Abstract
Aim
The high incidence of acute respiratory infection (ARI)-related morbidity and mortality is a major public health concern in developing countries. This study aimed to quantify regional inequalities and the degree of association between childhood ARI and background factors.
Methods
This study utilised information of 238 945 children aged below five years extracted from the Fourth Indian National Family Health Survey conducted in 2015–16. Inter-state and regional inequality in the prevalence of ARI were quantified and presented using a map of India and forest plot. The association of background characteristics and ARI was quantified using bivariate and multivariable binary logistic regression models.
Results
Significant inequalities in the prevalence of childhood ARI were observed across the six regions of India. Considering the children from north-east region as a reference, those from north, central and east regions were 0.68, 1.02 and 0.57 times more likely to suffer from ARI. Comorbidity, sex, age and nutritional status of children were significantly associated with the prevalence of ARI.
Conclusions
ARI remains a significant public health concern among Indian children. The results of this study showed that significant regional disparities in the prevalence of ARI exist in India. This study adds value to the better understanding of inequality patterns and quantifies within- and intra-region inequalities in the prevalence of ARI in India.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) set the target to end deaths from preventable diseases among new-borns and children under five years old by 2030 (Dahan & Gelb, 2015). Nevertheless, in 2017, an estimated 5.5 million children belonging to this age group died from preventable diseases (Hug et al., 2018). One of the impediments to achieve this goal adopted by all United Nations member states is the high prevalence of acute respiratory infection (ARI), a leading cause of childhood morbidity and mortality. In 2016, from 68.06 million episodes, an estimated 652 572 children aged below five years died because of lower respiratory infections (Troeger et al., 2018; Walker et al., 2013) reported that the incidence of severe ARI is the highest in Southeast Asian and African regions. India is one of the 15 highest burdened countries in terms of total pneumonia episodes and related childhood mortality. In India, around 400 000 children aged below five years die every year from ARI-related diseases. The figure accounts for 13–16% of all child deaths among paediatric hospital admissions (Jain et al., 2001; Vashishtha, 2010). As a cause of approximately one-fourth of global annual deaths of children aged below five years, ARI is a significant public health concern in India (Mathew et al., 2011).
The incidence of ARI is associated with a multitude of factors related to the demographics of children, socioeconomic background of their parents and place of residence and the household environment where they grow up. In Bangladesh and India, a relatively high incidence of ARI episodes has been observed among the young, non-exclusively breastfed, anaemic children and those with low birth weight (Budge et al., 2014; Hasan & Richardson, 2017; Prajapati et al., 2011; Sheikh Quyoom Hussain et al., 2014). As a primary career, the socio-cultural, economic and educational backgrounds of the mother are associated with the incidence of childhood ARI. Contemporary literature has reported the significant association between maternal illiteracy, knowledge base and access to mass media and incidence of ARI (Kamal et al., 2015; Nirmolia et al., 2018; Ramani et al., 2016; Sharma et al., 2013; Tazinya et al., 2018). However, the association between maternal education and the prevalence of ARI was insignificant in other studies (Asghar et al., 2017; Goel et al., 2012). The caste, religion and tribal status of a mother as a proxy to their social class showed significant association with the incidence of ARI amongst Indian children (Prakash, 2014). Unclean fuel sources, including biomass and charcoal, have been considered major determinants of childhood ARI (Mathew et al., 2011). Children living in large-size families and overcrowded houses are likely to suffer from ARI (Prajapati et al., 2011). Living at high altitude influences the prevalence of childhood ARI, and an altitude above 2500 m is a modest predictor for respiratory syncytial virus infection in the USA (Choudhuri et al., 2006). Rural–urban gap evidently affects the incidence of childhood ARI (Mathew et al., 2011). However, the unequal distribution of the prevalence of ARI episodes across the states and regions of India has not been completely explored. Any effort to improve the child mortality target of SDGs would largely depend on the progress made in India given that it contributes to one-fifth of global live births and more than a quarter of neonatal mortality (Sankar et al., 2016). Thus, the prevalence and determinants of ARI must be understood at the regional level because any burden estimates at the national level may camouflage regional variation across the country’s large and socio-economically diverse territory.
