Abstract
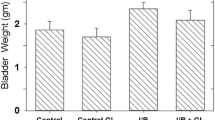
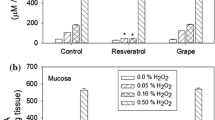
Purpose: Ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) is a major etiological factor in the bladder dysfunctions observed in men with lower tract obstruction, women with postmenopausal incontinence and with aging. A standardized grape suspension protects the rabbit urinary bladder from both the contractile dysfunctions and the morphologic changes mediated by I/R. Using a model of in vivo bilateral ischemia/reperfusion, the current study investigated the effect of this grape suspension on the endogenous antioxidant defense systems. Materials and methods: 24 NZW rabbits were separated into 6 groups of 4. Groups 1–3 were treated by gavage with aqueous grape suspensions; groups 4–6 received sugar-water vehicle. Groups 3 and 6 were controls. Groups 1 and 4 were subjected to bilateral ischemia for 2 h (I). Groups 2 and 5 underwent bilateral ischemia for 2 h and reperfusion for 1 week (I/R). For all rabbit bladders, the muscle and mucosa were separated by blunt dissection and analyzed separately. The effects of the various treatments on bladder antioxidant systems of cytoplasmic superoxide dismutase (Cu-Zn superoxide dismutase; SOD), and catalase (CAT) were evaluated. Results: The standardized grape suspension up-regulated both SOD and CAT activity of bladder muscle and mucosa in control animals. There were few differences in the grape suspension treated animals after ischemia, and in general the activities decreased following I/R. Conclusions: Increases of SOD and CAT activity in control animals as a result of grape suspension suggest a greater antioxidant capacity. This increase in the antioxidant defense system may explain the increased protection of grape suspension in the face of ischemia and I/R. However, the activities of both enzyme systems decreased in the smooth muscle subjected to I/R showing that reperfusion damages these systems probably via oxidation damage to the enzymes themselves.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barry MJ, Meigs JB: The Natural History of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia, pp 106–115. In Lepor, H. (Ed.) Prostatic Diseases. W.B. Saunders Co., Phila., 2000
Parekh MH, Chichester P, Lobel RW, Aikawa K, Levin RM: Effects of castration on female rabbit bladder physiology and morphology. Urology 64: 1048–1051, 2004
Aikawa K, Leggett RE, Levin RM: Effect of age on hydrogen peroxide mediated contraction damage in the male rat bladder. J Urol 170: 2082–2085, 2003
Lin, AD, Mannikarottu A, Chaudhry A, Whitbeck C, Kogan BA, Chichester P, Levin RM: Protective effects of grape suspension on rabbit bladder subjected to bilateral in vivo ischemia/reperfusion. BJU Int 96: 1397–1402, 2005
Agartan CA, Whitbeck C, Sokol R, Chichester P, Levin RM: Protection of urinary bladder function by grape suspension. Phytother Res 18: 1013–1018, 2004
Erdem E, Leggett R, Dicks B, Kogan BA, Levin RM: Effect of bladder ischaemia/reperfusion on superoxide dismutase activity and contraction. BJU Int 96: 169–174, 2005
Chan PH: Role of oxidants in ischemic brain damage. Stroke 27: 1124–1129, 1996
Choi-Kwon S, Park KA, Lee HJ, Park MS, Lee JH, Jeon SE, et al: Temporal changes in cerebral antioxidant enzyme activities after ischemia and reperfusion in a rat focal brain ischemia model: effect of dietary fish oil. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 152: 11–18, 2004
Balu M, Sangeetha P, Haripriya D, Panneerselvam C: Rejuvenation of antioxidant system in central nervous system of aged rats by grape seed extract. Neurosci Lett 383: 295–300, 2005
Hypolite JA, Longhurst PA, Gong C, Briscoe J, Wein AJ, Levin RM: Metabolic studies on rabbit bladder smooth muscle and mucosal epithelium. Mol Cell Biochem 125: 35–42, 1993
Mannikarottu AS, Kogan B, Levin RM: Ischemic etiology of obstructive bladder dysfunction: A review. Recent Res Devel Mol Cell Biochem 2: 15–34, 2005
