Abstract
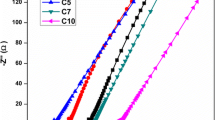
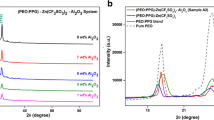
Nano-composite polymer electrolyte (NCPE), poly(vinylidenefluoride-hexafluoropropylene)-poly(methylmethacrylate) grafted natural rubber with lithium tetrafluoroborate and zirconia (PVdF-HFP/MG49-LiBF4-ZrO2) was prepared by a facile one-pot in situ sol–gel method. The influence of zirconia nano-fillers on the electrochemical, chemical and structural properties of polymer electrolyte was investigated. The interaction of polymer electrolyte and zirconia was explored via density functional theory (DFT). Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy study showed that the optimum ionic conductivity is 2.39 × 10−3 S cm−1 (6 wt% zirconia). X-ray diffractogram results revealed a decreasing trend of crystalline phases and no lithium salt peaks were observed upon the addition of zirconia. As a result, the LiBF4 salt was well-solvated in the polymer matrix with a one-fold increase in lithium transference number. Remarkably, a good electrochemical stability was achieved at 6.9 V from a linear sweep voltammetry (LSV) analysis. Observations from the infrared spectra indicate that chemical interactions occurred at the carbonyl and fluoride functional groups and is further corroborated by DFT studies. Micrograph images showed that the zirconia nano-particles were successfully produced (7–15 nm). The nanocomposite polymer electrolyte possesses promising charge/discharge performance and has the potential to be applied in lithium-ion polymer battery.

The high electrochemical stability and flexible nanocomposite for lithium ion polymer battery application.
Highlights
-
The sizes of ZrO2 nano-particles are in the range of 7–15 nm.
-
High ionic conductivity (2.39 × 10−3 S cm−1) and electrochemical stability (6.9 V) was achieved for the nanocomposite polymer electrolyte sample.
-
Nano-particle zirconia improved the lithium transference number by a fold from 0.103 to 0.216.
-
The nanocomposite polymer electrolyte was able to maintain a good ionic conductivity (~10−5 S cm−1) at a high temperature of 200 °C.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guangming Z, Feng L, Huiming C (2014) Progress in flexible lithium batteries and future prospects. Energy Environ Sci 4:1307–1338
Da QL, Chao YX, Xiao MX, Chun XZ, Ke SX, Xiaon QC, Shi BQ (2016) Sol–gel preparation of Li rich layered cathode material for lithioum ion battery with polymer polyacrylic acid+citric acid chelators. J Sol–Gel Sci Technol 78:403–410
Hyunhyub K, Rehan K, Kuniharu T, Toshitake T, Xiaobo Z, Ali J (2012) Multifunctional, flexible electronic systems based on engineering nanostructured materials. Nanotechnology 23:344001
Dae-Hyeong K, Jonathan V, Jason JA, Jianliang X, Leif V, Yun-Soung K, Justin AB, Bruce P, Eric SF, Diego C, David LK, Fiorenzo GO, Yonggang H, Keh-Chih H, Mitchell RZ, Brian L, John AR (2010) Dissolvable films of silk fibroin for ultrathin conformal bio-integrated electronics. Nat Mater 9(6):511–517
Razali I, Glasse MD, Latham RJ, Linford RG, Schlindwein WS (2001) Polymer electrolyes based on modified natural rubber for use in rechargeable lithium. Batter J Power Sources 94:206–211
TianKhoon L, Hassan NH, Rahman MYA, Vedarajan R, Matsumi N, Ahmad A (2015) One-pot synthesis nano-hybrid ZrO2–TiO2 fillers in 49% poly (methyl methacrylate) grafted natural rubber (MG49) based nano-composite polymer electrolyte for lithium ion battery application. Solid State Ion 276:72–79
