Abstract
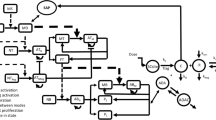
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) represent a therapeutic strategy that has been increasingly used in different diseases. mAbs are highly specific for their targets leading to induce specific effector functions. Despite their therapeutic benefits, the presence of immunogenic reactions is of growing concern. The immunogenicity identified as anti-drug antibodies (ADA) production due to the continuous administration of mAbs may affect the pharmacokinetics (PK) and/or the pharmacodynamics (PD) of mAbs administered to patients. Therefore, the immunogenicity and its clinical impact have been studied by several authors using PK modeling approaches. In this review, the authors try to present all those models under a unique theoretical mechanism-based framework incorporating the main considerations related to ADA formation, and how ADA may affect the efficacy or toxicity profile of some therapeutic biomolecules.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chames P, Van Regenmortel M, Weiss E, Baty D (2009) Therapeutic antibodies: successes, limitations and hopes for the future. Br J Pharmacol 157:220–233. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00190.x
Reichert JM (2013) Antibodies to watch in 2013: mid-year update. MAbs 5:513–517. doi:10.4161/mabs.24990
Sethu S, Govindappa K, Alhaidari M et al (2012) Immunogenicity to biologics: mechanisms, prediction and reduction. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 60:331–344. doi:10.1007/s00005-012-0189-7
Harding F a, Stickler MM, Razo J, DuBridge RB (2010) The immunogenicity of humanized and fully human antibodies: residual immunogenicity resides in the CDR regions. MAbs 2:256–265
Putnam WS, Prabhu S, Zheng Y et al (2010) Pharmacokinetic, pharmacodynamic and immunogenicity comparability assessment strategies for monoclonal antibodies. Trends Biotechnol 28:509–516. doi:10.1016/j.tibtech.2010.07.001
Bendtzen K (2003) Anti-IFN BAb and NAb antibodies: a minireview. Neurology 61:S6–S10
Schwickart M, Mehrzai F, Pearson J et al (2014) Identification and elimination of target-related matrix interference in a neutralizing anti-drug antibody assay. J Immunol Methods 403:52–61. doi:10.1016/j.jim.2013.11.018
Van Beers MMC, Bardor M (2012) Minimizing immunogenicity of biopharmaceuticals by controlling critical quality attributes of proteins. Biotechnol J 7:1473–1484. doi:10.1002/biot.201200065
Singh SK (2010) Impact of product-related factors on immunogenicity of biotherapeutics. J Pharm Sci 100:354–387. doi:10.1002/jps.22276
Ng CM, Loyet KM, Iyer S et al (2014) Modeling approach to investigate the effect of neonatal Fc receptor binding affinity and anti-therapeutic antibody on the pharmacokinetic of humanized monoclonal anti-tumor necrosis factor-α IgG antibody in cynomolgus monkey. Eur J Pharm Sci 51:51–58. doi:10.1016/j.ejps.2013.08.033
Steenholdt C (2013) Use of infliximab and anti-infliximab antibody measurements to evaluate and optimize efficacy and safety of infliximab maintenance therapy in Crohn’ s disease. Dan Med J 60:1–24
Shah B, Mayer L (2010) Current status of monoclonal antibody therapy for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Expert Rev Clin Immunol 6:607–620. doi:10.1586/eci.10.45.Current
Chen X, Hickling T, Kraynov E et al (2013) A mathematical model of the effect of immunogenicity on therapeutic protein pharmacokinetics. AAPS J 15:1141–1154. doi:10.1208/s12248-013-9517-z
Perez Ruixo JJ, Ma P, Chow AT (2013) The utility of modeling and simulation approaches to evaluate immunogenicity effect on the therapeutic protein pharmacokinetics. AAPS J 15:172–182. doi:10.1208/s12248-012-9424-8
Vande Casteele N, Gils A, Singh S et al (2013) Antibody response to infliximab and its impact on pharmacokinetics can be transient. Am J Gastroenterol 108:962–971. doi:10.1038/ajg.2013.12
Pouw MF, Krieckaert CL, Nurmohamed MT et al (2013) Key findings towards optimising adalimumab treatment: the concentration-effect curve. Ann Rheum Dis 60:1–6. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204172