This article aimed to quantify the regional inequalities and impacts of associated risk factors on the prevalence of ARI among pre-schoolers in India. The information extracted from the latest wave of Indian National Family Health Survey (NFHS–4) conducted in 2015–16 was utilised. The novelty of this study is therefore, the use of recent nationally representative samples of NFHS-4 at a disaggregated level to examine the prevalence and risk factors associated with ARI. Regional inequalities in the prevalence of ARI episode were quantified and presented through a map of India and forest plots. Risk factors of childhood ARI were identified using bivariate analyses and multivariable logistic regression model. The study outputs will fill the gaps in the literature by providing empirical evidence of regional inequalities in the prevalence of ARI in contemporary India. The findings may be helpful in developing policies at the regional and national levels to reduce the rate of ARI-related mortality and morbidity.
Methods
Description of the Indian National Family Health Survey (NFHS-4)
This study extracted and analysed information from NFHS–4 conducted in 2015–16. The NFHS–4 adopted a two-stage stratified sampling technique to achieve a representative sample of the whole country. The administrative districts were stratified into urban and rural areas to achieve appropriate representation. In addition, six strata were constructed with the slums of major cities (Chennai, Hyderabad, Indore, Kolkata, Meerut and Nagpur). The sampling frame for the first stage was the list of all primary sampling units (PSUs), which are the villages (rural settings) or census enumeration blocks (urban settings) and were achieved through the 2011 census. In the first stage, the PSUs were selected independently from each stratum using the probability proportional to size technique. A sample consisting of 28 586 PSUs (130 from metropolitan slums, 8 397 from urban and 20 059 from rural areas) was selected in this stage. These PSUs (or segments for large PSU) were considered clusters in the second stage sampling. The sampling frame for the second-stage sampling was the list of households within previously selected PSUs (clusters). With a systematic sampling technique, 22 households were randomly selected from each of the previously selected cluster and constituted the final sample. In field visits, 616 346 households were occupied, and finally, 601 509 households were successfully interviewed with a response rate of 98%. From the selected households, 699 686 ever-married women aged between 15 and 49 years were interviewed. The study was conducted on 238 945 children alive at the time of interview and born to the interviewed women within five years preceding the survey. Information regarding the children (gender, nutritional status, morbidity and age), their mother (age, religion, education, caste, parity and access to media) and household status (sources of cooking fuel, wealth and place of residence) were collected as the response of women and gathered through computer-assisted personal interviews. Detail of the sampling procedure can be obtained from the final report of the survey elsewhere (IIPS & ICF, 2017).
Variables used in the study
The dependent variable of this study is the incidence of childhood ARI, and the information was gathered from the responses of mothers of infants and not through medical examination. The variable, that is, ARI, is dichotomous in nature with various levels of suffering or not suffering from episodes, such as cold, cough, breathing difficulty and fever, within two weeks preceding the survey. A child having illness with a cough accompanied by short, rapid breathing or by difficulty in breathing was identified as an episode. The association of childhood ARI with a number of covariates was quantified and tested.
India is a federal country comprising of twenty-nine states and seven union territories which are categorised into six regions: North (Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Punjab, Chandigarh, Uttarakhand, Haryana and Delhi), Central (Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Chhattisgarh and Madhya Pradesh), East (West Bengal, Jharkhand, Odisha and Bihar), North-east (Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Manipur, Mizoram, Tripura, Meghalaya and Assam), West (Gujarat, Maharashtra and Goa) and South (Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu and Puducherry).