Lee TK, Siti A, Azizan A, Dahlan HM, Rahman MYA (2012) Temperature dependence of conductivity of plasticized poly (vinyl chloride)-low molecular weight liquid 50% epoxidized natural rubber solid polymer electrolyte. J Solid State Electrochem 16:2251–2260
Ferraria S, Quartaronea E, Mustarellia P, Magistrisa A, Fagnonib M, Prottib S, Gerbaldic AC (2010) Ion conducting PVdF-HFP composite gel electrolytes based on N-methoxyethyl-N-methylpyrrolidinium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)-imide ionic liquid. J Power Sources 195:559–566
Kuo CW, Huang CW, Chen BK, Li WB, Chen PR, Ho TH, Tseng CG, Wu TY (2013) Enhanced ionic conductivity in PAN–PEGME-LiClO4-PC composite polymer electrolytes. Int J Electrochem Sci 8:3834–3850
HyeKil E, HoChoi K, JeongHa H, Xu S, Rogers JA, RiKim M, GiLee Y, ManKim K, YoungCho K, YoungLee S (2013) Imprintable, bendable, and shape-conformable polymer electrolytes for versatile-shaped lithium-ion batteries. Mater 25:1395–1400
Vickraman P, Ramamurthy S (2006) A study on the blending effect of PVDF in the ionic transport mechanism of plasticized PVC-LiBF4 polymer electrolyte. Mater Lett 60:3431–3436
Yap YL, You AH, Teo LL, Hanapei H (2013) Inorganic filler sizes effect on ionic conductivity in polyethylene oxide (PEO) composite polymer electrolyte. Int J Electrochem Sci 8:2154–2163
Kedi C, Haijing J, Weihua P (2014) Comparative investigation of organic solution and ionic liquid as electrolyte under lithium-air battery. Int J Electrochem Sci 9:390–397
Tan C, Hackenberg K, Qiang F, Ajayan PM, Ardebili H (2012) High ion conducting polymer nanocomposite electrolytes using hybrid nanofillers. Nano Lett 3:1152–1156
Johnson P, Jacobsson P (2004) TiO2 nano particles in the polymer electrolytes: surface interactions. Solid State Ion 170:73–78
Chung SH, Wang Y, Persi L (2001) Enhancement of the ion transport in polymer electrolytes by addition of nanoscale inorganic oxides. J Power Sources 98:644–648
Croce F, Appetecchi GB, Persi L, Scrosati B (1998) Nanocomposite polymer electrolytes for lithium batteries. Nature 294:456–458
Kühnel RS, Böckenfeld N, Passerini S, Winter M, Balducci A (2011) Mixtures of ionic liquid and organic carbonate as electrolyte with improved safety and performance for rechargeable lithium batteries. Electrochim Acta 56:4092–4099
Xiang HF, Yin B, Wang H, Lin HW, Ge XW, Xie S, Chen CH (2010) Improving electrochemical properties of room temperature ionic liquid (RTIL) based electrolyte for Li-ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 55:5204–5209
GuangSun X, Dai S (2010) Electrochemical investigation of ionic liquid with vinylene carbonate for applications in rechargeable lithium ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 5:4618–4626
Yan C, Zaijun L, Hailang Z, Yinjun F, Xu F, Junkang L (2010) 1-Alkyl-2,3-dimethylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide ionic liquids as highly safe electrolyte for Li/LiFePO4 battery. Electrochim Acta 55:4728–4733
Padbury R, Xiangwu Z (2010) Lithium–oxygen batteries—limiting factors that affect performance. J Power Sources 196:4436–4444
Xiao J, Jianzhi H, Deyu W, Dehong H, Xu W, Graff GL, Zimin N, Liu J, GuangZhang J (2011) Investigation of the rechargeability of Li–O2 batteries in non-aqueous electrolyte. J Power Sources 196:5674–5678
Fernando P, Mariano R, Ricardo F, Álvaro WM (2017) Experimental and theoretical study of ionic pair dissociation in a lithium ion−linear polyethylenimine−polyacrylonitrile blend for solid polymer electrolytes. J Phys Chem B 121:6759–6765
