Abstract
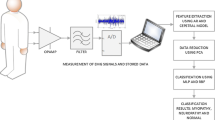
This work investigates the performance of neuro-fuzzy system for analyzing and classifying EMG signals recorded from normal, neuropathy, and myopathy subjects. EMG signals were obtained from 177 subjects, 60 of them had suffered from neuropathy disorder, 60 of them had suffered from myopathy disorder, and rest of them had been normal. Coefficients that were obtained from the EMG signals using Autoregressive (AR) analysis was applied to neuro-fuzzy system. The classification performance of the feature sets was investigated for three classes.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basmajian, J., and De Luca, C. J., Muscles alive. Williams&Wilkins, Baltimore, 1985.
Deluca, C. J., Towards understanding the EMG signal ch 3 of muscles alive, fourth edition. Williams&Wilkonson, Bultimore, 1978.
Stalberg, E., Andreassen, S., Falck, B., Lang, H., Rosenfalck, A., and Trojaborg, W., Quantitative analysis of individual motor unit potentials: a proposition for standardized terminology f1and criteria for measurement. Journal of Clinical Neurophysiology. 3:4313–348, 1986.
Cadzow, J. A. (1982). ARMA modeling of time series, IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence.
Marple, S. L., Digital Spectral analysis with application. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1987.
Graupe, D., and Cline, W. K., Functional Separation of EMG Signals via ARMA Identification Methods for Prosthetic Control Purposes. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics. 5:252–259, 1975.
Coatrieux, J. L., Interference electromyogram processing—Part II: experimental and simulated EMG AR modeling. Electromyography Clinical Neurophysiologie. 23:481–490, 1983.
Maranzana, M. F., Molinari, R., and Somma-Riva, G., The parametrization of the electromyographic signal: an approach based on simulated EMG signals. Electromyography Clinical Neurophysiologie. 24:47–65, 1984.
Basmajian, J. V. et al. (1985). Electrodiagnostic Model for Motor Unit Action Potential (MUAP) Generation, American Journal of Physical Medicine, 64(6).
Kang, W. J., Shiu, J. R., Cheng, C. K., Lai, J. S., Tsao, H. W., and Kuo, T. S., The application of cepstral coefficients and maximum likelihood method in EMG pattern recognition. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering. 42:8777–785, 1995. doi:10.1109/10.398638.
Abel, E. W., Zacharia, P. C., Forster, A., and Farrow, T. L., Farrow, neural network analysis of the EMG interference pattern. Medical engineering and physics. 18:12–17, 1996. doi:10.1016/1350-4533(95)00032-1.
Savelberg, H. H., and Herzog, W., Prediction of dynamic tendon forces from electromyographic signals: an artificial neural network approach. Journal of Neuroscience Methods. 30;78:1–265–74, 1997.
Kumaravel, N., and Kavitha, V., Automatic diagnosis of neuro-muscular diseases using neural network. Biomedical sciences instrumentation. 30:245–250, 1994.
Pattichis, C. S., and Elia, G. A., Autoregressive and cepstral analysis the motor unit potential. Medical engineering and physics. 21:405–419, 1999. doi:10.1016/S1350-4533(99)00072-7.
Nussbaum, M. A., Martin, B. J., and Chaffin, D. B., A neural network model for simulation of torso muscle coordination. Journal of Biomechanics. 30:3251–258, 1997. doi:10.1016/S0021-9290(96)00138-8.
Hiraiwa, A., Shimohara, K., Tokunaga, Y. (1989). EMG Pattern Analysis and Classification by Neural Network. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Systems,Man and Cybernetics. pp. 1113–1115.
Farry, K. A., and Walker, I. D., Myoelectric teleoperation of a complex robotic hand. IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation. 12:5775–788, 1996. doi:10.1109/70.538982.
Sarbadhikari, S. N., A neural network confirms that physical exercise reverses EEG changes in depressed rats. Medical engineering and physics. 17:18579–582, 1995.
