Abstract
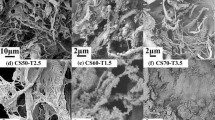
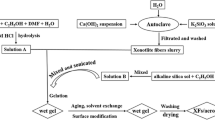
Highly porous and hydrophobic cellulose whiskers–silica aerogel composites were successfully fabricated by a novel co-precursor method based on sol–gel process under ambient pressure drying. Cellulose whiskers were dispersed in the initial sol and were finally inlaid in silica aerogel skeleton by physical combination, which retained the integrality of the aerogel matrix. With the increase of cellulose whiskers content from 0 to 15%, the volume shrinkage of alcogels during drying process decreased from 25.5 to 17.6%, while the porous nano-structure of aerogels were not significantly altered. The potential impact of cellulose whiskers on the thermal conductivity and thermal stability of the prepared composites was investigated. The new composite was intact and white, which exhibited typical properties of 0.137 g cm−3 density, 3.525 cm3 g−1 pore volume, and 139.6° contact angle, respectively. This work explained how the addition of an organic filler into the silica aerogels influenced their properties and provided a technique for silica aerogels to endure and remain monolithic under ambient pressure drying.
Graphical Abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fricke J, Emmerling A (1992) Aerogels. J Am Ceram Soc 75:2027–2036
Schmidt M, Schwertfeger F (1998) Applications for silica aerogel products. J Non Cryst Solids 225:364–368
Aegerter MA, Leventis N, Koebel MM (2011) Aerogels handbook. Springer, New York, NY
Jones SM (2006) Aerogel: space exploration applications. J Solgel Sci Technol 40:351–357
Laskowski J, Milow B, Ratke L (2016) Aerogel-aerogel composites for normal temperature range thermal insulations. J. Non Cryst Solids 441:42–48
Gutzov S, Danchova N, Karakashev SI, Khristov M, Ivanova J, Ulbikas J (2014) Preparation and thermal properties of chemically prepared nanoporous silica aerogels. J Solgel Sci Technol 70:511–516
Amiri TY, Moghaddas J, Khajeh SR (2016) Silica aerogel-supported copper catalyst prepared via ambient pressure drying process. J Solgel Sci Technol 77:627–635
García-González CA, Alnaief M, Smirnova I (2011) Polysaccharide-based aerogels—promising biodegradable carriers for drug delivery systems. Carbohydr Polym 86:1425–1438
Ulker Z, Erkey C (2014) An emerging platform for drug delivery: aerogel based systems. J Control Release 177:51–63
Leventis N, Sotiriou-Leventis C, Zhang GH, Rawashdeh AMM (2002) Nanoengineering strong silica aerogels. Nano Lett 2:957–960
Zhang GH, Dass A, Rawashdeh AMM, Thomas J, Counsil JA, Sotiriou-Leventis C, Fabrizio EF, Ilhan F, Vassilaras P, Scheiman DA, McCorkle L, Palczer A, Johnston JC, Meador MA, Leventis N (2004) Isocyanate-crosslinked silica aerogel monoliths preparation and characterization. J Non Cryst Solids 350:152–164
Katti A, Shimpi N, Roy S, Hb Lu, Fabrizio EF, Dass A, Capadona LA, Leventis N (2006) Chemical, physical, and mechanical characterization of isocyanate cross-linked amine-modified silica aerogels. Chem Mater 18:285–296
Williams JC, Meador MAB, McCorkle L, Mueller C, Wilmoth N (2014) Synthesis and properties of step-growth polyamide aerogels cross-Linked with triacid chlorides. Chem Mater 26:4163–4171
Meador MAB, Aleman CR, Hanson K, Ramirez N, Vivod SL, Wilmoth N, McCorkle L (2015) Polyimide aerogels with amide cross-links: a low cost alternative for mechanically strong polymer aerogels. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:1240–1249
Yang X, Sun Y, Shi D (2012) Experimental investigation and modeling of the creep behavior of ceramic fiber-reinforced SiO2 aerogel. J Non Cryst Solids 358:519–524
Liao Y, Wu H, Ding Y, Yin S, Wang M, Cao A (2012) Engineering thermal and mechanical properties of flexible fiber-reinforced aerogel composites. J Solgel Sci Technol 63:445–456
Shi D, Sun Y, Feng J, Yang X, Han Sh, Mi Ch, Jiang Y, Qi H (2013) Experimental investigation on high temperature anisotropic compression properties of ceramic fiber-reinforced SiO2 aerogel. Mater Sci Eng A 585:25–31
Koebel MM, Huber L, Zhao S, Malfait WJ (2016) Breakthroughs in cost-effective, scalable production of superinsulating, ambient-dried silica aerogel and silica-biopolymer hybrid aerogels: from laboratory to pilot scale. J Solgel Sci Technol 79:308–318
Feng JD, Le D, Nguyen ST, Nien VTC, Jewell D, Duong HM (2016) Silica-cellulose hybrid aerogels for thermal and acoustic insulation applications. Colloid Surf A 506:298–305
Markevicius G, Ladj R, Niemeyer P, Budtova T, Rigacci A (2017) Ambient-dried thermal superinsulating monolithic silica-based aerogels with short cellulosic fibers. J Mater Sci 52:2210–2221
Eichhorn SJ (2011) Cellulose nanowhiskers: promising materials for advanced applications. Soft Matter 7:303–315
Bhatnagar A, Sain M (2005) Processing of cellulose nanofiber-reinforced composites. J Reinf Plast Compos 24:1259–1268
Villarroel-Rocha J, Barrera D, Sapag K (2014) Introducing a self-consistent test and the corresponding modification in the Barrett, Joyner and Halenda method for pore-size determination. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 200:68–78
Barrett EP, Joyner LG, Halenda PP (1951) The determination of pore volume and area distributions in porous substances. I. computations from nitrogen isotherms. J Am Chem Soc 73:373–380
Kačuráková M, Smith AC, Gidley MJ, Wilson RH (2002) Molecular interactions in bacterial cellulose composites studied by 1D FT-IR and dynamic 2D FT-IR spectroscopy. Carbohydr Res 337:1145–1153
Naduparambath S, Purushothaman E (2016) Sago seed shell: determination of the composition and isolation of microcrystalline cellulose (MCC). Cellulose 23:1803–1812
Ciolacu D, Ciolacu F, Popa VI (2011) Amorphous cellulose—structure and characteration cellulose. Chem Technol 45:13–21
Rao AV, Kalesh RR (2003) Comparative studies of the physical and hydrophobic properties of TEOS based silica aerogels using different co-precursors. Sci Technol Adv Mater 4:509–515
Rodriguez JE, Anderson AM, Carroll MK (2014) Hydrophobicity and drag reduction properties of surfaces coated with silica aerogels and xerogels. J Solgel Sci Technol 71:490–500
Fricke J, Lu X, Wang P, Büttner D, Heinemann U (1992) Optimization of monolithic silica aerogel insulants. Int J Heat Mass Transf 35:2305–2309
Kaganer MG (1969) Thermal insulation in cryogenic engineering. Israel program forensic science translation, Jerusalem
Siller M, Amer H, Bacher M, Roggenstein W, Rosenau T, Potthast A (2015) Effects of periodate oxidation on cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 22:2245–2261
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M., Jiang, H., Xu, D. et al. A facile method to prepare cellulose whiskers–silica aerogel composites. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 83, 72–80 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-017-4384-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-017-4384-1