fisher WE, Lin PH, Yao Q, Chen C (2009) Profiling of 95 microRNAs in pancreatic cancer cell lines and surgical specimens by real-time PCR analysis. World J Surg 33:698
Mees ST, Schleicher C, Mardin WA, Senninger N, Colombo-Benkmann M, Haier J (2011) Analyzing miRNAs in ductal adenocarcinomas of the pancreas. J Surg Res 169:241–246
Du Rieu MC, Torrisani J, Selves J, Al Saati T, Souque A, Dufresne M, Tsongalis GJ, Suriawinata AA, Carrère N, Buscail L (2010) MicroRNA-21 is induced early in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma precursor lesions. Clin Chem 56:603–612
Nakata K, Ohuchida K, Mizumoto K, Kayashima T, Ikenaga N, Sakai H, Lin C, Fujita H, Otsuka T, Aishima S (2011) MicroRNA-10b is overexpressed in pancreatic cancer, promotes its invasiveness, and correlates with a poor prognosis. Surgery 150:916–922
Li X, Hou YS (2020) MiR-4282 contributes to inhibit pancreatic cancer metastasis by negatively interacting with ABCB5. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 24:9915–9923. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_202010_23202
Namkung J, Kwon W, Choi Y, Yi SG, Han S, Kang MJ, Kim SW, Park T, Jang JY (2016) Molecular subtypes of pancreatic cancer based on miRNA expression profiles have independent prognostic value. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 31:1160–1167
Greither T, Grochola LF, Udelnow A, Lautenschläger C, Würl P, Taubert H (2010) Elevated expression of microRNAs 155, 203, 210 and 222 in pancreatic tumors is associated with poorer survival. Int J Cancer 126:73–80
Giovannetti E, Funel N, Peters GJ, Del Chiaro M, Erozenci LA, Vasile E, Leon LG, Pollina LE, Groen A, Falcone A (2010) MicroRNA-21 in pancreatic cancer: correlation with clinical outcome and pharmacologic aspects underlying its role in the modulation of gemcitabine activity. Can Res 70:4528–4538
Asangani IA, Rasheed SA, Nikolova D, Leupold J, Colburn N, Post S, Allgayer H (2008) MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene 27:2128–2136
Guo S, Fesler A, Wang H, Ju J (2018) microRNA based prognostic biomarkers in pancreatic Cancer. Biomark Res 6:1–5
Bloomston M, Frankel WL, Petrocca F, Volinia S, Alder H, Hagan JP, Liu C-G, Bhatt D, Taccioli C, Croce CM (2007) MicroRNA expression patterns to differentiate pancreatic adenocarcinoma from normal pancreas and chronic pancreatitis. JAMA 297:1901–1908
Iwagami Y, Eguchi H, Nagano H, Akita H, Hama N, Wada H, Kawamoto K, Kobayashi S, Tomokuni A, Tomimaru Y (2013) miR-320c regulates gemcitabine-resistance in pancreatic cancer via SMARCC1. Br J Cancer 109:502–511
Namima D, Fujihara S, Iwama H, Fujita K, Matsui T, Nakahara M, Okamura M, Hirata M, Kono T, Fujita N, Yamana H, Kato K, Kamada H, Morishita A, Kobara H, Tsutsui K, Masaki T (2020) The effect of gemcitabine on cell cycle arrest and microRNA signatures in pancreatic cancer cells. Vivo 34:3195–3203. https://doi.org/10.21873/invivo.12155
Tu MJ, Duan Z, Liu Z, Zhang C, Bold RJ, Gonzalez FJ, Kim EJ, Yu AM (2020) MicroRNA-1291-5p sensitizes pancreatic carcinoma cells to arginine deprivation and chemotherapy through the regulation of arginolysis and glycolysis. Mol Pharmacol 98:686–694. https://doi.org/10.1124/molpharm.120.000130
Bader AG (2012) miR-34—a microRNA replacement therapy is headed to the clinic. Front Genet 3:120. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2012.00120
Pai P, Rachagani S, Are C, Batra SK (2013) Prospects of miRNA-based therapy for pancreatic cancer. Curr Drug Targets 14:1101–1109. https://doi.org/10.2174/13894501113149990181
Kent OA, Chivukula RR, Mullendore M, Wentzel EA, Feldmann G, Lee KH, Liu S, Leach SD, Maitra A, Mendell JT (2010) Repression of the miR-143/145 cluster by oncogenic Ras initiates a tumor-promoting feed-forward pathway. Genes Dev 24:2754–2759. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1950610
Hu Y, Ou Y, Wu K, Chen Y, Sun W (2012) miR-143 inhibits the metastasis of pancreatic cancer and an associated signaling pathway. Tumour Biol 33:1863–1870. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-012-0446-8
Srivastava SK, Bhardwaj A, Singh S, Arora S, Wang B, Grizzle WE, Singh AP (2011) MicroRNA-150 directly targets MUC4 and suppresses growth and malignant behavior of pancreatic cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 32:1832–1839. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgr223
Ji Q, Hao X, Zhang M, Tang W, Yang M, Li L, Xiang D, Desano JT, Bommer GT, Fan D, Fearon ER, Lawrence TS, Xu L (2009) MicroRNA miR-34 inhibits human pancreatic cancer tumor-initiating cells. PLoS ONE 4:e6816. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0006816
