Abstract
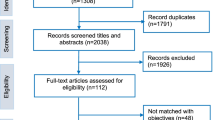
The city of Baltimore is a typical, large, urban center in the United States with several major academic medical institutions surrounded by disadvantaged neighborhoods with multiple poor health indices. In order to understand the extent to which academic research agendas reflect the health concerns of Baltimore’s local population, a systematic review was conducted to identify research about four key, health-related topic areas. We classified papers on: disease prevalence and health status, utilization of health services, population-based interventions, and the unmet health needs of Baltimore City residents. Approximately 4,150 citations were identified in the search and two levels of screening yielded a total of 288 papers. The majority of articles (n = 189) examined prevalence of health conditions such as Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV), mental health and mental disorders, and sexually transmitted diseases. Papers about specific target populations focused primarily on adults, African Americans, and females. Despite a significant body of research concerning several health conditions and priority populations, significant gaps in knowledge about health services utilization, community interventions, unmet health needs, and the prevalence of specific health issues remain. This review provides valuable insight into the extent of health research conducted about the city of Baltimore and whether community health priorities have been investigated. It provides a basis for examining the potential directions of academic research centers to effectively identify and address collective, urban health priorities of the communities in which they reside.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrulius, D. P., & Inner City Health Care. (1997). The urban health penalty: New dimensions and directions in inner city health care. Philadelphia: American College of Physicians.
Galea, S., & Vlahov, D. (2005). Handbook of urban health: Populations, methods, and practice. New York: Springer.
Galea, S., Freudenberg, N., & Vlahov, D. (2005). Cities and population health. Social Science and Medicine, 60, 1017–1033.
(2007). Baltimore City health status report 2004. Baltimore: Baltimore City Health Department.
(1999). The President’s council on urban health: report on an Urban Health initiative. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press.
Wu, Y., Burns, J., Stanton, B., et al. (2005). Influence of prior sexual risk experience on response to intervention targeting multiple risk behaviors among adolescents. Journal of Adolescent Health, 36(1), 56–63.
Loughlin, A., Schwartz, R., & Strathdee, S. (2004). Prevalence and correlates of HCV infection among methadone maintenance attendees: implications for HCV treatment. International Journal of Drug Policy, 15(2), 93–101.
Juday, T., Wu, A., Celentano, D., Frick, K., Wang, M., & Vlahov, D. (2003). The role of Medicaid HMO enrollment in the longitudinal utilization of medical care services in a cohort of injecting drug users in Baltimore, Maryland. Substance Abuse, 24(2), 27–41.
Latkin, C., Tobin, K. E., & Gilbert, S. H. (2002). Shun or support: The role of religious behaviors and HIV-related health care among drug users in Baltimore, Maryland. AIDS and Behavior, 6(4), 321–329.
Nelson, K., Galai, N., Safaeian, M., Strathdee, S., Celentano, D., & Vlahov, D. (2002). Temporal trends in the incidence of human immunodeficiency virus infection and risk behavior among injection drug users in Baltimore, Maryland, 1988–1998. American Journal of Epidemiology, 156(7), 641–653.
Vertefeuille, J., Marx, M., Tun, W., Huettner, S., Strathdee, S., & Vlahov, D. (2000). Decline in self-reported high-risk injection-related behaviors among HIV-seropositive participants in the Baltimore needle exchange program. AIDS and Behavior, 40(2), 381–388.
Carneiro, M., Fuller, C., Doherty, M., & Vlahov, D. (1999). HIV prevalence and risk behaviors among new initiates into injection drug use over the age of 40 years old. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 54(1), 83–86.
Allen, D. M., Onorato, I. M., & Green, T. A. (1992). HIV infection in intravenous drug users entering drug treatment, United States, 1988–1989: Field services branch of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. American Journal of Public Health, 82(4), 541–546.
Solomon, L., Frank, R., Vlahov, D., & Astemborski, J. (1991). Utilization of health services in a cohort of intravenous drug users with known HIV-1 serostatus. American Journal of Public Health, 81(2), 1285–1290.
