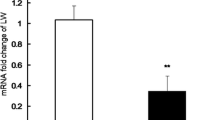
Abstract
IGF1 expression regulation attracts numerous interests because of its important role during mammalian growth and development. Domestic pig can be used as a valuable animal model to investigate human development since they share the high similarity in general physiology and metabolism. In this study, we examined the expression pattern of IGF1 and found it associated with liver C/EBP β expression pattern in porcine liver during embryonic and postnatal development. Both IGF1 and C/EBP β expression in liver maintained at low levels before birth and increased after birth. Correspondingly, C/EBP β demonstrated high binding activity to two sites at IGF1 promoter region in liver after birth. Additionally, IGF1 expression can be activated by C/EBP β overexpression in porcine primary hepatocytes. These results indicated that C/EBP β can activate IGF1 expression after birth by binding to IGF1 promoter. Our study may contribute to a better understanding of mammalian development and bring a novel anti-aging pathway in human.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Christoforidis A, Maniadaki I, Stanhope R (2005) Growth hormone/insulin-like growth factor-1 axis during puberty. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev PER 3:5–10
Miura Y, Kato H, Noguchi T (1992) Effect of dietary proteins on insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) messenger ribonucleic acid content in rat liver. Br J Nutr 67:257–265
Ohlsson C, Mohan S, Sjögren K, Tivesten Å, Isgaard J, Isaksson O et al (2009) The role of liver-derived insulin-like growth factor-I. Endocr Rev 30:494–535
Tannenbaum G, Guyda HJ, Posner BI (1983) Insulin-like growth factors: a role in growth hormone negative feedback and body weight regulation via brain. Science 220:77–79
Baker J, Liu J-P, Robertson EJ, Efstratiadis A (1993) Role of insulin-like growth factors in embryonic and postnatal growth. Cell 75:73–82
Jones JI, Clemmons DR (1995) Insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins: biological actions. Endocr Rev 16:3–34
Clemmons DR (1997) Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins and their role in controlling IGF actions. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 8:45–62
Annunziata M, Granata R, Ghigo E (2011) The IGF system. Acta Diabetol 48:1–9
Li S, Yakar S, Brodt P (2011) Role of the IGF-axis in liver metastasis: experimental and clinical evidence. liver metastasis: biology and clinical management. Springer, Dordecht, pp 233–271
Liu J-P, Baker J, Perkins AS, Robertson EJ, Efstratiadis A (1993) Mice carrying null mutations of the genes encoding insulin-like growth factor I (Igf-1) and type 1 IGF receptor (Igf1r). Cell 75:59–72
Loughna PT, Mason P, Bates PC (1992) Regulation of insulin-like growth factor 1 gene expression in skeletal muscle. Symposia of the Society for Experimental Biology, p. 319
Rosenbloom AL (2007) The role of recombinant insulin-like growth factor I in the treatment of the short child. Curr Opin Pediatr 19:458–464
Vaught J, Contreras P, Glicksman M, Neff N (2008) Potential utility of rhlGF-1 in neuromuscular and/or degenerative. Growth Factors Drugs Neurol Sens Disord 777:18
Pan Z, Zhang J, Zhang J, Zhou B, Chen J, Jiang Z et al (2012) Expression profiles of the insulin-like growth factor system components in liver tissue during embryonic and postnatal growth of Erhualian and Yorkshire reciprocal cross F-1 pigs. Asian Aust J Anim Sci 25:903–912
Hiney JK, Ojeda S, Dees WL (1991) Insulin-like growth factor I: a possible metabolic signal involved in the regulation of female puberty. Neuroendocrinology 54:420–423
Laron Z, Klinger B (1998) Effect of insulin-like growth factor-I treatment on serum androgens and testicular and penile size in males with Laron syndrome (primary growth hormone resistance). Eur J Endocrinol 138:176–180
Argente J, Barrios V, Pozo J, Munoz M, Hervas F, Stene M et al (1993) Normative data for insulin-like growth factors (IGFs), IGF-binding proteins, and growth hormone-binding protein in a healthy Spanish pediatric population: age-and sex-related changes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 77:1522–1528
Kitanaka S (2008) Role of HNF-1α and HNF-1β on insulin, IGF-1 and other potential target genes. Expert Rev Endocrinol Metabol. doi:10.1586/17446651.3.4.441
Wolfrum C, Besser D, Luca E, Stoffel M (2003) Insulin regulates the activity of forkhead transcription factor Hnf-3β/Foxa-2 by Akt-mediated phosphorylation and nuclear/cytosolic localization. Proc Natl Acad Sci 100:11624–11629
LaVoie HA, Nguyen JB, Kordus RJ, Hui YY (2010) GATA6 depletion reduces cyclic AMP-stimulated IGF1 mRNA and free protein levels in luteinizing porcine granulosa cells. Biology of Reproduction, Soc Study Reproduction 1603 MONROE ST, Madison, WI 53711-2021 USA, pp. 185–185