Dan Z, Rui Z, Chuanxiang C, Wu-Aik Y, Junhua K, Guoqiang D, Xuehong L (2013) Non-volatile polymer electrolyte based on poly(propylene carbonate), ionic liquid, and lithium perchlorate for electrochromic devices. J Phys Chem B 117:7783–7789
Miller TF, Wang ZG, Coates GW, Balsara NP (2017) Designing polymer electrolytes for safe and high capacity rechargeable lithium batteries. Acc Chem Res 50:590–593
Rahman MYA, Ahmad A, Lee TK, Farina Y, Dahlan HM (2012) LiClO4 salt concentration effect on the properties of PVC-modified low molecular weight LENR50-based solid polymer electrolyte. J Appl Polym Sci 124:2227–2233
Peng C, Xiaoping L, Jun W, Di Z, Shanmin Y, Weishan W, Wei Z, Xiaowei F, Dequan Y (2017) PEO/PVDF-based gel polymer electrolyte by incorporating nano-TiO2 for electrochromic glass. J Sol–Gel Sci Technol 81:850–858
Zou H, Lin YS (2014) Structural and surface chemical properties of Sol–Gel derived TiO2-ZrO2 oxides. Appl Catal A 265:35–42
Perez-Hernandez R, Mendoza-Anaya D, Fernandez ME, Gomez-Cortes A (2008) Synthesis of mixed ZrO2-TiO2 oxides by Sol–Gel: microstructural characterization and infrared spectroscopy studies of NOx. J Mol Catal A 281:200–206
Manriquez ME, Lopez T, Gomez R, Navarrete J (2004) Preparation of TiO2-ZrO2 mixed oxides with controlled acid-basic properties. J Mol Catal A 220:229–237
Wetjen M, Kim G, Joost M, Winter M, Passerini S (2013) Temperature dependence of electrochemical properties of cross-linked poly(ehtylne oxide) -lithium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl) imide - N-buty l-N-methylprrolidinium bis (trifluoromethanesulfonyl) imide solid polymer electrolytes for lithium batteries. Electrochim Acta 87:779–787
Tyagi B, Sidhpuria K, Shaik B, Jasra RV (2006) Synthesis of nanocrystalline zirconia using Sol–Gel and precipitation techniques. Ind Eng Chem Res 45:8643–8650
Park MS, Ma SB, Lee DJ, Im D, Doo SG, Yamamoto O (2013) Highly reversible lithium metal anode. Sci Rep 4:3815–3822
Becke AD (1988) Density-functional exchange-energy approximation with correct asymptotic behavior. Phys Rev A 38:3098–3100
Becke AD (1993) Density functional thermochemistry III: the role of exact exchange. J Chem Phys 98:5648–5652
Davidson ER, Feller D (1986) Basis set selection for molecular calculations. Chem Rev 86:681–696
Hehre WJ, Radom L, Schleyer PVR, Pople JA (1986) Ab initio molecular orbital theory. Acc Chem Res 9:399–406
Lee C, Yang W, Parr R (1988) Development of the Colle-Salvetti correlation energy formula into a functional of the electron density. Phys Rev B 37:785–789
Croce F, Persi L, Scrosati B, Serraino-Fiory F, Plichta E, Hendrickson MA (2001) Role of the ceramic fillers in enhancing the transport properties of composite polymer electrolytes. Electrochim Acta 46:2457–2461
Croce F, Curini R, Martinelli A, Persi L, Ronci F, Scrosati B, Caminiti R (1999) Physical and chemical properties of nanocomposite polymer electrolytes. J Phys Chem B 103:10632–10638
Puthirath AB, Patra S, Pal S, Manoj M, Balan AP, Jayalekshimi S, Tharangatu NN (2017) Transparent flexible lithium ion conducting solid polymer electrolyte. J Mater Chem A 5:11152–11162
Miyamoto T, Shibayama K (1973) Free-volume model for ionic conductivity in polymers. J Appl Phys 44:5372–5376
Arun KS, Vignesh M, Subramania A (2017) Dimensional stability and electrochemical behaviour of ZrO2 incorporated electrospun PVdF-HFP based nanocomposite polymer membrane electrolyte for Li-ion capacitors. Sci Rep 7:45390–45399
