Abstract
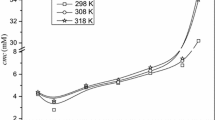
In the present paper, the micellization of an amphiphilic drug, promazine hydrochloride, and gemini surfactants (16-s-16) with s = 4–6 and the monomeric hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) counterparts has been examined conductometrically in the pure and mixed states in aqueous solutions at different compositions and temperatures (298.15–308.15 K). Dicationic gemini surfactants provide much better environment for the micellization behavior than the corresponding monocationic counterpart CTAB. The critical micelle concentration (cmc) values are lower than the cmc for ideal mixing, cmc id, suggesting attractive interactions between the two components in mixed micelles. The micellar mole fractions of surfactants, evaluated by different models, show greater contributions of surfactants in mixed micelles and increase with increasing concentrations of these surfactants. The negative values of β suggest synergism in the mixtures, which is highly beneficial as it reduces the total amount of surfactants required in a particular application, leading to reductions of cost and environmental impact. Activity coefficients (f 1 and f 2) are always less than unity showing nonideality in the systems. The data have been also used for evaluation of thermodynamic parameters.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aungst, B.J., Phang, S.: Metabolism of a neurotensin (8–13) analog by intestinal and nasal enzymes, and approaches to stabilize this peptide at these absorption sites. Int. J. Pharm. 117, 95–100 (1995)
Muranushi, N., Kinugawa, M., Nakajima, Y., Muranishi, S., Sekazi, H.: Mechanism for the inducement of the intestinal absorption of poorly absorbed drugs by mixed micelles. I. Effects of various lipid-bile salt mixed micelles on the intestinal absorption of streptomycin in rat. Int. J. Pharm. 4, 271–279 (1980)
Kabanov, A.V., Batrakova, E.V., Melik-Nubarov, N.S., Fedoseev, N.A., Dorodnich, T.Y., Alakhov, V.Y., Chekhonin, V.P., Nazarova, I.R., Kabanov, V.A.: A new class of drug carriers, micelles of poly(oxyethylene)-poly(oxypropylene) block copolymers as microcontainers for drug targeting from blood in brain. J. Control Release 22, 141–157 (1992)
Müller, R.H.: Colloidal Carriers for Controlled Drug Delivery and Targeting. Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft, Stuttgart. Germany, and CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL (1991)
Cohen, S., Bernstein, H. (eds.): Microparticulate Systems for the Delivery of Proteins and Vaccines. Marcel Dekker, New York (1996)
Jones, M., Leroux, J.: Polymeric micelles—a new generation of colloidal drug carriers. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 48, 101–111 (1999)
Torchilin, V.P.: Structure and design of polymeric surfactant-base drug delivery systems. J. Control. Release 73, 137–172 (2001)
Novel surfactants, preparation, applications, and biodegradability. In: Holmberg K. (ed.) Surfactant Science Series, vol. 74. Marcel Dekker, New York (1998)
Menger, F.M., Littau, C.A.: Gemini surfactants: a new class of self-assembling molecules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 115, 10083–10090 (1993)
Menger, F.M., Keiper, J.S.: Gemini surfactants. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 39, 1906–1920 (2000)
Xia, J., Zana, R.: Gemini Surfactants: Synthesis, Interfacial and Solution-Phase Behavior, and Applications. Marcel Dekker Inc., New York (2004)
Attwood, D., Florence, A.T.: Surfactant Systems, Their Chemistry, Pharmacy and Biology. Chapman and Hall, New York (1983)
Schreier, S., Malheiros, S.V.P., de Paula, E.: Surface active drugs: self-association and interaction with membranes and surfactants. Physicochemical and biological aspects. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1508, 210–234 (2000)
De, S., Aswal, V.K., Goyal, P.S., Bhattacharya, S.: Role of spacer chain length in dimeric micellar organization. Small angle neutron scattering and fluorescence studies. J. Phys. Chem. 100, 11664–11671 (1996)