Burke, J. G., Thieman, L. K., Gielen, A. C., O’Campo, P., & McDonnell, K. A. (2005). Intimate partner violence, substance use, and HIV among low-income women: Taking a closer look. Violence Against Women, 11(9), 1140–1161.
Lai, S., Lima, J. A., Lai, H., et al. (2005). Human immunodeficiency virus 1 infection, cocaine, and coronary calcification. Archives of Internal Medicine, 165(6), 690–695.
Tobin, K. E., Tang, A. M., Gilbert, S. H., & Latkin, C. A. (2004). Correlates of HIV antibody testing among a sample of injection drug users: The role of social and contextual factors. AIDS Behavior, 8(2), 303–310.
Latkin, C. A., Forman-Hoffman, V. L., D’Souza, G., & Knowlton, A. R. (2004). Associations between medical service use and HIV risk among HIV-positive drug users in Baltimore, MD. AIDS Care, 16(7), 901–908.
O’Toole, T. P., Arbelaez, J., & Haggerty, C. (2004). The urban safety net: Can it keep people healthy and out of the hospital? Journal of Urban Health, 81(2), 179–190.
Tun, W., Gange, S. J., Vlahov, D., Strathdee, S. A., & Celentano, D. D. (2004). Increase in sexual risk behavior associated with immunologic response to highly active antiretroviral therapy among HIV-infected injection drug users. Clinical Infectious Disease, 38(8), 1167–1174.
Solomon, L., Flynn, C., Muck, K., & Vertefeuille, J. (2004). Prevalence of HIV, syphilis, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C among entrants to Maryland correctional facilities. Journal of Urban Health, 81(1), 25–37.
Sethi, A. K., Celentano, D. D., Gange, S. J., Gallant, J. E., Vlahov, D., & Farzadegan, H. (2004). High-risk behavior and potential transmission of drug-resistant HIV among injection drug users. Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome, 35(5), 503–510.
Nettles, R. E., Mazo, D., Alwood, K., et al. (2004). Risk factors for relapse and acquired rifamycin resistance after directly observed tuberculosis treatment: A comparison by HIV serostatus and rifamycin use. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 38(5), 731–736.
Erbelding, E. J., Chung, S., & Zenilman, J. M. (2004). Following-up for HIV test results: what limits return in an STD clinic population? International Journal of STDs and AIDS, 15(2), 29–32.
Shan, H., Piwowar-Manning, E., Thompson, R. E., & Brooks Jackson, J. (2003). HIV-1 plasma RNA level and CD4 cell count in a large urban HIV-1-infected patient population from 1997 to 2000. International Journal of STD and AIDS, 14(11), 740–744.
Sethi, A. K., Celentano, D. D., Gange, S. J., Moore, R. D., & Gallant, J. E. (2003). Association between adherence to antiretroviral therapy and human immunodeficiency virus drug resistance. Clinical Infectious Disease, 37(8), 1112–1118.
McDonnell, K. A., Gielen, A. C., & O’Campo, P. (2003). Does HIV status make a difference in the experience of lifetime abuse? Descriptions of lifetime abuse and its context among low-income urban women. Journal of Urban Health, 80(3), 494–509.
Bernstein, K. T., Jacobson, L. P., Jenkins, F. J., Vlahov, D., & Armenian, H. K. (2003). Factors associated with human herpes virus type 8 infection in an injecting drug user cohort. Sexually Transmitted Diseases, 30(3), 199–204.
Semba, R. D., Shah, N., & Vlahov, D. (2002). Risk factors and cumulative incidence of anaemia among HIV-infected injection drug users. International Journal of STDs and AIDS, 13(2), 119–123.
Latkin, C. A., Knowlton, A. R., & Sherman, S. (2001). Routes of drug administration, differential affiliation, and lifestyle stability among cocaine and opiate users: implications to HIV prevention. Journal of Substance Abuse, 13(1–2), 89–102.
Knowlton, A. R., Hoover, D. R., Chung, S. E., Celentano, D. D., Vlahov, D., & Latkin, C. A. (2001). Access to medical care and service utilization among injection drug users with HIV/AIDS. Drug Alcohol Dependence, 64(2), 55–62.