Davis S, Propp S, Freier SM, Jones LE, Serra MJ, Kinberger G, Bhat B, Swayze EE, Bennett CF, Esau C (2009) Potent inhibition of microRNA in vivo without degradation. Nucleic Acids Res 37:70–77. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkn904
Davis S, Lollo B, Freier S, Esau C (2006) Improved targeting of miRNA with antisense oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res 34:2294–2304. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkl183
Esau CC (2008) Inhibition of microRNA with antisense oligonucleotides. Methods 44:55–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2007.11.001
Krützfeldt J, Rajewsky N, Braich R, Rajeev KG, Tuschl T, Manoharan M, Stoffel M (2005) Silencing of microRNAs in vivo with “antagomirs.” Nature 438:685–689. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04303
Gumireddy K, Young DD, Xiong X, Hogenesch JB, Huang Q, Deiters A (2008) Small-molecule inhibitors of microrna miR-21 function. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 47:7482–7484. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200801555
Young DD, Connelly CM, Grohmann C, Deiters A (2010) Small molecule modifiers of microRNA miR-122 function for the treatment of hepatitis C virus infection and hepatocellular carcinoma. J Am Chem Soc 132:7976–7981. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja910275u
Park JK, Lee EJ, Esau C, Schmittgen TD (2009) Antisense inhibition of microRNA-21 or -221 arrests cell cycle, induces apoptosis, and sensitizes the effects of gemcitabine in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Pancreas 38:e190–e199. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPA.0b013e3181ba82e1
Weiss FU, Marques IJ, Woltering JM, Vlecken DH, Aghdassi A, Partecke LI, Heidecke CD, Lerch MM, Bagowski CP (2009) Retinoic acid receptor antagonists inhibit miR-10a expression and block metastatic behavior of pancreatic cancer. Gastroenterology. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2009.08.065
Park JK, Henry JC, Jiang J, Esau C, Gusev Y, Lerner MR, Postier RG, Brackett DJ, Schmittgen TD (2011) miR-132 and miR-212 are increased in pancreatic cancer and target the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 406:518–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.02.065
Passadouro M, Pedroso de Lima MC, Faneca H (2014) MicroRNA modulation combined with sunitinib as a novel therapeutic strategy for pancreatic cancer. Int J Nanomed 9:3203–3217. https://doi.org/10.2147/ijn.s64456
Rachagani S, Macha MA, Heimann N, Seshacharyulu P, Haridas D, Chugh S, Batra SK (2015) Clinical implications of miRNAs in the pathogenesis, diagnosis and therapy of pancreatic cancer. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 81:16–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2014.10.020
Fu X, Hong L, Yang Z, Tu Y, Xin W, Zha M, Tu S, Sun G, Li Y, Xiao W (2020) MicroRNA-148a-3p suppresses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and stemness properties via Wnt1-mediated Wnt/β-catenin pathway in pancreatic cancer. J Cell Mol Med 24:13020–13035. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.15900
Li L, He Z, Zhu C, Chen S, Yang Z, Xu J, Bi N, Yu C, Sun C (2020) MiR-137 promotes anoikis through modulating the AKT signaling pathways in Pancreatic Cancer. J Cancer 11:6277–6285. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.44037
Singh S, Chitkara D, Kumar V, Behrman SW, Mahato RI (2013) miRNA profiling in pancreatic cancer and restoration of chemosensitivity. Cancer Lett 334:211–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2012.10.008
Bhutia YD, Hung SW, Krentz M, Patel D, Lovin D, Manoharan R, Thomson JM, Govindarajan R (2013) Differential processing of let-7a precursors influences RRM2 expression and chemosensitivity in pancreatic cancer: role of LIN-28 and SET oncoprotein. PLoS ONE 8:e53436–e53436. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0053436
Maftouh M, Avan A, Funel N, Frampton AE, Fiuji H, Pelliccioni S, Castellano L, Galla V, Peters GJ, Giovannetti E (2014) miR-211 modulates gemcitabine activity through downregulation of ribonucleotide reductase and inhibits the invasive behavior of pancreatic cancer cells. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 33:384–393. https://doi.org/10.1080/15257770.2014.891741