Flohe L, Otting F: Superoxide dismutase assays. Methods Enzymol 105: 93–99, 1984
Aebi H: Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105: 121–126, 1984
Danielisova V, Nemethova M, Gottlieb M, Burda J: Changes of endogenous antioxidant enzymes during ischemic tolerance acquisition. Neurochem Res 30: 559–565, 2005
Gulcan H, Ozturk IC, Arslan S: Alterations in antioxidant enzyme activities in cerebrospinal fluid related with severity of hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy in newborns. Biol Neonate 88: 87–91, 2005
Suzuki M, Takeuchi H, Kakita T, Unno M, Katayose Y, Matsuno S: The involvement of the intracellular superoxide production system in hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury. In vivo and in vitro experiments using transgenic mice manifesting excessive Cu-Zn SOD activity. Free Radic Biol Med 29: 756–763, 2000
Lin AM, Chen CF, Ho LT: Neuroprotective effect of intermittent hypoxia on iron-induced oxidative injury in rat brain. Exp Neurol 176: 328–335, 2002
Bagchi D, Bagchi M, Stohs SJ, Das DK, Ray SD, Kuszynski CA, Joshi SS, Pruess HG: Free radicals and grape seed proanthocyanidin extract: importance in human health and disease prevention. Toxicology 148: 187–197, 2000
Lu Y, Zhao WZ, Chang Z, Chen WX, Li L: Procyanidins from grape seeds protect against phorbol ester-induced oxidative cellular and genotoxic damage. Acta Pharmacol Sin 25: 1083–1089, 2004
Iwasaki Y, Matsui T, Arakawa Y: The protective and hormonal effects of proanthocyanidin against gastric mucosal injury in Wistar rats. J Gastroenterol 39: 831–837, 2004
Ray SD, Parikh H, Hickey E, Bagchi M, Bagchi D.: Differential effects of IH636 grape seed proanthocyanidin extract and a DNA repair modulator 4-aminobenzamide on liver microsomal cytochrome 4502E1-dependent aniline hydroxylation. Mol Cell Biochem 218: 27–33, 2001
Tong-Long Lin A, Monson FC, Kato K, Haugaard N, Wein AJ, Levin RM: Effect of chronic ischemia on glucose metabolism of rabbit urinary bladder. J Urol 142: 1127–1133, 1989
Inal M, Akyuz F, Turgut A, Getsfrid WM: Effect of aerobic and anaerobic metabolism on free radical generation swimmers. Med Sci Sports Exerc 33: 564–567, 2001
Sileri P, Schena S, Morini S, Rastellini C, Pham S, Benedetti E, et al: Pyruvate inhibits hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Transplantation 72: 27–30, 2001
Aikawa K, Sugino T, Matsumoto S, Chichester P, Whitbeck C, Levin RM: The Effect of Ovariectomy and Estradiol on Rabbit Bladder Smooth Muscle Contraction and Morphology. J Urol 170: 634–637, 2003
Parekh MH, Chichester PC, Lobel RW, Levin RM: Effects of castration on female rabbit bladder physiology and morphology. UROLOGY 64: 1048–1051, 2004
Cetinel S, Ercan F, Sirvanci S, Sehirli O, Ersoy Y, San T, et al: The ameliorating effect of melatonin on protamine sulfate induced bladder injury and its relationship to interstitial cystitis. J Urol 169: 1564–1568, 2003
Changolkar AK, Hypolite JA, Disanto M, Oates PJ, Wein AJ, Chacko S: Diabetes induced decrease in detrusor smooth muscle force is associated with oxidative stress and overactivity of aldose reductase. J Urol 173: 309–313, 2005
Sanchiz F, Milla A, Artola N, Julia JC, Moya LM, Pedro A, et al: Prevention of radioinduced cystitis by orgotein: a randomized study. Anticancer Res 16: 2025–2028, 1996
Romanenko A, Morimura K, Wanibuchi H, Salim EI, Kinoshita A, Kaneko M: Increased oxidative stress with gene alteration in urinary bladder urothelium after the Chernobyl accident. Int J Cancer 86: 790–798, 2000
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, A.DY., Mannikarottu, A., Kogan, B.A. et al. Effect of bilateral in vivo ischemia/reperfusion on the activities of superoxide dismutase and catalase: Response to a standardized grape suspension. Mol Cell Biochem 296, 11–16 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-005-9068-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-005-9068-4