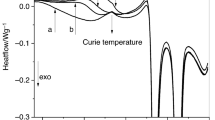
Abstract
The most extensively studied Heusler alloys are those based on the Ni–Mn–Ga system. However, to overcome the high cost of Gallium and the generally low martensitic transformation temperature, the search for Ga-free alloys has been recently attempted, particularly, by introducing In, Sn or Sb. In this work, two shape memory alloys, Mn50Ni50−xInx (x = 7.5 and 10), were obtained by rapid solidification. We outline their structural and thermal behaviour. The structural austenite–martensite transformation was checked by calorimetry. The transformation temperatures decrease as In content increases. The same pattern is reflected in entropy and enthalpy changes linked to transformation. The control of the valence electron by atom (e/a) determines the transformation temperatures range in this kind of alloys, and it is possible to develop alloys that can be candidates in applications such as sensors and actuators. In addition, X-ray diffraction was performed to verify the crystalline structure at room temperature.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ullakko K, Huang JK, Kantner C, O’Handley RC, Kokorin VV. Large magnetic-field-induced strains in Ni2Mn Ga single crystals. J Appl Phys Lett. 1996;69:1966–8.
Krenke T, Duman E, Acet M, Wassermann EF, Moya X, Mañosa L, et al. Magnetic superelasticity and inverse magnetocaloric effect in Ni–Mn–In. Phys Rev B. 2007;7575:104414.
Pons J, Chernenko VA, Santamarta R, Cesari E. Crystal structure of martensitic phases in Ni–Mn–Ga shape memory alloys. Acta Mater. 2000;48:3027–38.
Koike K, Ohtsuka M, Honda Y, Katsuyama H, Matsumoto M, Itagaki KJ. Magnetoresistance of Ni–Mn–Ga–Fe ferromagnetic shape memory films. Magn Magn Mater. 2007;310:996–8.
Marioni MA, O’Handley ROC, Allen SM, Hall SR, Paul DJ, Richard ML, et al. The ferromagnetic shape–memory effect in Ni–Mn–Ga. J Magn Magn Mater. 2005;290:35–41.
Sánchez-Llamazares JL, Sánchez T, Santos JD, Perez MJ, Sánchez ML, Hernando B, et al. Martensitic phase transformation in rapidly solidified Mn50Ni40In10 alloy ribbons. Appl Phys Lett. 2008;92:012513.
Santos JD, Sánchez T, Alvarez P, Sánchez ML, Sánchez-Llamazares JL, Hernando B, et al. Microstructure and magnetic properties of Ni50Mn37Sn13 Heusler alloy ribbons. J Appl Phys. 2008;103:07B326.
Sánchez Llamazares JL, Hernando B, García C, González J, Escoda L, Suñol JJ. Martensitic transformation in Ni50.4Mn34.9In14.7 melt spun ribbons. J Phys D Appl Phys. 2008;42:045002.
Lutterotti L. Maud: A Rietveld analysis program designed for the internet and experiment integration. Acta Cryst. 2000;A56:s54.
Petricek V, Dusek M. The crystallographic computing system. Praha: Institute of Physics; 2000.
Chernenko VA, Cesari E, Pons J, Seguí C. Phase transformations in rapidly quenched Ni–Mn–Ga alloys. J Mater Res. 2000;15:1496–504.
Zheng HX, Xia MX, Liu J, Li JG. Martensitic transformation of highly undercooled Ni–Fe–Ga magnetic shape memory alloys. J Alloy Compd. 2004;385:144.
Zheng HX, Liu J, Xia MX, Li JG. Martensitic transformation of Ni–Fe–Ga magnetic shape memory alloys. J Alloy Compd. 2005;387:265.
Kaufman L, Hullert M. Thermodynamics of martensite transformation. In: Olson GB, Owen WS, editors. martensite. Cambridge: ASM International; 1992. p. 41–58.
Krenke T, Acet M, Wassermann EF, Moya X, Mañosa L, Planes A. Ferromagnetism in the austenitic and martensitic states of Ni–Mn–In alloys. Phys Rev B. 2006;73:174413.
Krenke T, Acet M, Wassermann EF, Moya X, Mañosa L, Planes A. Martensitic transitions and the nature of ferromagnetism in the austenitic and martensitic states of Ni–Mn–Sn alloys. Phys Rev B. 2005;72:014412.
Liu ZH, Wu ZG, Yang H, Liu YN, Liu EK, Zhang HW. WU GH. Thermal and stress-induced martensitic transformations in quaternary Ni50Mn37(In, Sb)(13) ferromagnetic shape memory alloys. J Intermet. 2010;18:1690–4.
Khovailo VV, Oikawa K, Abe T, Tagaki T. Entropy change at the martensitic transformation in ferromagnetic shape memory alloys Ni2+xMn1−xGa. J Appl Phys. 2003;93:8483–5.
Krenke T, Acet M, Wassermann FE, Moya X, Mañosa L, Planes A. Ferromagnetism in the austenitic and martensitic states of Ni–Mn–In alloys. Phys Rev B. 2006;73:174413.
Coll R, Escoda L, Saurina J, Sanchez-Llamazares JL, Hernaudo B, Sunol JJ. Martensitic transformation in Mn–Ni–Sn Heusler alloys. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2010;99:905–9.
Chernenko VAJ. Composition instability of a phase in Ni–Mn–Ga alloys. J Sci Mater. 1999;40:523–7.
Safaa NS, Hamzah E, Abubakar T, Zamri M, Tanemura M. Influence of Ti additions on the martensitic phase transformation and mechanical properties of Cu–Al–Ni shape memory alloys. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2014;118:111–22.
Kök M, Yakinci ZD, Aydogdu A, Aydogdu Y. Thermal and magnetic properties of Ni51Mn28.5Ga19.5B magnetic-shape-memory alloy. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2014;115:555–9.
Yildiz K, Kok M. Study of martensite transformation and microstructural evolution of Cu–Al–Ni–Fe shape memory alloys. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2014;115:1509–14.
Kök M, Aydoğdu Y. Effect of composition on the thermal behavior of NiMnGa alloys. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2013;113:859–63.
Adorno AT, Silva RAG. Effect of Ag additions on the reverse martensitic transformation in the Cu-10 mass% al alloy. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2006;83:241–6.
Kreissl M, Neumann KU, Stephens T, Ziebeck KRA. The influence of atomic order on the magnetic and structural properties of the ferromagnetic shape memory compound Ni2MnGa. J Phys Condens Matter. 2003;15:3831–9.
Tsuchiya K, Ohtoyo D, Umemoto M, Ohtsuka H. Effect of isothermal aging on martensitic transformation in Ni–Mn–Ga alloys. Trans Mater Res Soc Jpn. 2000;25:521–3.
Besseghini S, Pasquale M, Passaretti F, Sciacca A, Villa E. NiMnGa polycrystalline magnetically activated shape memory alloy: A calorimetric investigation. Scripta Mater. 2001;44:2681–7.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the Tunisian National Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research and the Spanish Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research. This research was supported by the projects AP/039058/11, MAT2009-13108-C02-02 and 2014SGR1180.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bachaga, T., Daly, R., Escoda, L. et al. Influence of chemical composition on martensitic transformation of MnNiIn shape memory alloys. J Therm Anal Calorim 122, 167–173 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-015-4716-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-015-4716-8