Abstract
Non-Darcy resistance in peristaltic transport of Sutterby liquid in curved configuration is modeled. Variable characteristics of material (i.e., thermal conductivity and viscosity) are taken as temperature-dependent. Soret and Dufour features have also been retained. Problem is modeled by using conservation laws. Long wavelength and small Reynolds number have been invoked. Resulting problems have been solved numerically. Entropy optimization analysis is made. Axial velocity, temperature, concentration, entropy, Bejan number and heat transfer rate are examined for influential variables. It is found that velocity increases for variable viscosity coefficient and porous-space parameter. Temperature decreases for increased values of variable thermal conductivity. Opposite behavior of mass and energy is noted for Soret and Dufour parameters. Entropy minimized for thermal conductivity and viscosity coefficients. Entropy enhancement is noticed for Soret and Dufour parameters. Heat transfer rate at upper wall is enhanced for Soret and Dufour variables.






















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- W :
-
Velocity
- \( \left( {W_{1} ,W_{2} } \right) \) :
-
Velocity components
- \( v \) :
-
Wave speed
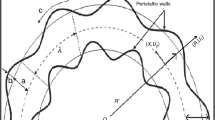
- \( (X,R) \) :
-
Axial and radial coordinates
- \( \left( {O,R^{\prime}} \right) \) :
-
Origin and radius of channel
- f :
-
Wavelength
- \( b_{1} \) :
-
Wave amplitude
- \( T,C \) :
-
Temperature and concentration
- \( \left( {C_{0} ,C_{1} } \right) \) :
-
Concentrations at upper and lower boundaries
- \( \left( {T_{0} ,T_{1} } \right) \) :
-
Temperatures at upper and lower boundaries
- \( \rho \) :
-
Fluid density
- \( c_{\text{p}} \) :
-
Specific heat
- \( D_{\text{B}} \) :
-
Mass diffusion coefficient
- \( c_{\text{s}} \) :
-
Concentration susceptibility
- \( k_{\text{T}} \) :
-
Thermal diffusion ratio
- \( {\varvec{\uptau}} \) :
-
Cauchy stress tensor
- \( \left( {\kappa \left( T \right),\mu \left( T \right)} \right) \) :
-
Thermal conductivity and viscosity as a function of temperature
- \( h \) :
-
Dimensionless peristaltic wall
- \( \delta \) :
-
Wave number
- k :
-
Curvature
- \( \eta \) :
-
Sutterby fluid parameter
- \( \kappa_{0} ,\mu_{0} \) :
-
Constant thermal conductivity and viscosity
- \( \beta^{\prime},\gamma^{\prime} \) :
-
Viscosity and thermal conductivity coefficients
- \( K \) :
-
Permeability parameter
- P :
-
Pressure
- \( Da \) :
-
Permeability parameter (Dimensionless)
- \( \left( {Sr,Du} \right) \) :
-
Soret and Dufour parameters
- \( \psi \) :
-
Stream function
- \( {\mathbf{S}} \) :
-
Extra stress tensor
- t :
-
Time
- \( S_{\text{RR}} ,S_{\text{XR}} ,S_{\text{XX}} \) :
-
Stress components
- \( {\mathbf{q}} \) :
-
Heat flux
- \( N_{\text{s}} \) :
-
Dimensionless entropy
- \( Be \) :
-
Bejan number
References
Latham TW. Fluid motion in a peristaltic pump. MS Thesis. MIT Cambridge, MA. 1966.
Shapiro AH, Jafrin MY, Weinberg SL. Peristaltic pumping with long wavelengths at low Reynolds number. J Fluid Mech. 1969;37:799–825.
Ali N, Sajid M, Javed T, Abbas Z. Heat transfer analysis of peristaltic flow in a curved channel. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2010;53:3319–25.
Riaz A, Khan SU, Zeeshan A, Khan SU, Hassan M, Muhammad T. Thermal analysis of peristaltic flow of nanosized particles within a curved channel with second-order partial slip and porous medium. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09454-9.
Raiz R, Ellahi R, Bhatti MM, Marin M. Study of heat and mass transfer in the Eyring–Powell model of fluid propagating peristaltically through a rectangular compliant channel. Heat Transf Res. 2019;50:1539–60.
Narla VK, Tripathi D, Bég OA. Analysis of entropy generation in biomimetic electroosmotic nanofluid pumping through a curved channel with Joule dissipation. Therm Sci Eng Prog. 2020;15:100424.
