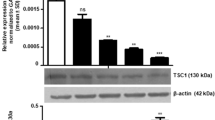
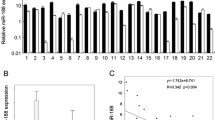
Abstract
MicroRNA (miRNA) is a small noncoding RNA molecule, 19–25 nucleotides in length, which regulates several pathways including cell development, cell proliferation, carcinogenesis, apoptosis, etc. In this study, the over-expression of microRNA-205 (miR-205) increased the number of apoptotic cells by at least 4 times compared to the control. In addition, over-expressed miRNA in KB oral cancer cells triggered apoptosis via the caspase cascade, including the cleavage of caspase-9, caspase-7, caspase-3, and PARP. Flow cytometry showed that apoptotic cell death was increased significantly by 35.33 % in KB oral cancer cells with over-expressed miR-205 compared to the control. The microarray data showed that axis inhibitor protein 2 (Axin2) was down-regulated in KB oral cancer cells transfected with miR-205. In addition, Axin2 was down-regulated by approximately 50 % by over-expressed miR-205 at both the mRNA and protein levels. Interestingly, Axin2 was up-regulated in KB oral cancer compared to human normal oral keratinocytes. Furthermore, the cell cytotoxicity and apoptotic population of KB oral cancer cells were increased significantly after Axin2 siRNA transfection. These results suggest that Axin2 is might be as potential oncogene in KB oral cancer cells. The luciferase assay showed that over-expressed miR-205 in KB oral cancer cells suppressed AXIN2 expression through an interaction with its own binding site at AXIN2 3′UTR (64–92). These results suggest that miR-205 is a novel anti-oncogenic miRNA in KB oral cancer cells, and may have potential applications in oral cancer therapy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cho HJ, Liu G, Jin SM, Parisiadou L, Xie C, Yu J, Sun L, Ma B, Ding J, Vancraenenbroeck R, Lobbestael E, Baekelandt V, Taymans JM, He P, Troncoso JC, Shen Y, Cai H (2013) MicroRNA-205 regulates the expression of Parkinson’s disease-related leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 protein. Hum Mol Genet 22:608–620. doi:10.1093/hmg/dds470
Zhang Y, Xie RL, Croce CM, Stein JL, Lian JB, van Wijnen AJ, Stein GS (2011) A program of microRNAs controls osteogenic lineage progression by targeting transcription factor Runx2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:9863–9868. doi:10.1073/pnas.1018493108
Liu J, Mao Q, Liu Y, Hao X, Zhang S, Zhang J (2013) Analysis of miR-205 and miR-155 expression in the blood of breast cancer patients. Chin J Cancer Res 25:46–54. doi:10.3978/j.issn.1000-9604.2012.11.04
Kim JS, Yu SK, Lee MH, Park MG, Park E, Kim SG, Lee SY, Kim CS, Kim HJ, Chun HS, Chun SW, Kim do K (2013) MicroRNA-205 directly regulates the tumor suppressor, interleukin-24, in human KB oral cancer cells. Mol Cells 35:17–24. doi:10.1007/s10059-013-2154-7
Majid S, Dar AA, Saini S, Yamamura S, Hirata H, Tanaka Y, Deng G, Dahiya R (2010) MicroRNA-205-directed transcriptional activation of tumor suppressor genes in prostate cancer. Cancer 116:5637–5649. doi:10.1002/cncr.25488
Tucci P, Agostini M, Grespi F, Markert EK, Terrinoni A, Vousden KH, Muller PA, Dotsch V, Kehrloesser S, Sayan BS, Giaccone G, Lowe SW, Takahashi N, Vandenabeele P, Knight RA, Levine AJ, Melino G (2012) Loss of p63 and its microRNA-205 target results in enhanced cell migration and metastasis in prostate cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:15312–15317. doi:10.1073/pnas.1110977109
Liu S, Tetzlaff MT, Liu A, Liegl-Atzwanger B, Guo J, Xu X (2012) Loss of microRNA-205 expression is associated with melanoma progression. Lab Invest 92:1084–1096. doi:10.1038/labinvest.2012.62
Yue X, Wang P, Xu J, Zhu Y, Sun G, Pang Q, Tao R (2012) MicroRNA-205 functions as a tumor suppressor in human glioblastoma cells by targeting VEGF-A. Oncol Rep 27:1200–1206. doi:10.3892/or.2011.1588
Song H, Bu G (2009) MicroRNA-205 inhibits tumor cell migration through down-regulating the expression of the LDL receptor-related protein 1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 388:400–405. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.08.020
Iorio MV, Casalini P, Piovan C, Di Leva G, Merlo A, Triulzi T, Menard S, Croce CM, Tagliabue E (2009) microRNA-205 regulates HER3 in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 69:2195–2200. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2920