Pilowsky, D. J., Knowlton, A. R., Latkin, C. A., Hoover, D. R., Chung, S. E., & Celentano, D. D. (2001). Children of injection drug users: impact of parental HIV status, AIDS, and depression. J Urban Health, 78(2), 327–339.
McDonnell, K. A., Gielen, A. C., Wu, A., O’Campo, P., & Faden, R. (2000). Measuring health related quality of life among women living with HIV. Quality of Life Research, 9(8), 931–940.
Song, J. Y., Safaeian, M., Strathdee, S. A., Vlahov, D., & Celentano, D. D. (2000). The prevalence of homelessness among injection drug users with and without HIV infection. Journal of Urban Health, 77(4), 678–687.
Monterroso, E. R., Hamburger, M. E., Vlahov, D., et al. (2000). Prevention of HIV infection in street-recruited injection drug users. The Collaborative Injection Drug User Study (CIDUS). Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome, 25(3), 63–70.
Shah, N. G., Celentano, D., Vlahov, D., et al. (2000). Correlates of enrollment in methadone maintenance treatment programs differ by HIV-serostatus. AIDS, 14(13), 2035–2043.
Doherty, M. C., Garfein, R., Monterroso, E. R., Latkin, C., & Vlahov, D. (2000). Gender differences in the initiation of injection drug use among young adults. Journal of Urban Health, 77(3), 396–414.
Ahdieh, L., Munoz, A., Vlahov, D., Trimble, C. L., Timpson, L. A., & Shah, K. (2000). Cervical neoplasia and repeated positivity of human papillomavirus infection in human immunodeficiency virus-seropositive and -seronegative women. American Journal of Epidemiology, 151(12), 1148–1157.
Strathdee, S. A., Celentano, D. D., Shah, N., et al. (1999). Needle-exchange attendance and health care utilization promote entry into detoxification. Journal of Urban Health, 76(2), 448–460.
Sterling, T. R., Alwood, K., Gachuhi, R., et al. (1999). Relapse rates after short-course (6-month) treatment of tuberculosis in HIV-infected and uninfected persons. AIDS, 13(14), 1899–1904.
Van Ameijden, E. J., Krol, A., Vlahov, D., Flynn, C., Van Haastrecht, H. J., & Coutinho, R. A. (1999). Pre-AIDS mortality and morbidity among injection drug users in Amsterdam and Baltimore: an ecological comparison. Substance Use and Misuse, 34(6), 845–865.
Celentano, D. D., Vlahov, D., Cohn, S., Shadle, V. M., Obasanjo, O., & Moore, R. D. (1998). Self-reported antiretroviral therapy in injection drug users. Journal of the American Medical Association, 280(2), 544–546.
Comer, J. A., Flynn, C., Regnery, R. L., Vlahov, D., & Childs, J. E. (1996). Antibodies to Bartonella species in inner-city intravenous drug users in Baltimore, Md. Archives of Internal Medicine, 156(21), 2491–2495.
Latkin, C. A., Mandell, W., Vlahov, D., Oziemkowska, M., & Celentano, D. D. (1996). The long-term outcome of a personal network-oriented HIV prevention intervention for injection drug users: The SAFE Study. American Journal of Community Psychology, 24(3), 341–364.
Garfein, R. S., Vlahov, D., Galai, N., Doherty, M. C., & Nelson, K. E. (1996). Viral infections in short-term injection drug users: the prevalence of the hepatitis C, hepatitis B, human immunodeficiency, and human T-lymphotropic viruses. American Journal of Public Health, 86(5), 655–661.
Crum, R. M., Lillie-Blanton, M., & Anthony, J. C. (1996). Neighborhood environment and opportunity to use cocaine and other drugs in late childhood and early adolescence. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 43(3), 155–161.
Levine, O. S., Vlahov, D., Brookmeyer, R., Cohn, S., & Nelson, K. E. (1996). Differences in the incidence of hepatitis B and human immunodeficiency virus infections among injecting drug users. Journal of Infectious Diseases, 173(3), 579–583.
Chaulk, C. P., Moore-Rice, K., Rizzo, R., & Chaisson, R. E. (1995). Eleven years of community-based directly observed therapy for tuberculosis. Journal of the American Medical Association, 274(12), 945–951.