Hasegawa S, Eguchi H, Nagano H, Konno M, Tomimaru Y, Wada H, Hama N, Kawamoto K, Kobayashi S, Nishida N, Koseki J, Nishimura T, Gotoh N, Ohno S, Yabuta N, Nojima H, Mori M, Doki Y, Ishii H (2014) MicroRNA-1246 expression associated with CCNG2-mediated chemoresistance and stemness in pancreatic cancer. Br J Cancer 111:1572–1580. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2014.454
Yan HJ, Liu WS, Sun WH, Wu J, Ji M, Wang Q, Zheng X, Jiang JT, Wu CP (2012) miR-17-5p inhibitor enhances chemosensitivity to gemcitabine via upregulating Bim expression in pancreatic cancer cells. Dig Dis Sci 57:3160–3167. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-012-2400-4
Giovannetti E, Funel N, Peters GJ, Del Chiaro M, Erozenci LA, Vasile E, Leon LG, Pollina LE, Groen A, Falcone A, Danesi R, Campani D, Verheul HM, Boggi U (2010) MicroRNA-21 in pancreatic cancer: correlation with clinical outcome and pharmacologic aspects underlying its role in the modulation of gemcitabine activity. Cancer Res 70:4528–4538. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-09-4467
Dong J, Zhao YP, Zhou L, Zhang TP, Chen G (2011) Bcl-2 upregulation induced by miR-21 via a direct interaction is associated with apoptosis and chemoresistance in MIA PaCa-2 pancreatic cancer cells. Arch Med Res 42:8–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arcmed.2011.01.006
Bera A, VenkataSubbaRao K, Manoharan MS, Hill P, Freeman JW (2014) A miRNA signature of chemoresistant mesenchymal phenotype identifies novel molecular targets associated with advanced pancreatic cancer. PLoS ONE 9:e106343. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0106343
Khan S, Ebeling MC, Zaman MS, Sikander M, Yallapu MM, Chauhan N, Yacoubian AM, Behrman SW, Zafar N, Kumar D, Thompson PA, Jaggi M, Chauhan SC (2014) MicroRNA-145 targets MUC13 and suppresses growth and invasion of pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget 5:7599–7609. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.2281
Huang C, Li H, Wu W, Jiang T, Qiu Z (2013) Regulation of miR-155 affects pancreatic cancer cell invasiveness and migration by modulating the STAT3 signaling pathway through SOCS1. Oncol Rep 30:1223–1230. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2013.2576
Chen Z, Sangwan V, Banerjee S, Mackenzie T, Dudeja V, Li X, Wang H, Vickers SM, Saluja AK (2013) miR-204 mediated loss of Myeloid cell leukemia-1 results in pancreatic cancer cell death. Mol Cancer 12:105. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-4598-12-105
Iwagami Y, Eguchi H, Nagano H, Akita H, Hama N, Wada H, Kawamoto K, Kobayashi S, Tomokuni A, Tomimaru Y, Mori M, Doki Y (2013) miR-320c regulates gemcitabine-resistance in pancreatic cancer via SMARCC1. Br J Cancer 109:502–511. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2013.320
Liu A, Zhou Y, Zhao T, Tang X, Zhou B, Xu J (2021) MiRNA-3662 reverses the gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer through regulating the tumor metabolism. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-021-04289-z
Panebianco C, Trivieri N, Villani A, Terracciano F, Latiano TP, Potenza A, Perri F, Binda E, Pazienza V (2021) Improving gemcitabine sensitivity in pancreatic cancer cells by restoring miRNA-217 levels. Biomolecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11050639
Meng Q, Liang C, Hua J, Zhang B, Liu J, Zhang Y, Wei M, Yu X, Xu J, Shi S (2020) A miR-146a-5p/TRAF6/NF-kB p65 axis regulates pancreatic cancer chemoresistance: functional validation and clinical significance. Theranostics 10:3967–3979. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.40566
Liu Y, Xia L, Dong L, Wang J, Xiao Q, Yu X, Zhu H (2020) CircHIPK3 promotes gemcitabine (GEM) resistance in pancreatic cancer cells by sponging miR-330-5p and targets RASSF1. Cancer Manag Res 12:921–929. https://doi.org/10.2147/cmar.s239326
Funding
This work was supported by the Zhejiang Provincial Science and Technology Projects (No. GF21H160100 to T.X).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
X–Y C: Conception, design and inviting co-authors to participate. T X: Writing original manuscript draft. Y-N Z: Review and editing of manuscript critically for important intellectual content and provided comments and feedback for the scientific contents of the manuscript. All authors read, revised and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, T., Chen, XY. & Zhang, YN. MicroRNAs as biomarkers and perspectives in the therapy of pancreatic cancer. Mol Cell Biochem 476, 4191–4203 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-021-04233-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-021-04233-y