Abstract
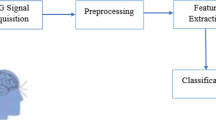
In this study, it has been intended to perform an automatic classification of Electroencephalography (EEG) signals via Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) and to investigate these signals using Wavelet Transform (WT) for diagnosing epilepsy syndrome. EEG signals have been decomposed into frequency sub-bands using WT and a set of feature vectors which were extracted from the sub-bands. Dimensions of these feature vectors have been reduced via Principal Component Analysis (PCA) method and then classified as epileptic or healthy using Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) and ELMAN ANN. Performance evaluation of the used ANN models have been carried out by performing Receiver Operation Characteristic (ROC) analysis.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Trevathan, E., The diagnosis of epilepsy and the art of listening. Neurology 61:13–14, 2003.
Motamedi, G., and Meador, K., Epilepsy and cognition. Epilepsy Behav. 4:S25–S38, 2003.
Faught, E., Epilepsy case studies. USA. Neurol. Clin. 24:291–307, 2006.
Blume, T. W., Diagnosis and management of epilepsy. CMAJ 168(4):441–8, 2003.
SEZER, E., Epilepsi Teşhisi için EEG Sinyal Analizi. Yüksek Lisans Tezi. Selçuk Üniversitesi, Konya, 2008.
Beach, R., and Reading, R., The importance of acknowledging clinical uncertainty in the diagnosis of epilepsy and non-epileptic events. Arch. Dis. Child. 90:1219–1222, 2005.
Noachtar, S., and Rémi, J., The role of EEG in epilepsy: A critical review. Epilepsy Behav. 15:22–33, 2009.
Tzallas, A. T., Tsipouras, M. G., Fotiadis, D. I, Automatic seizure detection based on time-frequency analysis and artificial neural networks. Hindawi Publishing Corporation Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience Vol. 2007, Article ID 80510, 13 Pages.
Patnaik, L. M., and Manyam, O. K., Epileptic EEG detection using neural networks and post-classification. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 91:100–109, 2008.
Subaşı, A., Epileptic seizure detection using dynamic wavelet network. Expert Systems Appl. 29:343–355, 2005.
Ebrahimi, F., Mikaeili, M., Estrada, E., Nazeran, H., Member, S., Automatic sleep stage classification based on EEG signals by using neural networks and wavelet packet coefficients. 30th Annual International IEEE EMBS Conference Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, August 20–24, 2008.
Subaşı, A., EEG signal classification using wavelet feature extraction and a mixture of expert model. Expert Systems Appl. 32:1084–1093, 2007.
Kannathal, N., Puthusserypady, S. K., Min, L. C., Elman neural networks for dynamic modeling of epileptic EEG. Proceedings of the 28th IEEE EMBS Annual International Conference New York City, USA, Aug 30–Sept 3, 2006.
Kıymık, K., İnan, G., Dizibüyük, A., and Akın, M., Comparison of STFT and wavelet transform methods in determining epileptic seizure activity in EEG signals for real time application. Comput. Biol. Med. 35(7):603–616, 2004.
Subaşı, A., and Erçelebi, E., Classification of EEG Signals Using Neural Network and Logistic Regression. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 78(2):87–99, 2005.
Mohseni, H. R., Maghsoudi, A., Shamsollahi, B., Seizure detection in EEG signals: A comparison of different approaches. Biomedical Signal and Image Processing Laboratory (BiSIPL), Sharif University of Technology, Tehran. Iran, 2006.
Jahankhani, P., Kodogiannis, V., Revett, C., EEG signal classification using wavelet feature extraction and neural networks. IEEE John Vincent Atanasoff 2006 International Symposium on Modern Computing (JVA'06) pp. 120–124, 2006.
Subaşı, A., Automatic recognition of alertness level from EEG by using neural network and wavelet coefficients. Expert Systems Appl. 28:701–711, 2005.
Güler, İ., Übeyli, E. D., Güler, N. F., A Mixture of experts network structure for EEG signals classification. Engineering in Medicine and Biology 27th Annual Conference Shanghai, China, September 1–4, 2005.
Anderson, C. W., Devulapalli, S. V., and Stolz, E. A., Determining mental state from EEG signals using neural networks. Sci. Program. 4:171–183, 1995.
Neural Networks, http://www.doc.ic.ac.uk∼nd/surprise_96/Journal/vol4/cs11/report.html, 2007.
Miner, N. E., An introduction to wavelet theory and analysis. Sandia Report, NM, October: 1–25, 1998.
Polikar, R., The wavelet tutorial. http://www.public.iastate.edu/%7erpolikar/WAVELETS/WTpart1.html, 2000.
Tansel, I. N., Mekdeci, C., Rodriguez, O., and Uragun, B., Monitoring drill conditions with wavelet based encoding and neural networks. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manufact 33(4):559–575, 1993.
Tangirala, A. K., Multirate control and multiscale monitoring of chemical processes. University of Alberta, Edmonton, pp. 133–165, 2001.
Güler, İ., and Übeyli, E. D., Adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system for classification of EEG signals using wavelet coefficients. J. Neurosci. Methods 148:113–121, 2005.
García-Altés, A., Santín, D., and Barenys, M., Applying artificial neural networks to the diagnosis of organic dyspepsia. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 16:331–346, 2007.
Bhattacharjee, C., Sen, D., Sarkar, P., Data, S., and Bhattacharya, P. K., Studies on the application of different ANNs to predict permeate flux in rotating disk membrane modules: A case study with MATLAB™. Desalination and Water Treatment 2:170–184, 2009.
Andrzejak, R. G., Lehnertz, K., Rieke, C., Mormann, F., David, P., Elger, C. E., Klinik für Epileptologie. http://www.epileptologie-bonn.de/cms/front_content.php?idcat=193, Germany: Bonn University, 2001.
Naz, E., Farooq, U., Naz, T., Analysis of principal component analysis-based and fisher discriminant analysis-based face recognition algorithms. 2nd International Conference on Emerging Technologies Peshawar, Pakistan, 13–14 November 2006.
Fawcett, T., An introduction to ROC analysis. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 27:861–874, 2006.
Metz, C. E., Basic principles of ROC analysis. Sem Nuc Med. 283–298, 1978.
Mitra, S., Indiveri, G., Spike-based synaptic plasticity and classification on VLSI. The Neuromorphic Engineer a publication of ine-web.org, 10.2417/1200904.1636.
Acknowledgements
This study has been conducted as the Graduate Thesis of Esma SEZER from S.U. Institute of Science. We would like to give our special thanks to Selçuk University for their material support and contributions towards scientific research projects [5].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Işik, H., Sezer, E. Diagnosis of Epilepsy from Electroencephalography Signals Using Multilayer Perceptron and Elman Artificial Neural Networks and Wavelet Transform. J Med Syst 36, 1–13 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-010-9440-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-010-9440-0