Nelson, K. E., Vlahov, D., Solomon, L., Cohn, S., & Munoz, A. (1995). Temporal trends of incident human immunodeficiency virus infection in a cohort of injecting drug users in Baltimore, Md. Archives of Internal Medicine, 155(12), 1305–1311.
Santelli, J. S., Celentano, D. D., Rozsenich, C., et al. (1995). Interim outcomes for a community-based program to prevent perinatal HIV transmission. AIDS Education and Prevention, 7(3), 210–220.
Thomas, D. L., Cannon, R. O., Shapiro, C. N., Hook, E. W. R., Alter, M. J., & Quinn, T. C. (1994). Hepatitis C, hepatitis B, and human immunodeficiency virus infections among non-intravenous drug-using patients attending clinics for sexually transmitted diseases. Journal of Infectious Disease, 169(5), 990–995.
Battjes, R. J., Pickens, R. W., Haverkos, H. W., & Sloboda, Z. (1994). HIV risk factors among injecting drug users in five US cities. AIDS, 8(5), 681–687.
Nelson, K. E., Vlahov, D., Galai, N., Astemborski, J., & Solomon, L. (1994). Preparations for AIDS vaccine trials. Incident human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infections in a cohort of injection drug users in Baltimore, Maryland. AIDS Research and Human Retroviruses, 10(Suppl 2), S201–S205.
Zuckerman, C. J., & Masters, C. F. (1993). Prevalence of human immunodeficiency virus-1 infection in a Baltimore acute care hospital. Maryland Medical Journal, 42(8), 765–769.
Butz, A. M., Hutton, N., Joyner, M., et al. (1993). HIV-infected women and infants. Social and health factors impeding utilization of health care. Journal of Nurse Midwifery, 38(2), 103–109.
Kelen, G. D., Green, G. B., Purcell, R. H., et al. (1992). Hepatitis B and hepatitis C in emergency department patients. The New England Journal of Medicine, 326(21), 1399–1404.
Wiktor, S. Z., Cannon, R. O., Atkinson, W. L., et al. (1992). Infection with human T lymphotropic virus types I and II in sexually transmitted disease clinics in Baltimore and New Orleans. Journal of Infectious Disease, 165(5), 920–924.
Quinn, T., Groseclose, S. L., Spence, M., Provost, V., & Hook, E. W. R. (1992). Evolution of the human immunodeficiency virus epidemic among patients attending sexually transmitted disease clinics: A decade of experience. Journal of Infectious Diseases, 165(3), 541–544.
Zenilman, J. M., Erickson, B., Fox, R., Reichart, C. A., & Hook, E. W. R. (1992). Effect of HIV posttest counseling on STD incidence. Journal of the American Medical Association, 267(6), 843–845.
Neims, S. R., Fantry, L. E., & Lee, E. U. (1992). Tuberculin positivity among the homeless. Journal of Health Care for the Poor and Underserved, 3(2), 263–269.
Nelson, K., Vlahov, D., Cohn, S., Lindsay, A., Solomon, L., & Anthony, J. C. (1991). Human immunodeficiency virus infection in diabetic intravenous drug users. Journal of American Medical Association, 266(16), 2259–2261.
Matuszak, D. L., Panny, S. R., Patel, J., & Israel, E. (1990). HIV antibody seroprevalence among childbearing women surveyed in Maryland. Public Health Reports, 105(6), 562–566.
Erickson, B., Wasserheit, J. N., Rompalo, A., Brathwaite, W., Glasser, D., & Hook, E. W. R. (1990). Routine voluntary screening in STD clinic clients: Characterization of infected clients. Sexually Transmitted Diseases, 17(4), 194–199.
Quinn, T. C., Cannon, R. O., Glasser, D., et al. (1990). The association of syphilis with risk of human immunodeficiency virus infection in patients attending sexually transmitted disease clinics. Archives of Internal Medicine, 150(6), 1297–1302.
Semba, R. D., Shah, N., & Vlahov, D. (2001). Improvement of anemia among HIV-infected injection drug users receiving highly active antiretroviral therapy. Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes, 26(4), 315–319.
