Abstract
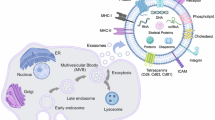
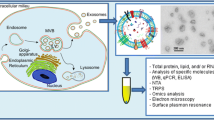
Exosomes are produced from mammalian cells when multivesicular endosomes fuse with the plasma membrane, releasing their intralumenal vesicles. In this study we assessed the effects of MOPIPP, a novel indole-based chalcone, and vacuolin-1, a distinct triazine-based compound, on exosome production in cultured glioblastoma and 293T cells. Both compounds promote vacuolization of late endosome compartments and interfere with trafficking of late endosomes to lysosomes, without significant cytotoxicity. The results show that vacuolated cells treated with these compounds release exosomes with morphologies similar to untreated controls. However, both compounds trigger multi-fold increases in release of exosome marker proteins (e.g., CD63, Alix) in exosome fractions collected from equivalent numbers of cells. Despite the marked increase in exosome production, the profiles of selected miRNA cargoes carried by the exosomes were generally similar in cells treated with the compounds. Insofar as MOPIPP and vacuolin-1 seem able to increase the overall yield of exosomes from cultured cells, they might be useful for efforts to develop exosome-based therapeutics.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vlassov AV, Magdaleno S, Setterquist R, Conrad R (2012) Exosomes: current knowledge of their composition, biological functions, and diagnostic and therapeutic potentials. Biochim Biophys Acta 1820(7):940–948
Andaloussi EL, Mager I, Breakefield XO, Wood MJ (2013) Extracellular vesicles: biology and emerging therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov 12(5):347–357
Hu G, Drescher KM, Chen XM (2012) Exosomal miRNAs: biological properties and therapeutic potential. Front Genet 3:56
Thind A, Wilson C (2016) Exosomal miRNAs as cancer biomarkers and therapeutic targets. J Extracell Vesicles 5:31292
Simons M, Raposo G (2009) Exosomes–vesicular carriers for intercellular communication. Curr Opin Cell Biol 21(4):575–581
Mathivanan S, Ji H, Simpson RJ (2010) Exosomes: extracellular organelles important in intercellular communication. J Proteomics 73(10):1907–1920
Azmi AS, Bao B, Sarkar FH (2013) Exosomes in cancer development, metastasis, and drug resistance: a comprehensive review. Cancer Metastasis Rev 32(3–4):623–642
Johnsen KB, Gudbergsson JM, Skov MN, Pilgaard L, Moos T, Duroux M (2014) A comprehensive overview of exosomes as drug delivery vehicles—endogenous nanocarriers for targeted cancer therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta 1846(1):75–87
Ha D, Yang N, Nadithe V (2016) Exosomes as therapeutic drug carriers and delivery vehicles across biological membranes: current perspectives and future challenges. Acta Pharm Sin B 6(4):287–296
Fevrier B, Raposo G (2004) Exosomes: endosomal-derived vesicles shipping extracellular messages. Curr Opin Cell Biol 16(4):415–421
Harding CV, Heuser JE, Stahl PD (2013) Exosomes: looking back three decades and into the future. J Cell Biol 200(4):367–371
Stahl PD, Barbieri MA (2002) Multivesicular bodies and multivesicular endosomes: the “ins and outs” of endosomal traffic. SciSTKE 141:E32
Piper RC, Katzmann DJ (2007) Biogenesis and function of multivesicular bodies. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 23:519–547
Raposo G, Stoorvogel W (2013) Extracellular vesicles: exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J Cell Biol 200(4):373–383
Trajkovic K, Hsu C, Chiantia S, Rajendran L, Wenzel D, Wieland F, Schwille P, Brugger B, Simons M (2008) Ceramide triggers budding of exosome vesicles into multivesicular endosomes. Science 319(5867):1244–1247
Savina A, Furlan M, Vidal M, Colombo MI (2003) Exosome release is regulated by a calcium-dependent mechanism in K562 cells. J Biol Chem 278(22):20083–20090
Parolini I, Federici C, Raggi C, Lugini L, Palleschi S, De Milito A, Coscia C, Iessi E, Logozzi M, Molinari A, Colone M, Tatti M, Sargiacomo M, Fais S (2009) Microenvironmental pH is a key factor for exosome traffic in tumor cells. J Biol Chem 284(49):34211–34222
Ostrowski M, Carmo NB, Krumeich S, Fanget I, Raposo G, Savina A, Moita CF, Schauer K, Hume AN, Freitas RP, Goud B, Benaroch P, Hacohen N, Fukuda M, Desnos C, Seabra MC, Darchen F, Amigorena S, Moita LF, Thery C (2010) Rab27a and Rab27b control different steps of the exosome secretion pathway. Nat Cell Biol 12(1):19–30
Hsu C, Morohashi Y, Yoshimura S, Manrique-Hoyos N, Jung S, Lauterbach MA, Bakhti M, Gronborg M, Mobius W, Rhee J, Barr FA, Simons M (2010) Regulation of exosome secretion by Rab35 and its GTPase-activating proteins TBC1D10A-C. J Cell Biol 189(2):223–232
Savina A, Vidal M, Colombo MI (2002) The exosome pathway in K562 cells is regulated by Rab11. J Cell Sci 115(Pt 12):2505–2515
Aki T, Nara A, Uemura K (2012) Cytoplasmic vacuolization during exposure to drugs and other substances. Cell BiolToxicol 28(3):125–131
