Abstract
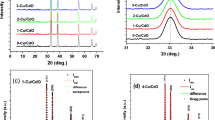
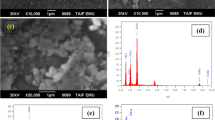
Zinc oxide (ZnO) nano-polycrystalline films were successfully prepared by modified successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction at room temperature technique which was based on the alternate immersion of substrate in the alkaline zinc precursor and deionized water. ZnO films were formed through accumulation of ZnO crystal clusters. The synthesis, microstructure, and optical properties of ZnO nano-polycrystalline films were investigated. Prepared ZnO films exhibited wurtzite structure, with good surface morphology and optical properties. Ethanolamine was employed as a complex reagent, which improved the adsorption of zinc complex with substrate. Effects of technique parameters on the properties of ZnO nano-polycrystalline films were studied in detail. Some parameters, including cycle number of preparation, ratio of zinc to ethanolamine, pH value of precursor and zinc concentration, played key roles in the deposition of ZnO nano-polycrystalline films. Intensive and sharp ultraviolet emission peaks at about 400 nm could be observed in the photoluminescence spectra.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Özgür Ü, Alivov YaI, Liu C, Teke A, Reshchikov MA, Doğan S, Avrutin V, Cho S-J, Morkoc H (2005) A comprehensive review of ZnO materials and devices. J Appl Phys 98(04):041301-103
Triboulet R (2001) Scope of ZnO growth. In: Rogaski A, Adamiec K, Madejczyk P (eds) International conference on solid state crystals 2000: growth, characterization, and applications of single crystals. Proceedings of SPIE 4412, pp 1–8
Pearton SJ, Norton DP, lp K, Heo YW, Steiner T (2004) Recent advances in processing of ZnO. J Vac Sci Technol B 22(3):932–948
Chawla AK, Kaur D, Chandra R (2007) Structural and optical characterization of ZnO nanocrystalline films deposited by sputtering. Opt Mater 29(8):995–998
Rozati SM, Akesteh Sh (2007) Characterization of ZnO:Al thin films obtained by spray pyrolysis technique. Mater Charact 58(4):319–322
Smith FTJ (1983) Metalorganic chemical vapor deposition of oriented ZnO films over large areas. Appl Phys Lett 43(12):1108–1110
Lee JH, Ko KH, Park BO (2003) Electrical and optical properties of ZnO transparent conducting films by the sol–gel method. J Cryst Growth 247(1–2):119–125
Jiménez-González A, Suárez-Parr R (1996) Effect of heat treatment on the properties of ZnO thin films prepared by successive ion layer adsorption and reaction (SILAR). J Cryst Growth 167(3–4):649–655
Nicolau YF (1985) Solution deposition of thin solid compound films by a successive ionic-layer adsorption and reaction process. Appl Surf Sci 22–23(2):1061–1074
Kale RB, Lokhande CD (2004) Room temperature deposition of ZnSe thin films by successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction (SILAR) method. Mat Res Bull 39(12):1829–1839
Pathan HM, Sankapal BR, Desai JD, Lokhande CD (2003) Preparation and characterization of nanocrystalline CdSe thin films deposited by SILAR method. Mat Chem Phys 78(1):11–14
Salunkhe RR, Dhawale DS, Gujar TP, Lokhande CD (2009) Structural, electrical and optical studies of SILAR deposited cadmium oxide thin films: annealing effect. Mat Res Bull 44(2):364–368
Puišo J, Tamulevicius S, Laukaitis G, Lindroos S, Leskelä M, Snitka V (2002) Growth of PbS thin films on silicon substrate by SILAR technique. Thin Solid Films 403–404, 457–461
Puigo J, Lindroos S, Tamulevicus S, Leskelä M, Snitkad V (2003) Growth of ultra thin PbS films by SILAR technique. Thin Solid Films 428(1–2):223–226
Deshpande NG, Sagade AA, Gudage Y, Lokhande CD, Sharma R (2007) Growth and characterization of tin disulfide (SnS2) thin film deposited by successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction (SILAR) technique. J Alloys Compd 436(1–2):421–426
Yang J, Jin Z, Chai Y, Du H, Liu T, Wang T (2009) Growth and characterization of CuInSe2 thin films prepared by successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction method with different deposition temperatures. Thin Solid Films 517(24):6617–6622
Park S, DiMasi E, Kim Y-I, Han W, Woodward PM, Vogt T (2006) The preparation and characterization of photocatalytically active TiO2 thin films and nanoparticles using successive-ionic-layer-adsorption-and-reaction. Thin Solid Films 515(4):1250–1254
More AM, Gunjakar JL, Lokhande CD, Joo OS (2009) Fabrication of hydrophobic surface of titanium dioxide films by successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction (SILAR) method. Appl Surf Sci 255(12):6067–6072
Gao XD, Li XM, Yu WD (2004) Synthesis and optical properties of ZnO nanocluster porous films deposited by modified SILAR method. Appl Surf Sci 229(1–4):275–281
Gao X-D, Li X-M, Yu W-D, Qiu J-J, Gan X-Y (2008) Room-temperature deposition of nanocrystalline CuSCN film by the modified successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction method. Thin Solid Films 517(2):554–559
Lupan O, Shishiyanu S, Chow L, Shishiyanu T (2008) Nanostructured zinc oxide gas sensors by successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction method and rapid photothermal processing. Thin Solid Films 516(10):3338–3345
Ghosh A, Deshpande NG, Gudage YG, Joshi RA, Sagade AA, Phase DM, Sharma R (2009) Effect of annealing on structural and optical properties of zinc oxide thin film deposited by successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction technique. J Alloys Compd 469(1–2):56–60
Vargas-Hernández C, Jiménez-García FN, Jurado JF, Henao Granada V (2008) XRD, μ-Raman and optical absorption investigations of ZnO deposited by SILAR method. Microelectronics J 39(11):1347–1348
Vargas-Hernández C, Jiménez-García FN, Jurado JF, Henao V (2008) Granada comparison of ZnO thin films deposited by three different SILAR processes. Microelectronics J 39(11):1349–1350
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the financial support of Hubei Provincial Natural Science Foundation (No. 2007ABA048). We wish to thank the Analytical and Testing Center of Huazhong University of Science and Technology for the help on measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, D., Zhang, J., Wu, Q. et al. Ultraviolet emission of ZnO nano-polycrystalline films by modified successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction technique. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 54, 165–173 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-010-2171-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-010-2171-3