Majid S, Saini S, Dar AA, Hirata H, Shahryari V, Tanaka Y, Yamamura S, Ueno K, Zaman MS, Singh K, Chang I, Deng G, Dahiya R (2011) MicroRNA-205 inhibits Src-mediated oncogenic pathways in renal cancer. Cancer Res 71:2611–2621. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-3666
Verdoodt B, Neid M, Vogt M, Kuhn V, Liffers ST, Palisaar RJ, Noldus J, Tannapfel A, Mirmohammadsadegh A (2013) MicroRNA-205, a novel regulator of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl2, is downregulated in prostate cancer. Int J Oncol 43:307–314. doi:10.3892/ijo.2013.1915
Noguchi S, Iwasaki J, Kumazaki M, Mori T, Maruo K, Sakai H, Yamada N, Shimada K, Naoe T, Kitade Y, Akao Y (2013) Chemically modified synthetic microRNA-205 inhibits the growth of melanoma cells in vitro and in vivo. Mol Ther. doi:10.1038/mt.2013.70
Gandellini P, Profumo V, Casamichele A, Fenderico N, Borrelli S, Petrovich G, Santilli G, Callari M, Colecchia M, Pozzi S, De Cesare M, Folini M, Valdagni R, Mantovani R, Zaffaroni N (2012) miR-205 regulates basement membrane deposition in human prostate: implications for cancer development. Cell Death Differ 19:1750–1760. doi:10.1038/cdd.2012.56
Jho EH, Zhang T, Domon C, Joo CK, Freund JN, Costantini F (2002) Wnt/beta-catenin/Tcf signaling induces the transcription of Axin2, a negative regulator of the signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biol 22:1172–1183
Lustig B, Jerchow B, Sachs M, Weiler S, Pietsch T, Karsten U, van de Wetering M, Clevers H, Schlag PM, Birchmeier W, Behrens J (2002) Negative feedback loop of Wnt signaling through upregulation of conductin/axin2 in colorectal and liver tumors. Mol Cell Biol 22:1184–1193
Cheng CW, Smith SK, Charnock-Jones DS (2003) Wnt-1 signaling inhibits human umbilical vein endothelial cell proliferation and alters cell morphology. Exp Cell Res 291:415–425
Masckauchan TN, Shawber CJ, Funahashi Y, Li CM, Kitajewski J (2005) Wnt/beta-catenin signaling induces proliferation, survival and interleukin-8 in human endothelial cells. Angiogenesis 8:43–51. doi:10.1007/s10456-005-5612-9
Ille F, Atanasoski S, Falk S, Ittner LM, Marki D, Buchmann-Moller S, Wurdak H, Suter U, Taketo MM, Sommer L (2007) Wnt/BMP signal integration regulates the balance between proliferation and differentiation of neuroepithelial cells in the dorsal spinal cord. Dev Biol 304:394–408. doi:10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.12.045
Espada J, Calvo MB, Diaz-Prado S, Medina V (2009) Wnt signalling and cancer stem cells. Clin Transl Oncol 11:411–427
Gaujoux S, Hantel C, Launay P, Bonnet S, Perlemoine K, Lefevre L, Guillaud-Bataille M, Beuschlein F, Tissier F, Bertherat J, Rizk-Rabin M, Ragazzon B (2013) Silencing mutated beta-catenin inhibits cell proliferation and stimulates apoptosis in the adrenocortical cancer cell line H295R. PLoS One 8:e55743. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0055743
Behrens J (2005) The role of the Wnt signalling pathway in colorectal tumorigenesis. Biochem Soc Trans 33:672–675. doi:10.1042/BST0330672
Pan KF, Liu WG, Zhang L, You WC, Lu YY (2008) Mutations in components of the Wnt signaling pathway in gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol 14:1570–1574
Kim MS, Kim SS, Ahn CH, Yoo NJ, Lee SH (2009) Frameshift mutations of Wnt pathway genes AXIN2 and TCF7L2 in gastric carcinomas with high microsatellite instability. Hum Pathol 40:58–64. doi:10.1016/j.humpath.2008.06.006
Kim NH, Cha YH, Kang SE, Lee Y, Lee I, Cha SY, Ryu JK, Na JM, Park C, Yoon HG, Park GJ, Yook JI, Kim HS (2013) p53 regulates nuclear GSK-3 levels through miR-34-mediated Axin2 suppression in colorectal cancer cells. Cell Cycle 12:1578–1587. doi:10.4161/cc.24739
Wu ZQ, Brabletz T, Fearon E, Willis AL, Hu CY, Li XY, Weiss SJ (2012) Canonical Wnt suppressor, Axin2, promotes colon carcinoma oncogenic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:11312–11317. doi:10.1073/pnas.1203015109
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (No. 2012R1A1A2001175).
Conflict of interest
We declare that there is no conflict of interest. No author has any financial interest or conflict of interest involved with this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, JS., Park, SY., Lee, S.A. et al. MicroRNA-205 suppresses the oral carcinoma oncogenic activity via down-regulation of Axin-2 in KB human oral cancer cell. Mol Cell Biochem 387, 71–79 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1872-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1872-7