Stubenrauch K, Wessels U, Birnboeck H et al (2010) Subset analysis of patients experiencing clinical events of a potentially immunogenic nature in the pivotal clinical trials of tocilizumab for rheumatoid arthritis: Evaluation of an antidrug antibody ELISA using clinical adverse event-driven immunogenicit. Clin Ther 32:1597–1609. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2010.07.021
Sailstad JM, Amaravadi L, Clements-Egan a et al (2014) A white paper-consensus and recommendations of a global harmonization team on assessing the impact of immunogenicity on pharmacokinetic measurements. AAPS J 16:488–498. doi:10.1208/s12248-014-9582-y
Ternant D, Ducourau E, Perdriger A et al (2013) Relationship between inflammation and infliximab pharmacokinetics in rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Clin Pharmacol 78:1–31. doi:10.1111/bcp.12313
Xu ZH, Lee H, Vu T et al (2010) Population pharmacokinetics of golimumab in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: impact of body weight and immunogenicity. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 48:596–607
Zhu Y, Hu C, Lu M et al (2009) Population pharmacokinetic modeling of ustekinumab, a human monoclonal antibody targeting IL-12/23p40, in patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. J Clin Pharmacol 49:162–175. doi:10.1177/0091270008329556
Ng CM, Stefanich E, Anand BS et al (2006) Pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics of nondepleting anti-CD4 monoclonal antibody (TRX1) in healthy human volunteers. Pharm Res 23:95–103. doi:10.1007/s11095-005-8814-3
Bauer RJ, Dedrick RL, White ML et al (1999) Population pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the anti-CD11a antibody hu1124 in human subjects with psoriasis. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 27:397–420. doi:10.1023/A:1020917122093
Ng CM, Joshi A, Dedrick RL et al (2005) Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic-efficacy analysis of efalizumab in patients with moderate to severe psoriasis. Pharm Res 22:1088–1100. doi:10.1007/s11095-005-5642-4
Kakkar T, Sung C, Gibiansky L et al (2011) Population PK and IgE pharmacodynamic analysis of a fully human monoclonal antibody against IL4 receptor. Pharm Res 28:2530–2542. doi:10.1007/s11095-011-0481-y
Shah DK, Betts AM (2012) Towards a platform PBPK model to characterize the plasma and tissue disposition of monoclonal antibodies in preclinical species and human. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn 39:67–86. doi:10.1007/s10928-011-9232-2
Bourdage JS, Lee TN, Taylor JM et al (2005) Effect of double antigen bridging immunoassay format on antigen coating concentration dependence and implications for designing immunogenicity assays for monoclonal antibodies. J Pharm Biomed Anal 39:685–690. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2005.03.037
Chirmule N, Jawa V, Meibohm B (2012) Immunogenicity to therapeutic proteins: impact on PK/PD and efficacy. AAPS J 14:296–302. doi:10.1208/s12248-012-9340-y
Swann PG, Tolnay M, Muthukkumar S et al (2008) Considerations for the development of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies. Curr Opin Immunol 20:493–499. doi:10.1016/j.coi.2008.05.013
Fasanmade a a, Adedokun OJ, Olson a et al (2010) Serum albumin concentration: a predictive factor of infliximab pharmacokinetics and clinical response in patients with ulcerative colitis. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 48:297–308
Zhou L, Hoofring S a, Wu Y et al (2013) Stratification of antibody-positive subjects by antibody level reveals an impact of immunogenicity on pharmacokinetics. AAPS J 15:30–40. doi:10.1208/s12248-012-9408-8
Joshi A, Bauer R, Kuebler P et al (2006) An overview of the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of efalizumab: a monoclonal antibody approved for use in psoriasis. J Clin Pharmacol 46:10–20. doi:10.1177/0091270005283282