Hetherington, S. E., Harris, R. M., Bausell, R. B., Kavanagh, K. H., & Scott, D. E. (1996). AIDS prevention in high-risk African American women: Behavioral, psychological, and gender issues. Journal of Sex and Marital Therapy, 22(3), 9–21.
Golden, M. R., Rompalo, A., Fantry, L. E., et al. (1996). Early intervention for human immunodeficiency virus in Baltimore sexually transmitted diseases clinics: Impact on gonorrhea incidence in patients infected with HIV. Sexually Transmitted Diseases, 23(5), 370–377.
Dancheck, B., Semba, R. D., Tang, A. M., Thomas, A. M., Smit, E., & Vlahov, D. (2005). Injection drug use is an independent risk factor for iron deficiency and iron deficiency anemia among HIV-seropositive and HIV-seronegative women. Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes, 40(2), 198–201.
Sherman, S. G., Rusch, M., & Golub, E. T. (2004). Correlates of safe syringe acquisition and disposal practices among young IDU’s: broadening our notion of risk. Journal of Drug Issues, 34(4), 895–912.
Latkin, C. (1998). Outreach in natural settings: The use of peer leaders for HIV prevention among injecting drug users’ networks. Public Health Reports, 113(Suppl 1), 151–159.
Goodwin, R., & Eaton, W. (2005). Asthma, suicidal ideation, and suicide attempts: Findings from the Baltimore Epidemiologic Catchment Area follow-up. American Journal of Public Health, 95(4), 717–722.
Larson, S., Owens, P., Ford, D., & Eaton, W. (2001). Depressive disorder, dysthymia, and risk of stroke: thirteen-year follow-up from the Baltimore Epidemiologic Catchment Area Study. Stroke, 32(9), 1979–1983.
Allen, E. C., Combs-Orme, T., McCarter, R., & Grossman, L. S. (2000). Self-reported depression symptoms in school-age children at the time of entry into foster care. Ambulatory Child Health, 6(1), 45–57.
Cooper-Patrick, L., Gallo, J., Powe, N., Steinwachs, D., Eaton, W., & Ford, D. (1999). Mental health service utilization by African Americans and Whites: The Baltimore epidemiologic catchment area follow-up. Medical Care, 37(10), 1034–1045.
Lyketsos, C. G., Chen, L. S., & Anthony, J. C. (1999). Cognitive decline in adulthood: an 11.5-year follow-up of the Baltimore Epidemiologic Catchment Area study. American Journal of Psychiatry, 156(1), 58–65.
Cooper-Patrick, L., Crum, R., Pratt, L., Eaton, W., & Ford, D. (1999). The psychiatric profile of patients with chronic diseases who do not receive regular medical care. International Journal of Psychiatry in Medicine, 29(2), 165–180.
Muntaner, C., Eaton, W., Diala, C., Kessler, R., & Sorlie, P. (1998). Social class, assets, organizational control and the prevalence of common groups of psychiatric disorders. Social Science and Medicine, 47(12), 2043–2053.
Weist, M., Paskewitz, D., Warner, B., & Flaherty, L. (1996). Treatment outcome of school-based mental health services for urban teenagers. Community Mental Health Journal, 32(2), 149–157.
Fishbein, D. H., Hyde, C., Eldreth, D., et al. (2005). Neurocognitive skills moderate urban male adolescents’ responses to preventive intervention materials. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 82(1), 47–60.
Gielen, A. C., McDonnell, K. A., O’Campo, P., & Burke, J. G. (2005). Suicide risk and mental health indicators: do they differ by abuse and HIV status? Women’s Health Issues, 15(2), 89–95.
Meyer, C. M., Armenian, H., Eaton, W., & Ford, D. (2004). Incident hypertension associated with depression in the Baltimore catchment area follow-up study. Journal of Affected Disorders, 83(2), 127–133.
Coccaro, E. F., Schmidt, C. A., Samuels, J. F., & Nestadt, G. (2004). Lifetime and 1-month prevalence rates of intermittent explosive disorder in a community sample. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 65(6), 820–824.
