Abstract
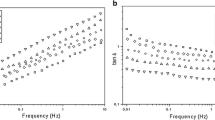
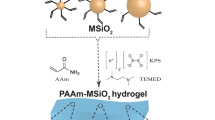
Highly stretchable silica/polyacrylamide (PAM) nanocomposite hydrogels were synthesized via in situ free radical polymerization in the presence of silica nanoparticles. The effect of particle size and content of silica nanoparticles on tensile properties and swelling behavior were investigated. The hydrogen bond between PAM molecule and silica nanoparticles was evidenced by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and the swelling behavior of hydrogels. The tensile strength of silica/PAM hydrogels is 2 times that of PAM gels, and the elongation at break is nearly 2800% when the silica particle size is 15 nm and the content is 10 wt%. This excellent stretching property of hydrogels was ascribed to the presence of hydrogen bond between PAM molecule and silica nanoparticles.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Klotz BJ, Gawlitta D, Rosenberg AJWP, Malda J, Melchels FPW (2016) Gelatin-Methacryloyl hydrogels: towards biofabrication-based tissue repair. Trends Biotechnol 34:394–407
Pan T, Song W, Cao X, Wang Y (2016) 3D bioplotting of gelatin/alginate scaffolds for tissue engineering: influence of crosslinking degree and pore architecture on physicochemical properties. J Mater Sci Technol 32:889–900
Nesrinne S, Djamel A (2017) Synthesis, characterization and rheological behavior of pH sensitive poly(acrylamide-co-acrylic acid) hydrogels. Arab J Chem 50:1916–1918
Li L, Stiadle JM, Levendoski EE, Lau HK, Thibeault SL, Kiick KL (2018) Biocompatibility of injectable Resilin-based hydrogels. J Biomed Mater Res A 106:2229–2242
Shakeel A, Singh A, Das S, Suhag D, Sharma AK, Rajput SK, Mukherjee M (2017) Synthesis and morphological insight of new biocompatible smart hydrogels. J Polym Res 24:113–122
Zhang W, Sha Z, Huang Y, Bai Y, Xi N, Zhang Y (2014) Glow discharge electrolysis plasma induced synthesis of cellulose-based ionic hydrogels and their multiple response behaviors. RSC Adv 5:6505–6511
Ziółkowski B, Florea L, Theobald J, Benito-Lopez F, Diamond D (2016) Porous self-protonating spiropyran-based NIPAAm gels with improved reswelling kinetics. J Mater Sci 51:1392–1399
Gradinaru LM, Ciobanu C, Drobota M, Vlad S (2017) Poly(alkylene sebacate ether)urethane hydrogels for indomethacin delivery formulations. J Polym Res 24:99–111
Zhang W, Ren G, Xu H, Zhang J, Liu H, Mu S, Cai X, Wu T (2016) Genipin cross-linked chitosan hydrogel for the controlled release of tetracycline with controlled release property, lower cytotoxicity, and long-term bioactivity. J Polym Res 23:156–164
Büning D, Ennen F, Walter S, Hennecke T, Ulbricht M (2018) Potassium-sensitive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-based hydrogels for sensor applications. Polym Chem 9:3600–3614
Jin R (2018) Injectable hydrogels for cartilage tissue engineering. Biomaterials 30:2544–2551
Jeong K-H, Park D, Lee Y-C (2017) Polymer-based hydrogel scaffolds for skin tissue engineering applications: a mini-review. J Polym Res 24:112–121
Illeperuma WRK, Sun JY, Suo Z, Vlassak JJ (2014) Fiber-reinforced tough hydrogels. Extreme Mech Lett 1:90–96
Dragan ES (2014) Design and applications of interpenetrating polymer network hydrogels. A review. Chem Eng J 243:572–590
Yan X, Chen Q, Zhu L, Chen H, Wei D, Chen F, Tang Z, Yang J, Zheng J (2017) High strength and self-healable gelatin/polyacrylamide double network hydrogels. J Mater Chem B 5:7683–7691
Piao Y, Chen B (2017) Synthesis and mechanical properties of double cross-linked gelatin-graphene oxide hydrogels. Int J Biol Macromol 101:791–798
Li HJ, Jiang H, Haraguchi K (2018) Ultrastiff, Thermoresponsive nanocomposite hydrogels composed of ternary polymer–clay–silica networks. Macromolecules 51:529–539
Bellingeri R, Mulko L, Molina M, Picco N, Alustiza F, Grosso C, Vivas A, Acevedo DF, Barbero CA (2018) Nanocomposites based on pH-sensitive hydrogels and chitosan decorated carbon nanotubes with antibacterial properties. Mater Sci Eng C 90:461–467