Based on hereditary, occupation and endogamy, a centuries-old social structure has developed in India, called the ‘caste system. The caste system is well documented in the Government of India (Scheduled Castes) Order, 1936 and also in the Constitution (Scheduled Castes) Order, 1950. In that system, the socially disadvantaged groups are identified as ‘scheduled castes’ (SCs) and ‘scheduled tribes’ (STs). Educationally or socially disadvantaged individuals have been classified as ‘other backward castes’ (OBCs) and the ‘forward caste’ (FC) constitutes with the high caste groups (but exclude some upper-class groups). In this study, the ‘Caste’ variable has entered with the levels: SCs, STs, OBCs and forward castes (FCs).
The selection of covariates was confirmed through contemporary literature. Table 1 presents the detailed categorisation of the covariates with percent distribution.
Statistical analyses
The incidence of ARI among children aged between 0 and 59 months and living across all the states of India were presented using maps. Within-region variations of the incidence were combined and compared using forest plots to visually explore the variability of ARI prevalence among regions. Bivariate and multivariate logistic regression models were used to quantify the association of socioeconomic and demographic characteristics with the prevalence of childhood ARI. Data processing and statistical analyses were conducted using SPSS 26.0 (Zou et al., 2020) and R 3.5.3 (Team, 2019). The sample weight of multi-stage cluster sampling was incorporated in the analytical procedure through R package by survey. Map tools (Bivand & Lewin-Koh, 2019) package in R was used to present the prevalence of ARI in the map of India, whereas the rmeta (Lumley & Lumley, 2018) package was used for meta-analysis.
Results
Subnational level inequalities are evident in the prevalence of ARI for a country with approximately 1.37 billion population and the highest possible socioeconomic and demographic diversities. Based on diversities in cultural settings, socioeconomic achievements and development indicators, contemporary public health research in India segregates the analyses into six geographical regions (Singh, 2013). This broad categorisation was adopted in the current research.
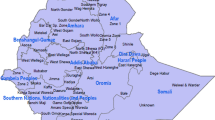
The percentages of children aged below five years and suffering from ARI in 29 states and 7 union territories were presented in the map of India (Fig. 1). Children from the states located at the northern region of India showed relatively high prevalence of ARI. Jammu and Kashmir (6.4%), Uttarakhand (4.9%), Uttar Pradesh (4.7%) and Punjab (4.6%) are among the states with relatively high prevalence of ARI. Among the states in the east region, West Bengal had the highest percentage of children suffering from ARI (3.3%). A state in the northeast region of India, Meghalaya (5.8%) had the highest prevalence, whereas Sikkim, Assam and Nagaland exhibited a relatively lower prevalence. The south and west regions of India presented low prevalence of ARI, with the highest prevalence occurring in Tamil Nadu (2.8%).
The forest plot in Fig. 2 presents the inequalities in the prevalence of childhood ARI within and between the regions of India. The prevalence of ARI incidence in each state in Fig. 2 is represented by a square, with a horizontal line indicating the confidence interval, whereas the size of the square reflects the weight of each studied state in the meta-analysis. The vertical line represents the pooled national proportion obtained using meta-analysis. The width of the diamond shows the 95% confidence interval, with the centre representing the pooled national or regional proportion. The pooled estimate of the prevalence of ARI for the states within the west region (1.4%) was significantly lower than the national pooled estimate (2.6%). The states within the region had consistently low estimated prevalence of ARI (between 1.3% and 2.2%). A relatively low confidence band was observed for Gujarat and Maharashtra, with the latter showing a higher prevalence. Except for Tamil Nadu and Puducherry, all states in the south region had significantly lower prevalence than the national average. The ARI rate in all other states in the northeast region had consistently low prevalence.