O’Toole, T. P., Arbelaez, J., & Lawrence, R. S. (2004). Medical debt and aggressive debt restitution practices: Predatory billing among the urban poor. Journal of General Internal Medicine, 19(7), 772–778.
Kuo, W. H., Gallo, J. J., & Eaton, W. W. (2004). Hopelessness, depression, substance disorder, and suicidality—A 13-year community-based study. Social Psychiatry Psychiatric Epidemiology, 39(6), 497–501.
Erbelding, E. J., Hutton, H. E., Zenilman, J. M., Hunt, W. P., & Lyketsos, C. G. (2004). The prevalence of psychiatric disorders in sexually transmitted disease clinic patients and their association with sexually transmitted disease risk. Sexually Transmitted Diseases, 31(1), 8–12.
Rosenblatt, A., Mehta, K. M., Romanoski, A., Eaton, W., & Lyketsos, C. (2003). Major depression and cognitive decline after 11.5 years: Findings from the ECA study. The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 191(12), 827–830.
Owens, P. L., Hoagwood, K., Horwitz, S. M., et al. (2002). Barriers to children’s mental health services. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 41(6), 731–738.
Samuels, J., Eaton, W. W., Bienvenu, O., Jr., Brown, C. H., Costa, P. T. J., & Nestadt, G. (2002). Prevalence and correlates of personality disorders in a community sample. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 180, 536–542.
Kuo, W. H., Gallo, J., & Tien, A. (2001). Incidence of suicide ideation and attempts in adults: The 13-year follow-up of a community sample in Baltimore, Maryland. Psychological Medicine, 31(7), 1181–1191.
Crum, R. M., & Pratt, L. A. (2001). Risk of heavy drinking and alcohol use disorders in social phobia: A prospective analysis. American Journal of Psychiatry, 158(10), 1693–1700.
Bovasso, G. (2001). The long-term treatment outcomes of depression and anxiety comorbid with substance abuse. The Journal of Behavioral Health Services and Research, 28(1), 42–57.
Walrath, C. M., Sharp, M. J., Zuber, M., & Leaf, P. J. (2001). Serving children with SED in urban systems of care: Referral agency differences in child characteristics in Baltimore and the Bronx. Journal of Emotional and Behavioral Disorders, 9(2), 94–105.
Robbins, B., Rye, R., German, P. S. et al. The Psychogeriatric Assessment and Treatment in City Housing (PATCH) program for elders with mental illness in public housing: Getting through the crack in the door. Archives of Psychiatric Nursing, 14(4), 163–172.
Neufeld, K. J., Swartz, K. L., Bienvenu, O. J., Eaton, W. W., & Cai, G. (1999). Incidence of DIS/DSM-IV social phobia in adults. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica, 100(3), 186–192.
Gallo, J. J., Rabins, P. V., & Anthony, J. C. (1999). Sadness in older persons: 13-year follow-up of a community sample in Baltimore, Maryland. Psychological Medicine, 29(2), 341–350.
Baker, F. M., Stokes-Thompson, J., Davis, O. A., Gonzo, R., & Hishinuma, E. S. (1999). Two-year outcomes of psychosocial rehabilitation of black patients with chronic mental illness. Psychiatric Services, 50(4), 535–539.
Eaton, W., Anthony, J. C., Romanoski, A., et al. (1998). Onset and recovery from panic disorder in the Baltimore catchment area follow-up. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 173, 501–507.
Lyketsos, C., Garrett, E., Liang, K., & Anthony, J. (1999). Cannabis use and cognitive decline in persons under 65 years of age. American Journal of Epidemiology, 149(9), 794–800.
Bienvenu, O. J., & Eaton, W. W. (1998). The epidemiology of blood-injection-injury phobia. Psychology Medicine, 28, 1129–1136.
Nestadt, G., Bienvenu, O. J., Cai, G., Samuels, J., & Eaton, W. W. (1998). Incidence of obsessive-compulsive disorder in adults. The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 186(7), 401–406.
Black, B. S., Rabins, P. V., German, P., Roca, R., McGuire, M., & Brant, L. J. (1998). Use of formal and informal sources of mental health care among older African-American public-housing residents. Psychology Medicine, 28(3), 519–530.
