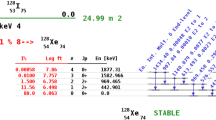
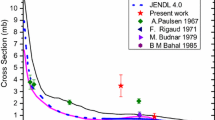
Abstract
Charged particle activation analysis (CPAA) utilizing an 8 MeV proton beam has been studied for general elemental quantification. We accumulate the reaction cross section and nuclear decay data by referring to nuclear database supplied by National Nuclear Data Center in Brookhaven National Laboratory. By using the database we have derived determination sensitivity of single element samples for each nuclide. The result indicates that, while the determination sensitivity tends to decrease gradually as the target nucleus becomes heavy, the CPAA analysis is possible over the whole elements including the heavy nuclear region. It may be concluded that CPAA can be applied to most of the stable nuclei and is one of the alternative methods to neutron activation analysis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ricci E, Hahn RL (1965) Theory and experiment in rapid, sensitive helium-3 activation analysis. Anal Chem 37:742–748
Sanni AO, Roche NG, Dowell HJ, Schweikert EA, Ramsey TH (1984) On the determination of carbon and oxygen impurities in silicon by 3He activation analysis. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 81:125–129
Valladon M, Debrun JL (1977) Determination of oxygen in metals and semiconductors by means of the 16O(T, n)18F reaction. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 39:385–395
Debefve P, Do HP, Friedli C, Lerch P (1981) Trace determination of oxygen in gold–copper alloys and in high purity gold using 3He and 4He activation analysis. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 64:213–223
Bottger ML, Birnstein D, Helbig W, Niese S (1980) Removal of disturbances in carbon determination by activation analysis for lowering the detection limit. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 58:173–181
Yagi M, Masumoto K (1985) Simultaneous determination of Ti, Cr, Fe, Cu, Ga and Zr in aluminium alloys by charged-particle activation analysis using the internal standard method. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 91:379–387
Masumoto K, Yagi M (1985) Determination of strontium in biological materials by charged-particle activation analysis using the stable isotope dilution method. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 91:369–378
Yagi M, Masumoto K, Muto M (1986) An automatic gamma-ray spectrometer equipped with a micro-robot for sample changing. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 98:31–38
Masumoto K, Yagi M (1987) Simultaneous determination of P, Cl, K and Ca in several control serums by alpha-particle activation analysis using the internal standard method. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 109:449–458
Yagi M, Masumoto K (1987) Instrumental charged-particle activation analysis of several selected elements in biological materials using the internal standard method. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 111:359–369
Masumoto K, Yagi M (1989) Determination of phosphorus in low-alloy steels by alpha-particle activation analysis. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 130:243–250
Shikano K, Yonezawa H, Shigematsu T (1993) Charged particle activation analysis of light elements at sub-ppb level. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 167:81–88
Masumoto K, Hara M, Hasegawa D, Iino E, Yagi M (1997) Photon and proton activation analysis of iron and steel standards using the internal standard method coupled with the standard addition method. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 217:247–253
Matsumura H, Masumoto K, Toyoda A, Kinoshita N (2008) List-mode coincidence data analysis for highly selective and low background detection of gamma-nuclides in activated samples. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 278:733–738
Kumada H, Matsumura A, Sakurai H, Sakae T, Yoshioka M, Kobayashi H, Matsumoto H, Kiyanagi Y, Shibata T, Nakashima H (2014) Project for the development of the linac based NCT facility in University of Tsukuba. Appl Radiat Isot 88:211–215
Experimental nuclear reaction data (EXFOR). http://www.nndc.bnl.gov/exfor/exfor.htm. Accessed 8 July 2015
NuDat 2.6. http://www.nndc.bnl.gov/nudat2/. Accessed 8 July 2015
JCAC report. https://www.jcac.or.jp/site/library/. Accessed 8 July 2015
Oshima M, Toh Y, Hatsukawa Y, Koizumi M, Kimura A, Haraga A, Ebihara M, Suishida K (2008) Multiple gamma-ray detection method and its application to nuclear chemistry. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 278:257–262
Hatsukawa Y, Oshima M, Hayakawa T, Toh Y, Shinohara N (2002) Application of multiparameter coincidence spectrometry using a Ge detectors array to neutron activation analysis. Nucl Instrum Methods A 482:328–333
Toh Y, Oshima M, Hatsukawa Y, Hayakawa T, Shinohara N (2001) Comparison method for neutron activation analysis with γ–γ matrix. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 250:373–376
Oshima M, Toh Y, Hatsukawa Y, Hayakawa T, Shinohara N (2002) A high-sensitivity and non-destructive trace element analysis based on multiple gamma-ray detection. J Nucl Sci Technol 39:292–294
Oshima M, Toh Y, Kimura A, Ebihara M, Oura Y, Itoh Y, Sawahata H, Matsuo M (2007) Multiple prompt gamma-ray analysis and construction of its beam line. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 271:317–321
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Drs. K. Masumoto, M. Matsuo, T. Otsuki, and H. Matsue for useful discussions regarding the activation analysis. They also wish to thank Drs. M. Asai and K. Tsukada for their kind encouragement and careful reading of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
W. Muramatsu: on leave from NSC Tsuruga.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oshima, M., Yamaguchi, Y., Muramatsu, W. et al. Study of charged particle activation analysis (I): determination sensitivity for single element samples. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 308, 711–719 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-015-4505-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-015-4505-7