The pooled prevalence of the incidence of childhood ARI in the northeast region of India was significantly lower than the overall prevalence in the country. However, the incidence was significantly high in Mizoram. As shown in the forest plot, the pooled prevalence of childhood ARI in the north region did not differ significantly from the national average. States in the north region showed the highest variation in the prevalence than any other regions of India. Out of the eight states in the region, the prevalence was significantly higher in four states (Haryana, Jammu and Kashmir, Punjab and Uttarakhand). In the region, the prevalence was significantly low in Himachal Pradesh and Rajasthan. The pooled estimate for the prevalence of childhood ARI in the east region was 2.8%, which did not differ significantly from the national level prevalence. However, the prevalence was significantly high in Jharkhand and West Bengal. For the two other states in the region (Bihar and Odisha), the prevalence showed no significant difference from the national average. The pooled estimate of the prevalence for the three states in the central region showed no significant difference from the national average. The prevalence was significantly higher (4.7%) in Uttar Pradesh, significantly lower in the Madhya Pradesh and exhibited no significant difference in Chhattrisgarh.
The incidence of diarrhoea, anaemia, stunting, gender and age of children were significantly associated with childhood ARI. For instance, the prevalence of ARI for the children suffering from diarrhoea was 8.8%. The percentage was 2.1% for those who were not suffering from diarrhoea within two weeks preceding the survey. Among those suffering from severe anaemia, the percentage of ARI was 3.7%, whereas the percentage was 2.6% for those who were not suffering from anaemia. Severely stunted children were more likely to suffer from ARI than those who were not stunted. Older children (aged 36–59 months) were less likely (2.2%) to suffer from ARI than the younger (aged less than one year) cohort (3.4%).
Children with teenage women were more likely (3.4%) to suffer from ARI than those whose mothers were aged between 25 and 49 years. No specific association was observed between the prevalence of ARI of children and educational attainment of mothers. Children of Muslim women were more likely (3.2%) to suffer from ARI than those whose mothers have other religious affiliation. The incidence of childhood ARI was significantly high among the children with schedule caste background. Children from households using unclean cooking fuel were significantly more likely to suffer from ARI (2.9%) than those from households using clean cooking fuel. Children from poor households were more likely (3.0%) to suffer from ARI than those from rich households (2.3%).
The incidence of childhood ARI was significantly lower in northeast (1.6%) and south (1.7%) regions and significantly higher in the central (3.8%) regions of India. Children living at high altitude were more likely to suffer from ARI than the others. However, the difference was not statistically significant. Children from rural areas were significantly more likely (2.9%) to suffer from ARI than those from their urban counterparts (2.3%).
The associations of childhood ARI (aged below five years) with a set of background characteristics were identified using a multivariable logistic regression model. Among the variables representing background characteristics of children, the incidence of diarrhoea, age and gender showed significant association with ARI. Religious affiliation, caste and parity of women were also significantly associated with the incidence of ARI of children. Significant variations in the prevalence of ARI were observed across Indian regions (Table 2).
Childhood co-morbidity was identified, that is, those who were suffering from diarrhoea were 2.75 times more likely to be exposed to ARI than those who were not suffering from such condition (adjusted odds ratio [AOR]: 3.75; confidence interval (CI): 3.40 to 4.13). Male children were 18% (AOR: 1.18; CI: 1.09 to 1.27) more likely to suffer from ARI than female children. The model considered children aged between 36 and 59 months as reference category. In comparison with the reference category, those aged below 11 months (AOR: 1.34; CI: 1.18 to 1.53) and those aged between 12 and 23 months (AOR: 1.17; CI: 1.05 to 1.31) were 34% and 17% more likely to suffer from ARI, respectively. After adjusting for other explanatory variables, age, education or access to electronic media of women showed no significant association with the incidence of ARI of their children. On the other hand, children whose mothers have Hindu religious background and from schedule tribes were significantly less likely to suffer from ARI. Children from mothers who gave birth once possessed 21% (AOR: 1.21; CI: 1.06–1.40) higher risk of suffering from ARI compared with those whose mother had 3 or more births. Urban–rural residence or wealth status of household showed no significant association with childhood ARI. In the multivariable analysis, the northeast region was considered the reference. With respect to the reference category, children from the north, central and east regions were 0.68 (AOR: 1.68; CI: 1.38–2.06), 1.02 (AOR: 2.02; CI: 1.97–2.43) and 0.57 (AOR: 1.57; CI: 1.28–1.92) times more likely to suffer from ARI than the others, respectively.