Kellner, B., Stief, C. G., Hinrichs, H., and Hartung, C., Computerized classification of corpus cavernosum EMG signals by use of discrimant analysis and ANN to support diagnosis of erectile dysfunction. Urological research. 28:6–13, 2000. doi:10.1007/s002400050002.
Güler N. F., Koçer S. (2005). Classification of EMG Signals Using PCA and FFT. Journal of Medical Systems, 29(3), (June 2005).
Güler N. F., Koçer S (2005). Use of Support Vector Machines and Neural Network in Diagnosis of Neuromuscular Disorders, Journal of Medical Systems, 29(3), (June 2005).
Nauck, D., and Kruse, R., A neuro-fuzzy method to learn fuzzy classification rules from data. Fuzzy sets and systems. 89:277–288, 1997. doi:10.1016/S0165-0114(97)00009-2.
Nauck, D., and Kruse, R., Obtaining interpretable fuzzy classification rules from medical data. Artificial intelligence in medicine. 16:149–169, 1999. doi:10.1016/S0933-3657(98)00070-0.
Şeker, H., Evans, D. H., Aydin, N., and Yazgan, E., Compensatory fuzzy neural Networks-based intelligent detection of abnormal neonatal cerebral Doppler ultrasound waveforms. IEEE transactions on information technology in biomedicine. 5:3187–194, 2001. doi:10.1109/4233.945289.
Guler, İ., Hardalaç, F., and Barisci, N., Application of FFT analyzed cardiac doppler signals to fuzzy algorithm. Computers in biology and medicine. 32:435–444, 2002. doi:10.1016/S0010-4825(02)00021-5.
Szabo, B., Szabo, R., Shankar, R., Urso, A, & Kolluri, S. (1990). A Data Acquisition and Signal Processing System for EMG and Acceleration Signals, IEEE Southeastcon, New Orleans, (April 1990).
Proakis, J. G., and Manolakis, D. G., Digital Signal Processing-Principles, Algorithms, and Applications. Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ, 1996.
Burg, J. P., Maximum entropy spectral analysis. Proceedings of the 37th Meeting of the Society of Exploration Geophysicists, Oklahoma City, 1967. In: ChilderD. G. (Ed.), Modern spectrum analysisIEEE, New York, 1967.
Kay, S. M., Maximum entropy spectral estimation using the analytical signal. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics Speech Signal Processing. 26:467–469, 1978. doi:10.1109/TASSP.1978.1163127.
Pardey, J., Roberts, S. & Tarassenko L. A review of parametric modeling techniques for EEG analysis.
Akaike, H., A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Transactions Automatic Control. 19:716–723, 1974. doi:10.1109/TAC.1974.1100705.
Nauck, D., Klawonn, F., and Kruse, R., Foundations of Neuro-Fuzzy systems. Wiley, Chichester, 1997.
Nauck, D., Kruse, R. (1997). What are Neuro-Fuzzy Classifiers, Proc. Seventh International Fuzzy Systems Association World Congress IFSA’97, 4:228–233, Academia Prague.
Buckley, J. J., and Hayashi, Y., Fuzzy neural networks: a survey. Fuzzy sets and systems. 66:1–13, 1994. doi:10.1016/0165-0114(94)90297-6.
Nauck, D., and Kruse, R., NEFCLASS-a neuro -fuzzy approach for the classification of data, Proc. 1995 ACM Symposium on Applied Computing, Nashville. ACM, New York, pp. 461–465, 1995.
Nauck, D., Nauck, U., Kruse, R. (1996). Generating classification rules with the neuro-fuzzy system NEFCLASS, Proc. Biennial Conference of the North American Fuzzy Information Processing Society NAFIPS’96, Berkeley, CA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koçer, S. Classification of Emg Signals Using Neuro-Fuzzy System and Diagnosis of Neuromuscular Diseases. J Med Syst 34, 321–329 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-008-9244-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-008-9244-7