Abstract
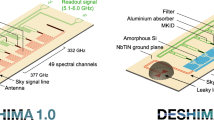
The South Pole Telescope Summertime Line Intensity Mapper (SPT-SLIM) is a pathfinder experiment that will demonstrate the use of on-chip filter-bank spectrometers for mm-wave line intensity mapping. The SPT-SLIM focal plane consists of 18 dual-polarization filter-bank spectrometers covering 120–180 GHz with resolving power of 300, coupled to aluminum kinetic inductance detectors. A compact cryostat holds the detectors at 100 mK. SPT-SLIM will be deployed to the 10-m South Pole Telescope for observations during the 2023–2024 austral summer without removing the primary receiver. We discuss the overall instrument design, expected detector performance, and sensitivity to the carbon monoxide line signal at \(0.5< z < 2\). The technology and observational techniques demonstrated by SPT-SLIM will enable next-generation line intensity mapping experiments that constrain cosmology beyond the redshift reach of galaxy surveys.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Kovetz et al. arXiv eprints:1709.09066 (2017)
K.S. Karkare et al., Phys. Rev. D. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevD.98.043529
A. Moradinezhad Dizgah et al., arXiv eprints:2110.00014 (2021)
Y. Gong et al., Astrophys. J. 745, 49 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1088/0004-637X/745/1/49
G. Keating et al., Astrophys. J. 901, 141 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3847/1538-4357/abb08e
E. Shirokoff et al., Proc. SPIE 8452, 84520R (2012). https://doi.org/10.1117/12.927070
A. Endo et al., J. Astron. Telesc. Instrum. Syst. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1117/1.JATIS.5.3.035004
G. Cataldo et al., Acta Astronaut. 162, 155 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actaastro.2019.06.012
A.T. Crites et al., Proc. SPIE 9153, 91531W (2014). https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2057207
N.F. Cothard et al., J. Low Temp. Phys. 199, 878 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-019-02297-1
G. Robson et al., J. Low Temp. Phys. This Special Issue (2021)
P. Barry et al., J. Low Temp. Phys. This Special Issue (2021)
S. Paine, The am atmospheric model. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.1193646 (2018)
G. Sun et al., Astrophys. J. 856, 107 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3847/1538-4357/aab3e3
A. Lidz et al., Astrophys. J. 825, 143 (2016). https://doi.org/10.3847/0004-637X/825/2/143
Y.T. Cheng et al., Astrophys. J. 901, 142 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3847/1538-4357/abb023
J.E. Carlstrom et al., Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 123, 568 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1086/659879
J.A. Sobrin et al., arXiv eprints:2106.11202 (2021)
J. Kim et al., Proc. SPIE 10708, 107082S (2018). https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2301005
J. Redford et al., Proc. SPIE 10708, 107081O (2018). https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2313666
K.S. Karkare et al., J. Low Temp. Phys. 199, 849 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-020-02407-4
Q.Y. Tang et al., J. Low Temp. Phys. 199, 362 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-020-02341-5
J. Baselmans et al., Astron. Astrophys. 601, A89 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/201629653
R. McGeehan et al., J. Low Temp. Phys. 193, 1024 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-018-2061-6
K. Bandura et al., J. Astron. Instrum. 5(4), 1641005 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1142/S2251171716410051
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by Fermilab under award LDRD-2021-048 and by the National Science Foundation under award AST-2108763. K. S. Karkare is supported by an NSF Astronomy and Astrophysics Postdoctoral Fellowship under award AST-2001802.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karkare, K.S., Anderson, A.J., Barry, P.S. et al. SPT-SLIM: A Line Intensity Mapping Pathfinder for the South Pole Telescope. J Low Temp Phys 209, 758–765 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-022-02702-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-022-02702-2