Discussion
This study is based on the information collected from the latest wave of the largest demographic and health survey data (NFHS-4) in India. Through mapping and meta-analyses, the study quantified regional inequalities in the incidence of childhood ARI in India. The degree of associations of socioeconomic, cultural and geographic variables of ARI were quantified using binary and multivariable analyses.
Socio-economic and environmental differences across the states and territories of India are evident in contemporary literature (Awasthi et al., 2018; Chakraborty & Ghosh, 2019; Gothankar et al., 2018; Mareeswaran et al., 2018). As observed in the result of this study, the differentials are transferred into the incidence of childhood morbidity. Differences in environmental quality, including air pollution and density of population, may be considered to form the uniqueness of a region in India regarding the prevalence of ARI among children under five years. Similar findings were reported in several studies conducted in rural parts of India (Bhat & Manjunath, 2013; Choube et al., 2014; Ladomenou et al., 2010; Sharma et al., 2013; Smith et al., 2000; Taksande & Yeole, 2015). According to the binary logistic regression analysis, those suffering from diarrhoea possess relatively high risk of suffering from ARI, although this relationship may work in the opposite manner. A similar interrelationship was observed in other studies in South Asian region (Hasan & Richardson, 2017; Mareeswaran et al., 2018). In line with other studies (Choube et al., 2014; Goel et al., 2012; Prajapati et al., 2012), this research confirms that male children are more vulnerable to ARI than their female counterparts. A possible reason may be the comparatively higher outgoing movements and weaker immune system and ‘male disadvantage’ of boys, which render them more susceptible to acquire respiratory infections from ambient air pollution than girls (Giefing-Kröll et al., 2015; Markle & Fish, 2014). This study identified significant age inequities in the incidence of childhood ARI, in which older children are considered more protected. Similar outputs have been observed in a number of studies conducted at the local (states across India), national and global levels (Acharya et al., 2003; Islam et al., 2013; Kumar et al., 2015; Mitra, 2001; Monto & Ullman, 1974; Prajapati et al., 2011; Reddaiah & Kapoor, 1990; Tupasi et al., 1988). Although other studies found insignificant association between age and the incidence of childhood ARI (Reddy et al., 2016; Sharma et al., 2013; Tazinya et al., 2018), the relatively high prevalence of ARI among 2–3-year-old children can be due to their high exposure to environmental factors.
The findings of this study may positively influence the ever-growing health issues of ARI among under-five children in India. At the same time, our study has several limitations. Firstly, the incidence of ARIs was collected from the reports of women without any medical validation. Secondly, the variables were self-reported and might suffer from reporting error or recall bias. Thirdly, we did not consider any data on whether the children have any pre-existing illness that might cause the symptoms of ARI. Fourthly, the data were drawn from secondary sources and may be inappropriate for any causal inferences. Lastly, given the cross-sectional nature of the study, a cause-effect relationship could not be demonstrated. Despite these limitations, our study has a number of strengths. This study used nationally representative data. Thus, results can be generalised at the national level. This research has implications for policy making and interventions at the national and sub-national levels. India’s states and territories vary widely in terms of their natural resource endowments, socio-economic structures and climate conditions. Most of the health care and healthcare delivery decisions and resource allocation planning are made and implemented at the state level. Childhood mortality and morbidity attributable to ARI must be assessed at the national and regional levels to inform policies and strategies and measure progress towards achieving child health outcomes of SDGs. This study adds value to the better understanding of inequality patterns and quantifies within- and intra-region inequalities of ARI prevalence in India.
