Abstract
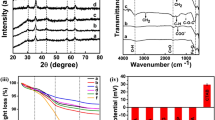
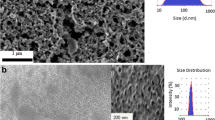
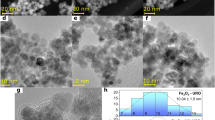
Magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles (NPs) with various morphologies obtained by varying solvent (water)-to-surfactant (polyethylene glycol, PEG) ratios have been investigated for magnetic hyperthermia (MHT) application. The water-to-PEG ratio influenced the size, shape, and chemical composition of the NPs, which changes their magnetic properties and hyperthermia (HPT) response. X-ray diffraction (XRD) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) studies reveal the formation of well crystalline inverse spinel structure of Fe3O4 with some Fe0 phases. Morphology of the NPs varies from nearly spherical to elongated to pseudohexagonal to cluster with an increased concentration of PEG. The NPs possess enhanced saturation magnetization ranging from 90 to 98 emu/g. The HPT studies indicated that the NPs show an enough specific absorption rate (SAR) under alternating magnetic field suitable for biological application with hexagonal Fe3O4 being more efficient.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nemati, Z., Alonso, J., Martinez, L.M., Khurshid, H., Garaio, E., Garcia, J.A., Phan, M.H., Srikanth, H.: Enhanced magnetic hyperthermia in iron oxide nano-octopods: size and anisotropy effects. J. Phys. Chem. C. 120, 8370–8379 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b01426
Jalilian, A.R., Panahifar, A., Mahmoudi, M., Akhlaghi, M., Simchi, A.: Preparation and biological evaluation of [67Ga]-labeled- superparamagnetic nanoparticles in normal rats. Radiochim. Acta. 97, 51–56 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1524/ract.2009.1566
Barrow, M., Taylor, A., Murray, P., Rosseinsky, M.J., Adams, D.J.: Design considerations for the synthesis of polymer coated iron oxide nanoparticles for stem cell labelling and tracking using MRI. Chem. Soc. Rev. 44, 6733–6748 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/c5cs00331h
Lartigue, L., Alloyeau, D., Kolosnjaj-Tabi, J., Javed, Y., Guardia, P., Riedinger, A., Péchoux, C., Pellegrino, T., Wilhelm, C., Gazeau, F.: Biodegradation of iron oxide nanocubes: high-resolution in situ monitoring. ACS Nano. 7, 3939–3952 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/nn305719y
Suk, J.S., Xu, Q., Kim, N., Hanes, J., Ensign, L.M.: PEGylation as a strategy for improving nanoparticle-based drug and gene delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 99, 28–51 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2015.09.012
Ling, D., Hyeon, T.: Chemical design of biocompatible iron oxide nanoparticles for medical applications. Small. 9, 1450–1466 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201202111
Cho, M., Cervadoro, A., Ramirez, M., Stigliano, C., Brazdeikis, A., Colvin, V., Civera, P., Key, J., Decuzzi, P.: Assembly of iron oxide nanocubes for enhanced cancer hyperthermia and magnetic resonance imaging. Nanomaterials. 7, 1–12 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7040072
Kumar, C.S.S.R., Mohammad, F.: Magnetic nanomaterials for hyperthermia-based therapy and controlled drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 63, 789–808 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2011.03.008
Fatima, H., Lee, D.W., Yun, H.J., Kim, K.S.: Shape-controlled synthesis of magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles with different iron precursors and capping agents. RSC Adv. 8, 22917–22923 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra02909a
Khurshid, H., Alonso, J., Nemati, Z., Phan, M.H., Mukherjee, P.: Anisotropy effects in magnetic hyperthermia: a comparison between spherical and cubic exchange-coupled FeO / Fe3O4 nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 117, 1–5 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4919250
Guardia, P., Di Corato, R., Lartigue, L., Wilhelm, C., Espinosa, A., Garcia-, M., Gazeau, F., Manna, L., Pellegrino, T.: Water soluble iron oxide nanocubes with high values of specific absorption rate for cancer cell hyperthermia treatment. ACS Nano. 6, 3080–3091 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/nn2048137
Das, R., Alonso, J., Porshokouh, Z.N., Kalappattil, V., Torres, D., Phan, M., Garaio, E., Jose, A., Luis, J., Llamazares, S., Srikanth, H.: Tunable high aspect ratio iron oxide nanorods for enhanced hyperthermia. J. Phys. Chem. C. 120, 10086–10093 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b02006
Simeonidis, K., Morales, M.P., Marciello, M., Angelakeris, M., Chubykalo-fesenko, O., Serantes, D.: In-situ particles reorientation during magnetic hyperthermia application: shape matters twice. Sci. Rep. 6, 1–11 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep38382
Sahu, N.K., Gupta, J., Bahadur, D.: PEGylated FePt–Fe 3 O 4 composite nanoassemblies (CNAs): in vitro hyperthermia, drug delivery and generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Dalton Trans. 44, 9103–9113 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4DT03470H
Rani, B., Punniyakoti, S., Sahu, N.K.: Polyol asserted hydrothermal synthesis of SnO2 nanoparticles for the fast adsorption and photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue cationic dye. New J. Chem. 42, 943–954 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/c7nj03341a
Li, C., Wei, R., Xu, Y., Sun, A., Wei, L.: Synthesis of hexagonal and triangular Fe3O4 nanosheets via seed-mediated solvothermal growth. Nano Res. 7, 536–543 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-014-0421-3
Liu, X.L., Fan, H.M., Yi, J.B., Yang, Y., Choo, E., S, G., Xue, J.M., Fana, D.D., Ding, J.: Optimization of surface coating on Fe3O4 nanoparticles for high performance magnetic hyperthermia agents. J. Mater. Chem. 22, 8235–8244 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/c2jm30472d.
Cullity, B.D., Graham, C.D.: Introduction to magnetic materials, vol. 103. Wiley-IEEE Press ISBN 0-471- 47741-9
Ge, S., Shi, X., Sun, K., Li, C., Uher, C., Baker, J.R., Banaszak Holl, M.M., Orr, B.G.: Facile hydrothermal synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles with tunable magnetic properties. J. Phys. Chem. C. 113, 13593–13599 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp902953t
Guardia, P., Pérez-Juste, J., Labarta, A., Batlle, X., Liz-Marzán, L.M.: Heating rate influence on the synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles: the case of decanoic acid. ChemComm. 46, 6108–6110 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1039/c0cc01179g
Ozel, F., Kockar, H., Karaagac, O.: Growth of Iron oxide nanoparticles by hydrothermal process: effect of reaction parameters on the nanoparticle size. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 28, 823–829 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-014-2707-9
Funding
The authors received financial support from DST-SERB (project grant no. ECR/2016/000301).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rajan, S.A., Sharma, M. & Sahu, N.K. Water-to-PEG Variation: Morphology and Hyperthermic Behaviour of Iron Oxide. J Supercond Nov Magn 33, 1603–1609 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-019-05155-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-019-05155-z