Abstract
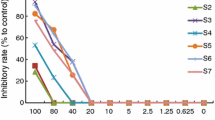
The power–time curves of mice splenic lymphocytes growth at 37 °C affected by ginsenoside Rh2 were determined by microcalorimetry using a 3114/3236 TAM air bioactivity monitor with ampoule mode. Then, the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of Rh2 on splenic lymphocytes growth was determined by serial dilution method. From factor analysis (FA) on six quantitative thermokinetic parameters from the power–time curves, the activity of Rh2 on splenic lymphocytes could be quickly evaluated by analyzing the changes in the two main parameters: growth rate constant k, and maximum heat-output power, P m. The results showed that Rh2 had strong inhibitory activity on splenic lymphocytes growth, and this inhibitory activity was strengthened with increasing concentration of Rh2 in the concentration range of 1.0–32.0 μg mL−1. This strong inhibitory also could be confirmed from the MIC of 50.0 μg mL−1 of Rh2 on splenic lymphocytes growth in RPMI-1640 culture medium. This study illustrated that microcalorimetry could not only offer a useful method for evaluating the activity of drugs, but also serve as a quantitative, sensitive, and simple analytic tool for the evaluation of drugs on cell growth.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim SN, Ha YW, Shin H, Son SH, Wu SJ, Kim YS. Simultaneous quantification of 14 ginsenosides in Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer (Korean red ginseng) by HPLC–ELSD and its application to quality control. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2007;45:164–70.
Park JD, Rhee DK, Lee YH. Biological activities and chemistry of saponins from Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer. Phytochem Rev. 2005;4:159–75.
Nah SY, Bhatia KS, Lyles J, Ellinwood EH, Lee TH. Effects of ginseng saponin on acute cocaine-induced alterations in evoked dopamine release and uptake in rat brain nucleus accumbens. Brain Res. 2009;1248:184–90.
Ham YM, Chun KH, Choi JS, Kim DH, Lee SK. SEK1-dependent JNK1 activation prolongs cell survival during G-Rh2-induced apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003;304:358–64.
Fei XF, Wang BX, Tashiro S, Li TJ, Ma JS, Ikejima T. Apoptotic effects of ginsenoside Rh2 on human malignant melanoma A375-S2 cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2002;23:315–22.
Cheng CC, Yang SM, Huang CY, Chen JC, Chang WM, Hsu SL. Molecular mechanisms of Ginsenoside Rh2-mediated G1 growth arrest and apoptosis in human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2005;55:531–40.
Wadsö I. Characterization of microbial activity in soil by use of isothermal microcalorimetry. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2009;95:843–50.
Kong WJ, Li ZL, Xiao XH, Zhao YL, Zhang P. Activity of berberine on Shigella dysenteriae investigated by microcalorimetry and multivariate analysis. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2010;102:33–6.
Afzal AB, Akhtar MJ, Svensson LG. Thermal studies of DBSA-doped polyaniline/PVC blends by isothermal microcalorimetry. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2010;100:1017–25.
Zhao YL, Yan D, Wang JB, Zhang P, Xiao XH. Anti-fungal effect of berberine on Candida albicans by microcalorimetry with correspondence analysis. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2010;102:49–55.
Zhao H, Bennici S, Shen J, Auroux A. Calorimetric study of the acidic character of V2O5–TiO2/SO4 2− catalysts used in methanol oxidation to dimethoxymethane. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2010;99:843–7.
Bellavia G, Cordone L, Cupane A. Calorimetric study of myoglobin embedded in trehalose-water matrixes. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2009;95:699–702.
Wang J, Cheng DH, Zeng N, Xia HL, Fu Y, Yan D, Zhao YL, Xiao XH. Application of microcalorimetry and principal component analysis. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2010;102:137–42.
Barros N, Salgado J, Rodrŕguez-Añón JA, Proupŕn J, Villanueva M, Hansen LD. Calorimetric approach to metabolic carbon conversion efficiency in soils. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2010;99:771–7.
Yang LN, Sun LX, Xu F, Zhang J, Zhao JN, Zhao ZB, Song CG, Wu RH, Ozao R. Inhibitory study of two cephalosporins on E. coli by microcalorimetry. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2010;100:589–92.
Li X, Zhang T, Min XM, Liu P. Toxicity of aromatic compounds to Tetrahymena estimated by microcalorimetry, QSAR. Aquat Toxicol. 2010;98:322–7.
Zhao YL, Wang JB, Zhang P, Li RS, Xiao XH. Microcalorimetric study of the opposing effects of ginsenosides Rg1 and Rb1 on the growth of mice splenic lymphocytes. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2010. doi:10.1007/s10973-010-1003-6.
Tetteh J, Mader KT, Andanson JM, McAuley WJ, Lane ME, Hadgraft J, Kazarian SG, Mitchell JC. Local examination of skin diffusion using FTIR spectroscopic imaging and multivariate target factor analysis. Anal Chim Acta. 2009;642:246–56.
Popovich DG, Kitts DD. Structure-function relationship exists for ginsenosides in reducing cell proliferation and inducing apoptosis in the human leukemia (THP-1) cell line. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2002;406:1–8.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Foundation of National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2007CB512607) and the National Nature Science Foundation (No. 30772740).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Y., Wang, J., Shan, L. et al. Activity of ginsenoside Rh2 on the growth of mice splenic lymphocytes investigated by microcalorimetry and factor analysis. J Therm Anal Calorim 105, 1037–1041 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-010-1146-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-010-1146-5