Conclusions
With empirical evidence, this research highlighted the regional variation and risk factors of ARI in India. The statistical analyses were conducted to test the association between ARI and several risk factors. Education, age, place of residence and access to electronic media of mothers, wealth status of household, and anaemia and nutritional status of children were not significantly associated with ARI. Children’s sex, age and incidence of diarrhoea had significant association with ARI. Specific groups of children with higher prevalence of ARI include those living in central region, aged between 0 and 23 months and suffering from diarrhoea. Therefore, these important risk factors of ARI must be addressed to prevent the associated morbidity and mortality and fulfil the SDG on children’s health.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are openly available in National Family Health Survey at https://www.dhsprogram.com/.
References
Acharya, D., Prasanna, K., Nair, S., & Rao, R. (2003). Acute respiratory infections in children: a community based longitudinal study in south India. Indian journal of public health, 47(1), 7–13
Asghar, S. A., Srivastava, M. R., Srivastava, J., Gupta, P., & Zaidi, Z. H. (2017). Prevalence of acute respiratory infections among children under five years of age attending rural health training centre of Era’s Lucknow Medical College and Hospital. Int J Community Med Public Health, 4(3752), h2017
Awasthi, S., Verma, T., Agarwal, M., & Pandey, C. M. (2018). To assess the effectiveness of various communication strategies for improving childhood pneumonia case management: study protocol of a community based behavioral open labeled trial in rural Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh, India. BMC pediatrics, 18(1), 279
Bhat, R., & Manjunath, N. (2013). Correlates of acute lower respiratory tract infections in children under 5 years of age in India. The international journal of tuberculosis and lung disease, 17(3), 418–422
Bivand, R., & Lewin-Koh, N. (2019). maptools: tools for handling spatial objects. R package version 0.9, 5
Budge, P. J., Griffin, M. R., Edwards, K. M., Williams, J. V., Verastegui, H., Hartinger, S. M., & Gil, A. I. (2014). Acute viral respiratory illnesses in Andean children: a household-based cohort study. The Pediatric infectious disease journal, 33(5), 443
Chakraborty, M., & Ghosh, S. (2019). Common Childhood Morbidity and Treatment Seeking Behaviour in an Indian Megacity: A Case Study of North Kolkata. J. Indian Anthrop. Soc, 54, 30–50
Choube, A., Kumar, B., Mahmood, S. E., & Srivastava, A. (2014). Potential risk factors contributing to acute respiratory infections in under five age group children. International Journal of Medical Science and Public Health, 3(11), 1385–1389
Choudhuri, J. A., Ogden, L. G., Ruttenber, A. J., Thomas, D. S., Todd, J. K., & Simoes, E. A. (2006). Effect of altitude on hospitalizations for respiratory syncytial virus infection. Pediatrics, 117(2), 349–356
Dahan, M., & Gelb, A. (2015). The Identity Target in the Post-2015 Development Agenda
Giefing-Kröll, C., Berger, P., Lepperdinger, G., & Grubeck‐Loebenstein, B. (2015). How sex and age affect immune responses, susceptibility to infections, and response to vaccination. Aging cell, 14(3), 309–321
Goel, K., Ahmad, S., Agarwal, G., Goel, P., & Kumar, V. (2012). A cross sectional study on prevalence of acute respiratory infections (ARI) in under-five children of Meerut District. India. J Comm Med Health Educ, 2(9), 176
Gothankar, J., Doke, P., Dhumale, G., Pore, P., Lalwani, S., Quraishi, S., & Dhobale, R. (2018). Reported incidence and risk factors of childhood pneumonia in India: a community-based cross-sectional study. BMC public health, 18(1), 1–11
