Abstract
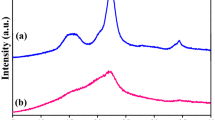
Activated carbon with high surface area was prepared from sodium salt of carboxyl methyl cellulose by physical activation at 400 °C followed by treatment in boiling water. The carbon was characterized by XRD, SEM, EPR, TG, IR, surface areas and porosity measurements. The carbon showed alkaline reaction in aqueous solution. It showed high surface area and pore volume in comparison to two commercially available carbons.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Serp P, Figueiredo JL. Carbon materials for catalysis. Hoboken: John Wiley and Sons; 2009. ISBN 978-0-470-17885-0.
Figueiredo JL, Pereira MFR, Freitas MMA, Órfão JJM. Modification of the surface active sites on carbon catalysts. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2007;46:4110–5.
Job N, Pirard R, Marien J, Pirard JP. Porous carbon xerogels with texture tailored by pH control during sol-gel process. Carbon. 2004;42:619–24.
Samant PV, Gonçalves F, Freitas MMA, Pereira MFR, Figueiredo JL. Surface activation of a polymer based carbon. Carbon. 2004;42:1321–5.
Samant PV, Rangel CM, Romero MH, Fernandes JB, Figueiredo JL. Carbon supports for methanol oxidation catalyst. J Power Sour. 2005;151:79–84.
Samant PV, Fernandes JB, Rangel CM, Figueiredo JL. Carbon xerogel supported Pt and Pt–Ni catalysts for electro-oxidation of methanol in basic medium. Catal Today. 2005;102–103:173–6.
Rengaraj S, Arabindo B, Murupesam V. Preparation, characterization of activated carbons, from agricultural wastes. Indian J Chem Technol. 1999;6:1–4.
Singh DK. Basic dyes removal from waste water by adsorption on rice husk carbon. Indian J Chem Technol. 2001;8:133–9.
Saxena RK, Kum AK. Effect of heating rate on the char yield and pore structure of chars prepared from viscose rayon cloth. Indian J Chem Technol. 2001;8:149–52.
Toles CA, Marshall WE, Johns MM. Surface functional groups on acid-activated nut shell carbons. Carbon. 1999;37:1207–14.
Bansal RC, Donnet JB, Stoecki F. Active carbons. New York: Marcel Dekker; 1988.
Shen W, Li Z, Liu Y. Surface chemical functional groups modification of carbon recent patents in chemical engineering, vol. 1. 2008. pp 27–40.
McEnancy B, Devaston N. Carbon, vol. 13. 1975. p. 515.
McCrae PD, Zhang T, Walker DRB. Shaped activated carbon. US Patent No. 6472343. http://www.freepatentsonline.com/6472343.html.
Wang Q, Cao F, Chen Q, Chen C. Preparation of carbon micro-spheres by hydrothermal treatment of methylcellulose sol. Mater Lett. 2005;59:3738–41.
Nabais JMV, Carrot PJM. Chemical characterization of activated carbon fibres and activated carbons. J Chem Edu. 2006;83:436–8.
Smisek M, Cerny D. Active carbons, manufacture, properties, and applications. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 1970.
Mackay DM, Devaston N. Carbon, vol. 20. 1982. p. 95.
Rand B, Marsh H. The process of activation of carbons by gasification with CO2. Carbon. 1971;9:79.
Fanning PF, Vannice MA. Carbon, vol. 31., Physicochemical properties of carbon materials obtained by combustion synthesis 1993. p. 721–30.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to UGC-SAP (F.540/25/DRS/2007/(SAP-II, New Delhi, 2008) for the financial support received for this investigation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martins, S., Fernandes, J.B. A simple method to prepare high surface area activated carbon from carboxyl methyl cellulose by low temperature physical activation. J Therm Anal Calorim 112, 1007–1011 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-012-2819-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-012-2819-z