Bonate PL, Sung C, Welch K, Richards S (2009) Conditional modeling of antibody titers using a zero-inflated poisson random effects model: application to Fabrazyme. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn 36:443–459. doi:10.1007/s10928-009-9132-x
Murphy K, Travers P, Walport M (2008) Janeway’s immunobiology. Garl Sci 7:887. doi:10.1086/596249
Savic RM, Jonker DM, Kerbusch T, Karlsson MO (2007) Implementation of a transit compartment model for describing drug absorption in pharmacokinetic studies. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn 34:711–726. doi:10.1007/s10928-007-9066-0
Friberg LE, Karlsson MO (2003) Mechanistic models for myelosuppression. Invest New Drugs 21:183–194
Soto E, Keizer RJ, Trocóniz IF et al (2011) Predictive ability of a semi-mechanistic model for neutropenia in the development of novel anti-cancer agents: two case studies. Invest New Drugs 29:984–995. doi:10.1007/s10637-010-9437-z
Reverberi R, Reverberi L (2007) Factors affecting the antigen-antibody reaction. Blood Transfus 5:227–240. doi:10.2450/2007.0047-07
Foote J, Eisent HN (1995) Kinetic and affinity limits on antibodies produced during immune responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:1254–1256
Barderas R, Desmet J, Timmerman P et al (2008) Affinity maturation of antibodies assisted by in silico modeling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:9029–9034. doi:10.1073/pnas.0801221105
Björkelund H, Gedda L, Andersson K (2011) Avoiding false negative results in specificity analysis of protein–protein interactions. J Mol Recognit 24:81–89. doi:10.1002/jmr.1026
Shah DK, Betts AM (2013) Antibody biodistribution coefficients: inferring tissue concentrations of monoclonal antibodies based on the plasma concentrations in several preclinical species and human. MAbs 5:1–9. doi:10.4161/mabs.23684
Tabrizi M, Bornstein GG, Suria H (2010) Biodistribution mechanisms of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies in health and disease. AAPS J 12:33–43. doi:10.1208/s12248-009-9157-5
Kelley M, Ahene AB, Gorovits B et al (2013) Theoretical considerations and practical approaches to address the effect of anti-drug antibody (ADA) on quantification of biotherapeutics in circulation. AAPS J 15:646–658. doi:10.1208/s12248-013-9468-4
Lee JW, Kelley M, King LE et al (2011) Bioanalytical approaches to quantify “total” and “free” therapeutic antibodies and their targets: technical challenges and PK/PD applications over the course of drug development. AAPS J 13:99–110. doi:10.1208/s12248-011-9251-3
Rojas JR, Taylor RP, Cunningham MR et al (2005) Formation, distribution, and elimination of infliximab and anti-infliximab immune complexes in cynomolgus monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 313:578–585. doi:10.1124/jpet.104.079277.coincident
Mager DE, Jusko WJ (2001) General pharmacokinetic model for drugs exhibiting target-mediated drug disposition. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn 28:507–532
Mager DE (2006) Target-mediated drug disposition and dynamics. Biochem Pharmacol 72:1–10. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2005.12.041
Parra-Guillen ZP, Janda A, Alzuguren P et al (2013) Target-mediated disposition model describing the dynamics of IL12 and IFNγ after administration of a mifepristone-inducible adenoviral vector for IL-12 expression in mice. AAPS J 15:183–194. doi:10.1208/s12248-012-9423-9
Mager DE, Neuteboom B, Efthymiopoulos C et al (2003) Receptor-mediated pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of interferon-beta1a in monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 306:262–270. doi:10.1124/jpet.103.049502
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gómez-Mantilla, J.D., Trocóniz, I.F., Parra-Guillén, Z. et al. Review on modeling anti-antibody responses to monoclonal antibodies. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn 41, 523–536 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10928-014-9367-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10928-014-9367-z