Hasan, M. M., & Richardson, A. (2017). How sustainable household environment and knowledge of healthy practices relate to childhood morbidity in South Asia: analysis of survey data from Bangladesh, Nepal and Pakistan.BMJ open, 7(6), e015019
Hug, L., Sharrow, D., Zhong, K., & You, D. (2018). Estimation Levels & Trends in Child Mortality: Report 2018, Estimates Developed by the United Nations Inter-agency Group for Child Mortality UNICEF. WHO: World Bank Group
IIPS, & ICF. (2017). National Family Health Survey (NFHS-4), 2015–16: India. India: In: International Institute for Population Sciences Mumbai
Islam, F., Sarma, R., Debroy, A., Kar, S., & Pai, R. (2013). Profiling acute respiratory tract infections in children from Assam, India. J Glob Infect Dis. 2013 July; 5 (1): 8–14. In
Jain, N., Lodha, R., & Kabra, S. (2001). Upper respiratory tract infections. The Indian Journal of Pediatrics, 68(12), 1135–1138
Kamal, M. M., Hasan, M. M., & Davey, R. (2015). Determinants of childhood morbidity in Bangladesh: evidence from the demographic and health survey 2011.BMJ open, 5(10), e007538
Kumar, S. G., Majumdar, A., Kumar, V., Naik, B. N., Selvaraj, K., & Balajee, K. (2015). Prevalence of acute respiratory infection among under-five children in urban and rural areas of puducherry, India. Journal of natural science, biology, and medicine, 6(1), 3
Ladomenou, F., Moschandreas, J., Kafatos, A., Tselentis, Y., & Galanakis, E. (2010). Protective effect of exclusive breastfeeding against infections during infancy: a prospective study. Archives of disease in childhood, 95(12), 1004–1008
Lumley, T., & Lumley, M. T. (2018). Package ‘rmeta’
Mareeswaran, N., Savitha, A., & Gopalakrishnan, S. (2018). Prevalence of intestinal parasites among urban and rural population in Kancheepuram district of Tamil Nadu. Int J Community Med Public Health, 5(6), 2585–2589
Markle, J., & Fish, E. N. (2014). SeXX matters in immunity. Trends in immunology, 35(3), 97–104
Mathew, J. L., Patwari, A. K., Gupta, P., Shah, D., Gera, T., Gogia, S., & Menon, S. (2011). Acute respiratory infection and pneumonia in India: a systematic review of literature for advocacy and action: UNICEF-PHFI series on newborn and child health, India. Indian pediatrics, 48(3), 191
Mitra, N. K. (2001). A longitudinal study on ARI among rural under fives. Indian journal of community medicine, 26(1), 8
Monto, A. S., & Ullman, B. M. (1974). Acute respiratory illness in an American community: the Tecumseh study. Jama, 227(2), 164–169
Nirmolia, N., Mahanta, T. G., Boruah, M., Rasaily, R., Kotoky, R. P., & Bora, R. (2018). Prevalence and risk factors of pneumonia in under five children living in slums of Dibrugarh town. Clinical Epidemiology and Global Health, 6(1), 1–4
Prajapati, B., Talsania, N., & Sonaliya, K. (2011). A study on prevalence of acute respiratory tract infections (ARI) in under five children in urban and rural communities of Ahmedabad district, Gujarat. National Journal of Community Medicine, 2(2), 255–259
Prajapati, B., Talsania, N. J., Lala, M. K., & Sonalia, K. N. (2012). Epidemiological profile of acute respiratory infections (ARI) in under five age group of children in urban and rural communities of Ahmedabad district, Gujarat. Int J Med Sci Public Health, 1(2), 52–58
Prakash, L. K. P. (2014). Acute Respiratory Infection among Children and Health Seeking Behaviour in India. International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, 4(11), 1
Ramani, V. K., Pattankar, J., & Puttahonnappa, S. K. (2016). Acute respiratory infections among under-five age group children at urban slums of gulbarga city: A longitudinal study. Journal of clinical and diagnostic research: JCDR, 10(5), LC08
Reddaiah, V., & Kapoor, S. (1990). Epidemiology of pneumonia in rural underfives. The Indian Journal of Pediatrics, 57(5), 701–704