Hayat T, Alsaadi F, Rafiq M, Ahmad B. On effects of thermal radiation and radial magnetic field for peristalsis of Sutterby liquid in a curved channel with wall properties. Chin J Phys. 2017;55:2005–24.
Bhatti MM, Rashidi MM. Study of heat and mass transfer with Joule heating on magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) peristaltic blood flow under the influence of Hall effect. Propuls Power Res. 2017;6:177–85.
Sinha A, Shit GC, Ranjit NK. Peristaltic transport of MHD flow and heat transfer in an asymmetric channel: effects of variable viscosity, velocity-slip and temperature jump. Alex Eng J. 2015;54:691–704.
Reddy MG. Heat and mass transfer on magnetohydrodynamic peristaltic flow in a porous medium with partial slip. Alex Eng J. 2016;55:1225–34.
Khan I, Khan WA. Effect of viscous dissipation on MHD water-Cu and EG–Cu nanofluids flowing through a porous medium. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;135:645–56.
Mekheimer KS, Salem AM, Zaher AZ. Peristaltically induced MHD slip flow in a porous medium due to a surface acoustic wavy wall. J Egypt Math Soc. 2014;22:143–51.
Khan LA, Raza M, Mir NA, Ellahi R. Effects of different shapes of nanoparticles on peristaltic flow of MHD nanofluids filled in an asymmetric channel. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2020;140:879–90.
Raza M, Ellahi R, Sait SM, Sarafraz MM, Shadloo MS, Waheed I. Enhancement of heat transfer in peristaltic flow in a permeable channel under induced magnetic field using different CNTs. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2020;140:1277–97.
Awais M, Bilal S, Malik MY. Numerical analysis of magnetohydrodynamic Navier’s slip visco nanofluid flow induced by rotating disk with heat source/sink. Commun Theor Phys. 2019;71:1075–83.
Rehman KU, Malik MY, Zahri M, Al-Mdallal QM, Jameel M, Khan MI. Finite element technique for the analysis of buoyantly convective multiply connected domain as a trapezium enclosure with heated circular obstacle. J Mol Liq. 2019;286(1–10):110892.
Alderremy AA, Nazira U, Saleem S, Nawaz M, Sadiq MA. Study of transport phenomenon in Carreau fluid using Cattaneo-Christov heat flux model with temperature dependent diffusion coefficients. Phys A Stat Mech Appl. 2020;554:123921.
Awais M, Bilal S, Ur Rehman K, Malik MY. Numerical investigation of MHD Prandtl melted fluid flow towards a cylindrical surface: comprehensive outcomes. Can J Phys. 2020;98:223–32.
Rashid M, Ansar K, Nadeem S. Effects of induced magnetic field for peristaltic flow of Williamson fluid in a curved channel. Phys A Stat Mech Appl. 2020;553:123979.
Eldabe NT, El-Sayed MF, Ghaly AY, Sayed HM. Mixed convective heat and mass transfer in a non-Newtonian fluid at a peristaltic surface with temperature-dependent viscosity. J Arch Appl Mech. 2008;78:599–624.
Bibi F, Hayat T, Farooq S, Khan AA, Alsaedi A. Entropy generation analysis in peristaltic motion of Sisko material with variable viscosity and thermal conductivity. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-09125-4.
Ramesh K. Influence of heat and mass transfer on peristaltic flow of a couple stress fluid through porous medium in the presence of inclined magnetic field in an inclined asymmetric channel. J Mol Liq. 2016;219:256–71.
Sadiq MA, Hayat T. Darcy–Forchheimer stretched flow of MHD Maxwell material with heterogeneous and homogeneous reactions. Neural Comput Appl. 2019;31:857–64.
Bejan A. Second law analysis in heat transfer. Energy. 1980;5:720–32.
Bejan A. Entropy generation minimization: the method of thermodynamic optimization of finite-size systems and finite-time processes. New York: CRC Press; 2013. p. 1996.
Erbay LB, Altaç Z, Sülüş B. Entropy generation in a square enclosure with partial heating from a vertical lateral wall. Heat Mass Transf. 2004;40:909–18.
Souidi F, Ayachi K, Benyahia N. Entropy generation rate for a peristaltic pump. J Non-Eqm Therms. 2009;34:171–94.
Sheikholeslami M, Jafaryar M, Shafee A, Li Z. Nanofluid heat transfer and entropy generation through a heat exchanger considering a new turbulator and CuO nanoparticles. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018;134:2295–303.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hayat, T., Bibi, F., Khan, A.A. et al. Entropy production minimization and non-Darcy resistance within wavy motion of Sutterby liquid subject to variable physical characteristics. J Therm Anal Calorim 143, 2215–2225 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-10007-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-10007-3