Kabir-ud-Din, Fatma, W., Khatoon, S., Khan, Z.A., Naqvi, A.Z.: Surface and solution properties of alkanediyl-α,ω-bis(dimethylcetylammonium bromide) gemini surfactants in the presence of additives. J. Chem. Eng. Data 53, 2291–2300 (2008)
Mukerjee, P., Mysels, K.J.: Critical Micelle Concentrations of Aqueous Surfactant Systems. NSRDS-NB-36, Washington, D.C. (1971)
Rodriguez, A., Junquera, E., del Burgo, P., Aicart, E.: Conductometric and spectrofluorimetric characterization of the mixed micelles constituted by dodecyltrimethylammonium bromide and a tricyclic antidepressant drug in aqueous solution. J. Coll. Interface Sci. 269, 476–483 (2004)
Kabir-ud-Din, Rub, M.A., Naqvi, A.Z.: Mixed micelles of amphiphilic drug promethazine hydrochloride and surfactants (conventional and gemini) at 293.15 K to 308.15 K: Composition, interaction and stability of the aggregates. J. Coll. Interface Sci. 354, 700–708 (2011)
Rub, M.A., Asiri, A.M., Naqvi, A.Z., Rahman, M.M., Khan, S.B., Kabir-ud-Din: Mixed micellization between amphiphilic drug promethazine hydrochloride and cationic surfactant (conventional as well as gemini). J. Mol. Liq. 177, 19–25 (2013)
Rub, M.A., Asiri, A.M., Azum, N., Khan, A., Khan, A.A.P., Khan, S.B., Rahman, M.M., Kabir-ud-Din: Amphiphilic antidepressant drug amitriptyline hydrochloride under the influence of ionic and nonionic hydrotropes; micellization and phase separation. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 19, 1774–1780 (2013)
Rub, M.A., Asiri, A.M., Azum, N., Kabir-ud-Din: Investigation of micellar and phase separation phenomenon of phenothiazine drug promazine hydrochloride with anionic hydrotropes. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. (2013). doi:10.1016/j.jiec.2013.09.027
Clint, J.H.: Micellization of mixed nonionic surface active agents. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1 71, 1327–1334 (1975)
Stead, J.A., Taylor, H.: Some solution properties of certain surface-active N-alkylpyridinium halides: I. Effect of temperature on the critical micelle concentrations. J. Coll. Interfac. Sci. 30, 482–488 (1969)
Kabir-ud-Din, Siddiqui, U.S., Kumar, S., Dar, A.A.: Micellization of monomeric and dimeric (gemini) surfactants in polar nonaqueous–water–mixed solvents. Colloid Polym. Sci. 284, 807–812 (2006)
Ruiz, C.C., Diaz-Lopez, L., Aguiar, J.: Self-assembly of tetradecyltrimethylammonium bromide in glycerol aqueous mixtures: a thermodynamic and structural study. J. Coll. Interface Sci. 305, 293–300 (2007)
Meguro, K., Ueno, M., Esumi, K.: Nonionic Surfactants: Physical Chemistry. In: Schick M.J. (ed.) Marcel Dekker, New York (1987)
Lopez Fontan, J.L., Costa, J., Ruso, J.M., Prieto, G., Sarmiento, F.: Electrical conductivities and critical micelle concentrations (determined by the local polynomial regression method) of imipramine and clomipramine hydrochlorides from (283 to 313) K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 49, 1008–1012 (2004)
Kabir-ud-Din, Rub, M.A., Naqvi, A.Z.: Mixed micelle formation between amphiphilic drug amitriptyline hydrochloride and surfactants (conventional and gemini) at 293.15–308.15 K. J. Phys. Chem. B 114, 6354–6364 (2010)
Asakawa, T., Kitano, H., Ohta, A., Miyagishi, S.: Convenient estimation for counterion dissociation of cationic micelles using chloride-sensitive fluorescence probe. J. Coll. Interface Sci. 242, 284–287 (2001)
Evans, H.C.: Alkyl sulphates. Part I. Critical micelle concentrations of the sodium salts. J. Chem. Soc. 60, 579–586 (1956)
Iijima, H., Kato, T., Soderman, A.: Variation in degree of counterion binding to cesium perfluorooctanoate micelles with surfactant concentration studied by 133Cs and 19F NMR. Langmuir 16, 318–323 (2000)
Zana, R.: Ionization of cationic micelles: effect of the detergent structure. J. Coll. Interface Sci. 78, 330–337 (1980)
Gorski, N., Kalus, J.: Temperature dependence of the sizes of tetradecyltrimethylammonium bromide micelles in aqueous solutions. Langmuir 17, 4211–4215 (2001)
Tanford, C.: The Hydrophobic Effect: Formation of Micelles and Biological Membranes. Wiley, New York (1980)
