Abstract
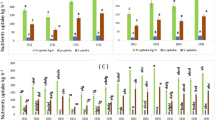
We investigated the optimal timing and quantity of K to reduce radiocesium in brown rice. The concentration of 137Cs in brown rice was reduced from 32 Bq kg−1 without K fertilizer to 2.0 Bq kg−1 with 16 g m−2 of basal K. The concentration of exchangeable 137Cs in the soil decreased from 234 to 25 Bq kg−1 with increasing application of K fertilizer from 0 to 57 g m−2. Hence, heavy application of K fertilizer in the early growing period can decrease the uptake of 137Cs by rice plants and the concentration of exchangeable 137Cs in the soil.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tsukada H, Takeda A, Nakao A (2012) Vertical distribution and physicochemical form of fallout 137Cs in an Allophanic andisol acidified by long-term fertilizer application. Pedologist 55:435–441
Tanaka K, Takahashi Y, Sakagichi A, Umeo H, Hayakawa S, Tanida H, Saito T, Kanai Y (2012) Vertical profiles of iodine-131 and cesium-137 in soils in Fukushima prefecture related to the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power station accident. Geochem J 46:73–76
Takata Y, Kohyama K, Obara H, Saito T, Taniyama I (2012) Map of the distribution of 134Cs and 137Cs concentrations in farmland soil after the Fukushima nuclear accident, int sci symp combating radionuclide contamination in agro-soil environment, Fukushima, Japan, 2012.3.8–10, p 362
Agriculture, forestry and fisheries department, fukushima prefecture: the results of the emergency investigation of radioactive materials in brown rice (Compilation), http://www.pref.fukushima.lg.jp/uploaded/attachment/43728.pdf (in Japanese). Accessed 5 Oct 2014
Saito T, Ohkoshi S, Fujimura S, Iwabuchi K, Saito M, Nemoto T, Sato M, Sato M, Yoshioka K, Tsukada H (2012) Effect of potassium application on root uptake of radiocesium in rice, KUR research program for scientific basis of nuclear safety, 165–169
Tsukada H, Hasegawa H, Hisamatsua S, Yamasaki S (2002) Transfer of 137Cs and stable Cs from paddy soil to polished rice in Aomori, Japan. J Environ Radioact 59:351–363
van Bergeijk KE, Noordijk H, Lembrechts J, Frissel MJ (1992) Influence of pH, soil organic matter content on soil-to-plant transfer of radiocesium and strontium as analyzed by a nonparametric method. J Environ Radioact 15:265–276
Wang CJ, Lai SY, Wang JJ, Lin YM (1997) Transfer of radionuclides from soil to grass in northern Taiwan. Appl Radiat Isot 48:301–303
Kato N (2012) Countermeasures to reduce radiocaesium contamination in paddy rice, soybean and cabbage, int sci symp combating radionuclide contamination in agro-soil environment, Fukushima Japan, 2012. 3.8–10, p 317–318
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saito, T., Takahashi, K., Makino, T. et al. Effect of application timing of potassium fertilizer on root uptake of 137Cs in brown rice. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 303, 1585–1587 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-014-3609-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-014-3609-9