Paneroa S, Scrosati B, Sumathipalaa HH, Wieczorek W (2007) Dual-composite polymer electrolytes with enhanced transport properties. J Power Sources 167:510–514
Xing L, Guohua G, Yindan L, Zeyuan G, Pengliang L, Guangming W (2017) Carbon nanotubes/vanadium oxide composites as cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries. J Sol–Gel Sci Technol 82:224–232
Ying T, Danqing Y, Baojun Z (2018) Synthesis of LiNiPO4 via citrate sol–gel route. J Sol–Gel Sci Technol 87:240–244
Croce F, Persi L, Ronci F, Scrosati B (2000) Nanocomposite polymer electrolytes and their impact on the lithium battery technology. Solid State Ion 135:47–52
Ataollahi N, Ahmad A, Hamzah H, Rahman MYA, Mohamed NS (2012) Preparation and characterization of PVDF-HFP/MG49 based polymer blend electrolyte. Int J Electrochem Sci 7:6693–6703
Wu CG, Lu MI, Tsai CH, Chuang HJ (2006) PVDF-HFP/metal oxide nanocomposite: the matrices for high-conducting, low leakage porous polymer electrolytes. J Power Sources 159:295–300
TianKhoon L, Ataollahi N, Hassan NH, Ahmad A (2016) Studies of porous solid polymeric electrolytes based on poly (vinylidene fluoride) and poly (methyl methacrylate) grafted natural rubber for applications in electrochemical devices. J Solid State Electrochem 20:203–213
Mahmood WAK, Khan MMR, Azarian MH (2013) Sol–gel synthesis and morphology, thermal and optical properties of epoxidized natural rubber/zirconia hybrid films. J Non-Cryst Solids 378:152–157
Chuanglong W, Monica S, James AK, Leon LS (2015) Roles of processing, structural defects and ionic conductivity in the electrochemical performance of Na3MnCO3PO4 cathode material. J Electrochem Soc 162(8):1601–1609
Chuanglong W, Monica S, Satya E, Caihong L, Leon LS (2015) Na3MnCO3PO4—a high capacity, multi-electron transfers redox cathode material for sodium ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 161:322–328
Kim DW, Noh KA, Chun JH, Kim SH, Ko JM (2011) Highly conductive polymer electrolytes supported by microporous membrane. Solid State Ion 144:329–337
Fang S, Zhang Z, Jin Y, Yang L, Hirano S, Tachibana K, Katayama S (2011) New functionalized ionic liquids based on pyrrolidinium and piperidinium cations with two ether groups as electrolytes for lithium battery. J Power Sources 196:5637–5644
Appetecchi GB, Kim GT, Montanino M, Alessandrini F, Passerini S (2011) Room temperature lithium polymer batteries based on ionic liquids. J Power Sources 196:6703–6709
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge National University of Malaysia for the research facilities and sponsoring this project under Modal Insan UKM (MI-2018-002 and MI-2018-012) and INOVASI-2017-011. We would also like to thank UKM and Mr. Patrick Tan Sang Hup from KGC Resources Sdn. Bhd. for providing part of the financial support under INOVASI-2017-011. Special thanks to the Japan Student Services Organization (JASSO) for sponsoring the internship program in Japan. Many thanks to Prof. Hideaki Kasai, Prof. Wilson Agerico Diño and Osaka University, Japan for supporting us with the quantum computational facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khoon, L.T., Fui, ML.W., Hassan, N.H. et al. In situ sol–gel preparation of ZrO2 in nano-composite polymer electrolyte of PVDF-HFP/MG49 for lithium-ion polymer battery. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 90, 665–675 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-019-04936-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-019-04936-1