Clint, J.H.: Surfactant Aggregation. Blackie/Chapman and Hall, New York (1992)
Zana, R.: Critical micellization concentration of surfactants in aqueous solution and free energy of micellization. Langmuir 12, 1208–1211 (1996)
Taboada, P., Ruso, J.M., Garcia, M., Mosquera, V.: Surface properties of some amphiphilic antidepressant drugs. Colloids Surf. A 179, 125–128 (2001)
Taboada, P., Martinez-Landeira, P., Ruso, J.M., Garcia, M., Mosquera, V.: Aggregation energies of some amphiphilic antidepressant drugs. Colloids Surf. A 197, 95–99 (2002)
Rub, M.A., Asiri, A.M., Azum, N., Khan, A., Khan, A.A.P., Khan, S.B., Rahman, M.M., Kumar, D., Al-Youbi, A.O.: Analysis of mixed micellar behavior of promazine hydrochloride with surfactants in aqueous medium at different temperatures and compositions. Z. Phys. Chem. 227, 1671–1686 (2013)
Attwood, D., Boitard, E., Dubes, J.P., Tachoire, H.: Calorimetric study of the influence of electrolyte on the micellization of phenothiazine drugs in aqueous solution. J. Phys. Chem. B 101, 9586–9592 (1997)
Nusselder, J.J.H., Engberts, J.B.F.N.: Toward a better understanding of the driving force for micelle formation and micellar growth. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 148, 353–361 (1992)
Kresheck, G.C.: In: Franks F. (ed.) Water. A Comprehensive Treatise. Plenum, New York (1995)
Rubingh, D.N.: In: Mittal, K.L. (ed.) Solution Chemistry of Surfactants. Plenum, New York (1979)
Motomura, K., Yamanaka, M., Aratono, M.: Thermodynamic consideration of the mixed micelle of surfactants. Colloid Polym. Sci. 262, 948–955 (1984)
Rodenas, V., Valiente, M., Villafruela, M.S.: Different theoretical approaches for the study of the mixed tetraethylene glycol mono-n-dodecyl ether/hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide micelles. J. Phys. Chem. B 103, 4549–4554 (1999)
Lange, H., Beck, K.H.: Zur mizellbildung in mischl¨osungen homologer und nichthomologer tenside. Kolloid Z. Z. Polym. 251, 424–431 (1973)
Rosen, M.J.: Surfactants and Interfacial Phenomena, 3rd edn. Wiley, New York (2004)
Rub, M.A, Asiri, A.M., Khan, A., Khan, A.A.P., Azum, N., Khan, S.B., Kabir-ud-Din: Investigation of micellar and phase separation phenomenon of the amphiphilic drug amitriptyline hydrochloride with cationic hydrotropes. J. Solution Chem. 42, 390–411 (3013)
Rub, M.A., Sheikh, M.S., Asiri, A.M., Azum, N., Khan, A., Khan, A.A.P., Khan, S.B., Kabir-ud-Din: Aggregation behaviour of amphiphilic drug and bile salt mixtures at different compositions and temperatures. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 64, 28–39 (2013)
Rub, M.A., Azum, N., Kumar, D., Asiri, A.M., Marwani, H.M.: Micellization and microstructural studies between amphiphilic drug ibuprofen with nonionic surfactant in aqueous urea solution. J. Chem. Thermodyn. (2014). doi:10.1016/j.jct.2014.01.005
Zana, R., Benrraou, M., Rueff, R.: Alkanediyl-α,ω-bis(dimethylalkylammonium bromide) surfactants. 1. Effect of the spacer chain length on the critical micelle concentration and micelle ionization degree. Langmuir 7, 1072–1075 (1991)
Hoffmann, H., Possnecker, G.: The mixing behavior of surfactants. Langmuir 10, 381–389 (1994)
Maeda, H.: A thermodynamic analysis of charged mixed micelles in water. J. Phys. Chem. B 109, 15933–15940 (2005)
Acknowledgments
Chemistry Department and Center of Excellence for Advanced Materials Research, King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah are highly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10953_2014_174_MOESM1_ESM.doc
Supplementary data Supplementary data associated with this article can be found, at www.springerlink.com. (DOC 146 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rub, M.A., Kumar, D., Azum, N. et al. Study of the Interaction Between Promazine Hydrochloride and Surfactant (Conventional/Gemini) Mixtures at Different Temperatures. J Solution Chem 43, 930–949 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-014-0174-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-014-0174-3