Abstract
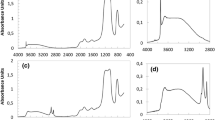
Three samples of silicon dioxide were syhthesized and their surface areas were measured. A thermo-chemical cycle was designed to calculate the molar formation enthalpy. The molar formation enthalpy, Δf H Φm , for three amorphous silica with the Langmuir surface area 198.0854, 25.1108 and 11.9821 m2 g−1 gave −895.52, −910.86 and −915.67 kJ mol−1, respectively. With the increasing surface area, the values of Δf H Φm increased accordingly.
The results suggest that the silica with larger surface area is more unstable. The wetting heat was also measured by adding the silica powder into water. With the rehydration of the more SiOH groups on the surface, the larger surface areas of silica lead to the more wetting heat. A smaller particle has the more unstable hydroxyl groups and surface energy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. C. F. K. Fung and M. F. Burke, J. Chromatogr. A, 752 (1996) 41.
K. Ishikiriyama and M. Todoki, Thermochim. Acta, 256 (1995) 213.
P. Mack, R. G. White, J. Wolstenholme and T. Conard, Appl. Surf. Sci., 252 (2006) 8270.
K. Wu, T. C. Bailey, C. G. Willson and J. G. Ekerdt, Langmuir, 21 (2005) 11795.
C. Di Franco, N. Cioffi, N. Ditaranto, M. S. Vitiello, M. Sibilano, L. Torsi and G. Scamarcio, Thin Solid Films, 515 (2007) 7195.
S. S. Qu, T. Z. Wang, Y. Liu, D. C. Wen, Y. Yu, L. W. Li and Q. G. Li, Thermochim, Acta, 381 (2002) 61.
H. G. Yu, Y. Liu, Z. C. Tan, J. X. Dong, T. Z. Zou, X. M. Huang and S. S. Qu, Thermochim. Acta, 401 (2003) 217.
Y. Xu, Y. F. Zhou and P. Liu, General Chem. Eng., Chemical Industry Press, Beijing 2007.
P. Gilli, V. Ferretti and G. Gilli, J. Phys. Chem., 98 (1994) 1515.
Y. N. Nkolo Meze’e, J. Noah Ngamveng and S. Bardet, Thermochim. Acta, 468 (2008) 1.
G. Curthoys, V. Y. Davydov and A. V. Kiselev, S. A. Kiselev and B. V. Kusnetsov, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 48 (1974) 58.
R. Mueller, H. K. Kammler, K. Wegner and S. E. Pratsinis, Langmuir, 19 (2003) 160.
S. Shioji, M. Hanada, Y. Hayashi, K. Tokami and H. Yamamoto, Adv. Powder Technol., 18 (2007) 467.
G. Rezaei Behbehani and A. A. Saboury, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 89 (2007) 857.
M. Day, A. Victoria Nawaby and X. Liao, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 86 (2006) 623.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, L., Qisui, W., Xi, L. et al. The molar formation enthalpy of nano-SiO2 with different surface area. J Therm Anal Calorim 95, 667–670 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-008-9325-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-008-9325-3