Reddy, V. B., Kusuma, Y. S., Pandav, C. S., Goswami, A. K., & Krishnan, A. (2016). Prevalence of malnutrition, diarrhea, and acute respiratory infections among under-five children of Sugali tribe of Chittoor district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Journal of natural science, biology, and medicine, 7(2), 155
Singh, P.K. (2013). Trends in child immunization across geographical regions in India: Focus on urban-rural and gender differentials. PLOS ONE, 8(9), e73102
Sankar, M., Neogi, S., Sharma, J., Chauhan, M., Srivastava, R., Prabhakar, P., & Paul, V. (2016). State of newborn health in India. Journal of Perinatology, 36(3), S3–S8
Sharma, D., Kuppusamy, K., & Bhoorasamy, A. (2013). Prevalence of acute respiratory infections (ARI) and their determinants in under five children in urban and rural areas of Kancheepuram district, South India. Annals of Tropical Medicine and Public Health, 6(5), 513
Sheikh Quyoom Hussain, M. A., Wani, J. G., & Ahmed, J. (2014). Low hemoglobin level a risk factor for acute lower respiratory tract infections (ALRTI) in children. Journal of clinical and diagnostic research: JCDR, 8(4), PC01
Smith, K. R., Samet, J. M., Romieu, I., & Bruce, N. (2000). Indoor air pollution in developing countries and acute lower respiratory infections in children. Thorax, 55(6), 518–532
Taksande, A. M., & Yeole, M. (2015). Risk factors of Acute Respiratory Infection (ARI) in under-fives in a rural hospital of Central India.Journal of Pediatric and Neonatal Individualized Medicine (JPNIM), 5(1), e050105
Tazinya, A. A., Halle-Ekane, G. E., Mbuagbaw, L. T., Abanda, M., Atashili, J., & Obama, M. T. (2018). Risk factors for acute respiratory infections in children under five years attending the Bamenda Regional Hospital in Cameroon. BMC pulmonary medicine, 18(1), 7
Team, R. C. (2019). R: a language and environment for statistical computing (version 3.5. 3)[software]. In
Troeger, C., Blacker, B. F., Khalil, I. A., Rao, P. C., Cao, S., Zimsen, S. R., & Abebe, Z. (2018). Estimates of the global, regional, and national morbidity, mortality, and aetiologies of diarrhoea in 195 countries: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. The Lancet Infectious Diseases, 18(11), 1211–1228
Tupasi, T. E., Velmonte, M. A., Sanvictores, M. E. G., Abraham, L., De Leon, L. E., Tan, S. A., & Saniel, M. C. (1988). Determinants of morbidity and mortality due to acute respiratory infections: implications for intervention. Journal of Infectious Diseases, 157(4), 615–623
Vashishtha, V. M. (2010). Current status of tuberculosis and acute respiratory infections in India: much more needs to be done!. Indian pediatrics, 47(1), 88–89
Walker, C. L. F., Rudan, I., Liu, L., Nair, H., Theodoratou, E., Bhutta, Z. A., & Black, R. E. (2013). Global burden of childhood pneumonia and diarrhoea. The Lancet, 381(9875), 1405–1416
Zou, D., Lloyd, J. E., & Baumbusch, J. L. (2020). Using SPSS to analyze complex survey data: a primer. Journal of Modern Applied Statistical Methods, 18(1), 16
Funding
Open Access funding enabled and organized by CAUL and its Member Institutions
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Md Masud Hasan and Kamal Kumar Saha conceptualized the study. Md Masud Hasan, Kamal Kumar Saha, Rossita Mohamad Yunus and Khorshed Alam performed the data analysis and interpretation. All authors contributed to the writing of the paper and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
Ethics approval is not required for the study as it used secondary data from the National Family Health Survey in India. There is no identifiable information of individuals in the data.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Hasan, M.M., Saha, K.K., Yunus, R.M. et al. Prevalence of acute respiratory infections among children in India: Regional inequalities and risk factors. Matern Child Health J 26, 1594–1602 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10995-022-03424-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10995-022-03424-3