Bardajee GR, Mizani F, Hosseini SS (2017) pH sensitive release of doxorubicin anticancer drug from gold nanocomposite hydrogel based on poly(acrylic acid) grafted onto salep biopolymer. J Polym Res 24:48–60
Jin T, Stanciulescu I (2017) Numerical investigation of the influence of pattern topology on the mechanical behavior of PEGDA hydrogels. Acta Biomater 49:247–259
Guo H, Mussault C, Brûlet A, Marcellan A, Hourdet D, Sanson N (2016) Thermoresponsive toughening in LCST-type hydrogels with opposite topology: from structure to fracture properties. Macromolecules 49:4295–4306
Wang Q, Gao Z (2016) A constitutive model of nanocomposite hydrogels with nanoparticle crosslinkers. J Mech Phys Solids 94:127–147
Wahid F, Yin JJ, Xue DD, Xue H, Lu YS, Zhong C, Chu LQ (2016) Synthesis and characterization of antibacterial carboxymethyl chitosan/ZnO nanocomposite hydrogels. Int J Biol Macromol 88:273–279
Wahid F, Wang HS, Lu YS, Zhong C, Chu LQ (2017) Preparation, characterization and antibacterial applications of carboxymethyl chitosan/CuO nanocomposite hydrogels. Int J Biol Macromol 101:690–695
Haraguchi K, Takehisa T (2002) Nanocomposite hydrogels: a unique organic–inorganic network structure with extraordinary mechanical, optical, and swelling/deswelling properties. Adv Mater 14:1120–1124
Liu R, Liang S, Tang XZ, Yan D, Li X, Yu ZZ (2012) Tough and highly stretchable graphene oxide/polyacrylamide nanocomposite hydrogels. J Mater Chem 22:14160–14167
Jiang H, Zhang G, Feng X, Liu H, Li F, Wang M, Li H (2017) Room-temperature self-healing tough nanocomposite hydrogel crosslinked by zirconium hydroxide nanoparticles. Compos Sci Technol 140:54–62
Wu L, Zeng L, Chen H, Zhang C (2012) Effects of silica sol content on the properties of poly(acrylamide)/silica composite hydrogel. Polym Bull 68:309–316
Durme KV, Mele BV, Loos W, Prez FED (2005) Introduction of silica into thermo-responsive poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide) hydrogels: a novel approach to improve response rates. Polymer 46:9851–9862
Yin D, Ma L, Liu J, Zhang Q (2014) Pickering emulsion: A novel template for microencapsulated phase change materials with polymer-silica hybrid shell. Energy 64:575–581
Bhardwaj P, Singh V, Mandal UK, Aggarwal S (2010) Polyacrylamide and poly(acrylamide-co-2-acrylamido-2-methyl-1-propanesulfonic acid)-silica composite nanogels through in situ microemulsion polymerisation. J Mater Sci 45:1008–1016
Shao C, Chang H, Meng W, Feng X, Yang J (2017) High-strength, tough, and self-healing nanocomposite physical hydrogels based on the synergistic effects of dynamic hydrogen bond and dual coordination bonds. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:28305–28318
Li P, Siddaramaiah KNH, Yoo GH, Lee JH (2010) Poly(acrylamide/laponite) nanocomposite hydrogels: swelling and cationic dye adsorption properties. J Appl Polym Sci 111:1786–1798
Huggins ML (1941) Solutions of long chain compounds. J Chem Phys 9:440–440
Tan Y, Wu R, Li H, Ren W, Du J, Xu S, Wang J (2015) Electric field-induced gradient strength in nanocomposite hydrogel through gradient crosslinking of clay. J Mater Chem B 3:4426–4430
Zhao F, Qin X, Feng S (2011) Effects of microgel content and n -methylolacrylamide on the properties of microgel composite hydrogels prepared by postcrosslinking method. Polym Compos 33:44–51
Acknowledgements
This work has been sponsored by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2016YFC0301302), Seed Foundation of Innovation and Creation for Graduate Students of NWPU (Jinhua Chen).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, Y., Chen, J., Liu, W. et al. Construction of highly stretchable silica/polyacrylamide nanocomposite hydrogels through hydrogen bond strategy. J Polym Res 26, 119 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-019-1761-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-019-1761-1