Abstract
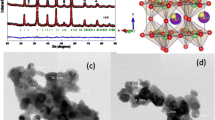
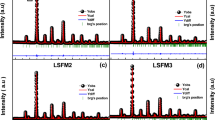
Effect of simultaneous Sm and Mn substitutions around half-doping level on the structural, magnetic and low temperature electronic behaviour of LaFeO3 nanoparticle is extensively studied. The SXRD and FESEM data shows a single-phase nanoparticle of size 33 nm. A drastic magnetic phase change with a low temperature non-ergodic phase is seen compared to the parent LaFeO3 (G-type antiferromagnetic) and this typical behaviour stems from the facts that, simultaneous presence of Sm and Mn alters the Fe crystal environment as well as its multiplicity which leads to improved exchange interactions among different ions. The doped nanoparticle shows a colossal dielectric response. Impedance, modulus spectra and ac conductivity analysis are used to find the conduction process involved in the system and it is related to the hopping conduction through grain and grain boundary resistances. The possibility of the polaronic part may arise from the interactions among mixed-valence state of Fe (Fe3+/Fe2+), Mn (Mn3+/Mn2+) and from the oxygen vacancies. Moreover, the ac-electrical conductivity is analysed using Jonscher’s double-power law and Jump relaxation model.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The authors can confirm that all relevant data are included in the article.
References
Parkin, S.P., Roche, K.P., Samant, M.G., Rice, P.M., Beyers, R.B.: J. Appl. Phys. 85, 5828 (1999)
Li, E., Feng, Z., Kang, B., Zhang, J., Ren, W., Cao, S.: J. Alloys Comp. 811, 152043 (2019)
Cheng, Y., Peng, B., Hu, Z., Zhou, Z., Liu, M.: Phys. Lett. A. 382, 3018 (2018)
Smolenskii, G.A., Bokov, V.A.: J. Appl. Phys. 35, 915 (1964)
Zhou, Z., Guo, L., Yang, H., Liu, Q., Ye, F.: J. Alloys. Comp. 583, 21 (2014)
Bhagav, K.K., Ram, S., Majumdar, S.B.: J. Appl. Phys. 115, 204109 (2014)
Gaikwad, V.M., Acharya, S.A.: RSC Adv. 5, 14366 (2015)
Lakshmana Rao, T., Pradhan, M.K., Goutam, U.K., Siruguri, V., Reddy, V.R., Dash, S.: J. Appl. Phys. 126, 064104 (2019)
Koebler, W., Wallan, E., Wilkinson, M.: Phys. Rev. 118, 58 (1960)
Kuhn, J.N., Matter, P.H., Millet, J.M., Watson, R.B., Ozkan, U.S.: J. Phys. Chem. C 112(2008), 12468 (2008)
Komine, S.E., Iguchi, E.: J. Phys. Chem. Solids 68, 1504 (2007)
Benali, A., Aziz, S., Bejar, M., Dhahri, E., Graca, M.F.P.: Ceram. Int. 40, 14367 (2014)
Andoulsi, R., Naifer, K.H., Ferid, M.: Powder Technol. 230, 183 (2012)
Natali Sora, I., et al.: J. Solid State Chem. 191, 33 (2012)
Sun, L., Qin, H., Wang, K., Zhao, M., Hu, J.: Mater. Chem. Phys. 125, 305 (2011)
Bellakki, M.B., Kelly, B.J., Manivannan, V.: J. Alloys. Compd. 489, 64 (2010)
Selvadurai, P.B., Pazhanivelu, A., Jagadeeshwaran, V., Murugaraj, C., Panneer Muthuselvam, R., Chou, F.C.: J. Alloys Compd. 646, 924 (2015)
Wei, X., Wang, Y., Liu, J.P., Xiao, C.M., Zeng, W.W., Ye, S.B.: J. Mater. Sci. 48, 1117 (2013)
Mukhopadhay, K., Mohapatra, A.S., Chakrabarti, P.K.: J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 329, 133 (2013)
Tokura, Y.: Colossal Magnetoresistive Oxides, CRC Press (2000)
CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics 85th edition (2003)
Carvaja, J.R.: Physica B 192, 55 (1993)
Joy, P.A., Anil Kumar, P.S., Date, S.K.: J. Phys. Condens. Matter 10, 11049 (1998)
Li, M., Feterira, A., Sinclair, D.C.: J. Appl. Phys. 105, 114109 (2009)
Yoshii, K., Ikeda, N., Nakamura, A.: Phys. B 378, 585 (2006)
Ma, Y., Chen, X.M., Lin, Y.Q.: J. Appl. Phys. 103, 124111 (2008)
Soman, V.V., Nanoti, V.M., Kulkarni, D.K.: Ceram. Int. 39, 5713 (2013)
Mahato, D.K., Dutta, A., Sinha, T.P.: Solid State Sci. 14, 21 (2012)
Suchanicz, J.: Mater. Sci. Eng. B 55, 114 (1998)
Driver, M.C., Wright, G.T.: Proc. Phys. Soc. 81, 141 (1963)
Nadeem, M., Akhtar, M.J., Khan, A.Y., Shaheen, R., Haque, M.N.: Chem. Phys. Lett. 366, 433 (2002)
Iguchi, E., Nakamura, N., Aoki, A.: J. Phys. Chem. Solids 58, 755 (1997)
Barsoukov, E., Macdonald, J.R.: Impedance Spectroscopy Theory, Experiments and Applications 2nd edn (Hoboken, NJ: Wiley) 1, 34, 46 (2005)
Kao, K.C.: Dielectric Phenomena in Solids (San Diego, CA: Elsevier) 75–8 (2004)
Kumar, N., Ghosh, A., Choudhary, R.N.P.: Mater. Chem. Phys. 130, 381 (2011)
Sahoo, P.S., Panigrahi, A., Patri, S.K., Choudhary, R.N.P.: Mater. Sci. Pol. 28, 764 (2010)
Di, W., Li, A.: Appl. Phys. A 95, 517 (2009)
Jonscher, A.K.: The ‘universal’ dielectric response. Nature 267, 673 (1977)
Li, W., Schwartza, R.W.: Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 242906 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S. Dash: wrote the paper, supervision; T. Lakshmana Rao: collected the data, analysis tools. All authors have been personally and actively involved in substantial work leading to the paper, and will take public responsibility for its content.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dash, S., Rao, T.L. Tunable Magnetic Phase Change and Polaronic Hopping Conductions in (Sm, Mn) Half Doped LaFeO3 Nanoparticle. J Supercond Nov Magn 36, 1521–1532 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-023-06595-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-023-06595-4