Abstract
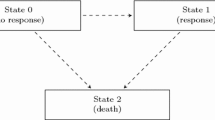
In this article we introduce a general approach to dynamic path analysis. This is an extension of classical path analysis to the situation where variables may be time-dependent and where the outcome of main interest is a stochastic process. In particular we will focus on the survival and event history analysis setting where the main outcome is a counting process. Our approach will be especially fruitful for analyzing event history data with internal time-dependent covariates, where an ordinary regression analysis may fail. The approach enables us to describe how the effect of a fixed covariate partly is working directly and partly indirectly through internal time-dependent covariates. For the sequence of times of event, we define a sequence of path analysis models. At each time of an event, ordinary linear regression is used to estimate the relation between the covariates, while the additive hazard model is used for the regression of the counting process on the covariates. The methodology is illustrated using data from a randomized trial on survival for patients with liver cirrhosis.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aalen OO (1980) A model for nonparametric regression analysis of counting processes. Springer Lect Notes Stat 2:1–25
Aalen OO (1987) Dynamic modelling and causality. Scand Actuarial J 12:177–190
Aalen OO (1989) A linear regression model for the analysis of life times. Stat Med 8:907–925
Aalen OO, Fosen J, Wedon-Fekjær H, Borgan Ø, Husebye E (2004) Dynamic analysis of multivariate failure time data. Biometrics 60:764–773
Andersen PK, Borgan Ø, Gill RD, Keiding N (1993) Statistical models based on counting processes. Springer-Verlag
Andersen PK, Liestøl K (2003) Attenuation caused by infrequently updated covariates in survival analysis. Biostatistics 4:633–649
Cleveland WS (1979) Robust locally weighted regression and smoothing scatterplots. J Am Stat Assoc 74:829–836
Cox DR, Wermuth N (1996) Multivariate dependencies. Chapman & Hall
Didelez V (2000) Graphical models for event history data based on local independence. PhD thesis, Universität Dortmund, Germany
Edwards D (2000) Introduction to graphical modelling, 2nd edn. Springer-Verlag
Efron B (1981) Censored data and the bootstrap. J Am Stat Assoc 76:312–319
Fosen J, Borgan Ø, Weedon-Fekjær H, Aalen OO (2006) Dynamic analysis of recurrent event data using the additive hazard model. Biometrical J, DOI: 10.1002/bimj.200510217
Hastie T, Tibshirani R, Friedman J (2001) The elements of statistical learning - data mining, inference and prediction. Springer-Verlag
Hesslow G (1976) Discussion: two notes on the probabilistic approach to causality. Philos Sci 43:290–292
Kalbfleisch J, Prentice RL (2002) The statistical analysis of failure time data, 2nd edn. Wiley
Lauritzen S (1996) Graphical models. Oxford University Press
Loehlin JC (2004) Latent variable models: an introduction to factor, path, and structural analysis, 4th edn. Lawrence Erlbaum, Hillsdale, NJ
Pearl J (2001) Direct and indirect effects. In: Breese J, Koller D (eds) Proceedings of the seventeenth conference on uncertainty in artificial intelligence. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, San Francisco, pp 411–420
Wright S (1921) Correlation and causation. J Agr Res 20:557–585
Wright S (1934) The method of path coefficients. Ann Math Stat 5:161–215
Acknowledgement
Fosen was sponsored by The Norwegian Cancer Society and Ferkingstad was supported by The National Programme for Research in Functional Genomics in Norway (FUGE) from The Research Council of Norway. Parts of the work on this project was done while Aalen, Borgan and Fosen were working at the Centre for Advanced study at the Norwegian Academy of Science and Letters.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fosen, J., Ferkingstad, E., Borgan, Ø. et al. Dynamic path analysis—a new approach to analyzing time-dependent covariates. Lifetime Data Anal 12, 143–167 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10985-006-9004-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10985-006-9004-2