LaVoie HA, Kordus RJ, Nguyen JB, Barth JL, Hui YY (2010) GATA depletion impacts insulin-like growth factor 1 mRNA and protein levels in luteinizing porcine granulosa cells. Biol Reprod 83:1015–1026
Joung Y-H, Lee M-Y, Lim E-J, Kim M-S, Hwang TS, Kim S-Y et al (2007) Hypoxia activates the IGF-1 expression through STAT5b in human HepG2 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 358:733–738
Hemati N, Ross SE, Erickson RL, Groblewski GE, MacDougald OA (1997) Signaling pathways through which insulin regulates CCAAT/enhancer binding protein α (C/EBPα) phosphorylation and gene expression in 3T3-L1 adipocytes correlation with GLUT4 gene Expression. J Biol Chem 272:25913–25919
Li F, Zhao R, Xu Q, Chen W, Ma Y, Chen J (2003) Characteristics of testosterone secretion in male Erhualian and Large White pigs in different developmental stages. J Nanjing Agric Univ 26:117–119
Sjögren K, Liu J-L, Blad K, Skrtic S, Vidal O, Wallenius V et al (1999) Liver-derived insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) is the principal source of IGF-I in blood but is not required for postnatal body growth in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci 96:7088–7092
Kovács KA, Steinmann M, Magistretti PJ, Halfon O, Cardinaux J-R (2003) CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein family members recruit the coactivator CREB-binding protein and trigger its phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 278:36959–36965
Ramji D, Foka P (2002) CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins: structure, function and regulation. Biochem J 365:561–575
Ruffell D, Mourkioti F, Gambardella A, Kirstetter P, Lopez RG, Rosenthal N et al (2009) A CREB-C/EBPβ cascade induces M2 macrophage-specific gene expression and promotes muscle injury repair. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106:17475–17480
Harries LW, Pilling LC, Hernandez LDG, Bradley-Smith R, Henley W, Singleton AB et al (2012) CCAAT-enhancer-binding protein-beta expression in vivo is associated with muscle strength. Aging Cell 11:262–268
Wessells J, Yakar S, Johnson PF (2004) Critical prosurvival roles for C/EBPβ and insulin-like growth factor I in macrophage tumor cells. Mol Cell Biol 24:3238–3250
Umayahara Y, Kajimoto Y, Fujitani Y, Gorogawa S-I, Yasuda T, Kuroda A et al (2002) Protein kinase C-dependent, CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein β-mediated expression of insulin-like growth factor I gene. J Biol Chem 277:15261–15270
Staiger J, Lueben MJ, Berrigan D, Malik R, Perkins SN, Hursting SD et al (2009) C/EBPβ regulates body composition, energy balance-related hormones and tumor growth. Carcinogenesis 30:832–840
Cesi V, Giuffrida ML, Vitali R, Tanno B, Mancini C, Calabretta B et al (2005) C/EBP α and β mimic retinoic acid activation of IGFBP-5 in neuroblastoma cells by a mechanism independent from binding to their site. Exp Cell Res 305:179–189
Barzilai N, Bartke A (2009) Biological approaches to mechanistically understand the healthy life span extension achieved by calorie restriction and modulation of hormones. J Gerontol Ser A 64:187–191
Bartke A (2011) Single-gene mutations and healthy ageing in mammals. Philos Trans R Soc B 366:28–34
Suh Y, Atzmon G, Cho M-O, Hwang D, Liu B, Leahy DJ et al (2008) Functionally significant insulin-like growth factor I receptor mutations in centenarians. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105:3438–3442
Van Heemst D, Beekman M, Mooijaart SP, Heijmans BT, Brandt BW, Zwaan BJ et al (2005) Reduced insulin/IGF-1 signalling and human longevity. Aging Cell 4:79–85
Pawlikowska L, Hu D, Huntsman S, Sung A, Chu C, Chen J et al (2009) Association of common genetic variation in the insulin/IGF1 signaling pathway with human longevity. Aging Cell 8:460–472
Guevara-Aguirre J, Balasubramanian P, Guevara-Aguirre M, Wei M, Madia F, Cheng C-W et al (2011) Growth hormone receptor deficiency is associated with a major reduction in pro-aging signaling, cancer and diabetes in humans. Sci Transl Med 3:70ra13
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Grants from the following Projects: Study on the regulation of IGF1 gene in pig liver (National Natural Science Foundation of China 31472073 2015-2019); Cultivating New Varieties by Transgenic Technology (#2012ZX08006-003); and China Scholarship Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
DNA size range analysis by agrose gel electrophoresis after 5min and 10min of sonication. Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, Y., Xiong, K., Shen, M. et al. CCAAT-enhancer binding protein (C/EBP) β regulates insulin-like growth factor (IGF) 1 expression in porcine liver during prenatal and postnatal development. Mol Cell Biochem 401, 209–218 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-014-2308-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-014-2308-8