Maltese WA, Overmeyer JH (2014) Methuosis: nonapoptotic cell death associated with vacuolization of macropinosome and endosome compartments. Am J Pathol 184(6):1630–1642
Robinson MW, Overmeyer JH, Young AM, Erhardt PW, Maltese WA (2012) Synthesis and evaluation of indole-based chalcones as inducers of methuosis, a novel type of nonapoptotic cell death. J Med Chem 55(5):1940–1956
Trabbic CJ, Dietsch HM, Alexander EM, Nagy PI, Robinson MW, Overmeyer JH, Maltese WA, Erhardt PW (2014) Differential induction of cytoplasmic vacuolization and methuosis by novel 2-indolyl-substituted pyridinylpropenones. ACS Med Chem Lett 5(1):73–77
Trabbic CJ, Overmeyer JH, Alexander EM, Crissman EJ, Kvale HM, Smith MA, Erhardt PW, Maltese WA (2015) Synthesis and biological evaluation of indolyl-pyridinyl-propenones having either methuosis or microtubule disruption activity. J Med Chem 58(5):2489–2512
Mbah NE, Overmeyer JH, Maltese WA (2017) Disruption of endolysosomal trafficking pathways in glioma cells by methuosis-inducing indole-based chalcones. Cell Biol Toxicol 33:263–281
Feng Y, Yu S, Lasell TK, Jadhav AP, Macia E, Chardin P, Melancon P, Roth M, Mitchison T, Kirchhausen T (2003) Exo1: a new chemical inhibitor of the exocytic pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(11):6469–6474
Cerny J, Feng Y, Yu A, Miyake K, Borgonovo B, Klumperman J, Meldolesi J, McNeil PL, Kirchhausen T (2004) The small chemical vacuolin-1 inhibits Ca(2+)-dependent lysosomal exocytosis but not cell resealing. EMBO Rep 5(9):883–888
Lu Y, Dong S, Hao B, Li C, Zhu K, Guo W, Wang Q, Cheung KH, Wong CW, Wu WT, Markus H, Yue J (2014) Vacuolin-1 potently and reversibly inhibits autophagosome-lysosome fusion by activating RAB5A. Autophagy 10(11):1895–1905
Johnson EE, Overmeyer JH, Gunning WT, Maltese WA (2006) Gene silencing reveals a specific function of hVps34 phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in late versus early endosomes. J Cell Sci 119(Pt 7):1219–1232
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Maltese WA, Wilson S, Tan Y, Suomensaari S, Sinha S, Barbour R, McConlogue L (2001) Retention of the Alzheimer’s amyloid precursor fragment C99 in the endoplasmic reticulum prevents formation of amyloid beta-peptide. J Biol Chem 276(23):20267–20279
Bissig C, Gruenberg J (2014) ALIX and the multivesicular endosome: ALIX in Wonderland. Trends Cell Biol 24(1):19–25
Zoller M (2009) Tetraspanins: push and pull in suppressing and promoting metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer 9(1):40–55
Logozzi M, De Milito A, Lugini L, Borghi M, Calabro L, Spada M, Perdicchio M, Marino ML, Federici C, Iessi E, Brambilla D, Venturi G, Lozupone F, Santinami M, Huber V, Maio M, Rivoltini L, Fais S (2009) High levels of exosomes expressing CD63 and caveolin-1 in plasma of melanoma patients. PLoS ONE 4(4):e5219
Sheldon H, Heikamp E, Turley H, Dragovic R, Thomas P, Oon CE, Leek R, Edelmann M, Kessler B, Sainson RC, Sargent I, Li JL, Harris AL (2010) New mechanism for Notch signaling to endothelium at a distance by Delta-like 4 incorporation into exosomes. Blood 116(13):2385–2394
Li J, Chen X, Yi J, Liu Y, Li D, Wang J, Hou D, Jiang X, Zhang J, Wang J, Zen K, Yang F, Zhang CY, Zhang Y (2016) Identification and characterization of 293T cell-derived exosomes by profiling the protein, mRNA and microRNA components. PLoS ONE 11(9):e0163043
Abd-El-Fattah AA, Sadik NA, Shaker OG, Aboulftouh ML (2013) Differential microRNAs expression in serum of patients with lung cancer, pulmonary tuberculosis, and pneumonia. Cell Biochem Biophys 67(3):875–884
Zhang J, Li S, Li L, Li M, Guo C, Yao J, Mi S (2015) Exosome and exosomal microRNA: trafficking, sorting, and function. Genomics Proteomics Bioinform 13(1):17–24
Janas T, Janas MM, Sapon K, Janas T (2015) Mechanisms of RNA loading into exosomes. FEBS Lett 589(13):1391–1398
Shurtleff MJ, Temoche-Diaz MM, Karfilis KV, Ri S, Schekman R (2016) Y-box protein 1 is required to sort microRNAs into exosomes in cells and in a cell-free reaction. eLife. doi:10.7554/eLife.19276
Santangelo L, Giurato G, Cicchini C, Montaldo C, Mancone C, Tarallo R, Battistelli C, Alonzi T, Weisz A, Tripodi M (2016) The RNA-binding protein SYNCRIP is a component of the hepatocyte exosomal machinery controlling microRNA sorting. Cell Rep 17(3):799–808
Acknowledgements
We thank Christopher J. Trabbic and Paul W. Erhardt for supplying MOPIPP, and William T. Gunning III for assistance with electron microscopy of cells. This work was supported by NIH Grant R01 CA115495 and by the Harold and Helen McMaster Endowment for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Mbah, N.E. & Maltese, W.A. Vacuole-inducing compounds that disrupt endolysosomal trafficking stimulate production of exosomes by glioblastoma cells. Mol Cell Biochem 439, 1–9 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-3130-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-3130-x