Ensign, J., & Santelli, J. (1998). Health status and service use. Comparison of adolescents at a school-based health clinic with homeless adolescents. Archives of Pediatric Adolescent Medicine, 152(1), 20–24.
Pratt, L. A., Ford, D., Crum, R. M., Armenian, H., Gallo, J., & Eaton, W. (1996). Depression, psychotropic medication and risk of myocardial infarction: Prospective data from the Baltimore ECA follow-up. Circulation, 94(12), 3123–3129.
Orr, S. T., James, S. A., Miller, C. A., et al. (1996). Psychosocial stressors and low birth weight in an urban population. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 12(6), 459–466.
Cohen, B. J., Nestadt, G., Samuels, J., Romanoski, A., McHugh, P. R., & Rabins, P. V. (1994). Personality disorder in later life: A community study. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 165(4), 493–499.
Samuels, J. F., Nestadt, G., Romanoski, A. J., Folstein, M. F., & McHugh, P. R. (1994). DSM-III personality disorders in the community. American Journal of Psychiatry, 151(7), 1055–1062.
Kellam, S., Rebok, G. W., Ialongo, N., & Mayer, L. (1994). The course and malleability of aggressive behavior from early first grade into middle school: Results of a developmental epidemiologically-based preventive trial. The Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 35(2), 259–281.
Lehman, A. F., Postrado, L. T., Roth, D., McNary, S. W., & Goldman, H. H. (1994). Continuity of care and client outcomes in the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation program on chronic mental illness. Milbank Quarterly, 72(3), 105–122.
Peyrot, M., Yen, S., & Baldassano, C. A. (1994). Short-term substance abuse prevention in jail: A cognitive behavioral approach. Journal of Drug Education, 24(1), 33–47.
Bassett, S. S., & Folstein, M. F. (1993). Memory complaint, memory performance, and psychiatric diagnosis: A community study. Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry and Neurology, 6(2), 105–111.
Nestadt, G., Romanoski, A., Samuels, J., Folstein, M. F., & McHugh, P. R. (1992). The relationship between personality and DSM-III axis I disorders in the population: Results from an epidemiological survey. American Journal of Psychiatry, 149(9), 1228–1233.
Folstein, M. F., Bassett, S. S., Anthony, J. C., Romanoski, A. J., & Nestadt, G. R. (1991). Dementia: Case ascertainment in a community survey. Journal of Gerontology, 46(4), M132–M138.
Nestadt, G., Romanoski, A. J., Brown, C. H., et al. (1991). DSM-III compulsive personality disorder: An epidemiological survey. Psychology Medicine, 21(2), 461–471.
Bassett, S. S., & Folstein, M. F. (1991). Cognitive impairment and functional disability in the absence of psychiatric diagnosis. Psychology Medicine, 21(1), 77–84.
Folstein, M. F., Bassett, S. S., Romanoski, A. J., & Nestadt, G. (1991). The epidemiology of delirium in the community: The Eastern Baltimore Mental Health Survey. International Psychogeriatrics, 3(2), 169–176.
Roca, R. P., Storer, D. J., Robbins, B. M., Tlasek, M. E., & Rabins, P. V. (1990). Psychogeriatric assessment and treatment in urban public housing. Hospital & Community Psychiatry, 41(8), 916–920.
Brown, D. R., Eaton, W. W., & Sussman, L. (1990). Racial differences in prevalence of phobic disorders. The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 178(7), 434–441.
Nestadt, G., Romanoski, A. J., Chahal, R., et al. (1990). An epidemiological study of histrionic personality disorder. Psychology Medicine, 20(2), 413–422.
Trinkoff, A. M., Anthony, J. C., & Munoz, A. (1990). Predictors of the initiation of psychotherapeutic medicine use. American Journal of Public Health, 80(1), 61–65.
Kim, M. T., Han, H. R., Hill, M. N., Rose, L., & Roary, M. C. (2003). Depression, substance use, adherence behaviors, and blood pressure in urban hypertensive black men. Annals of Behavioral Medicine, 26(1), 24–31.
Rabins, P. V., Black, B. S., Roca, R., et al. (2000). Effectiveness of a nurse-based outreach program for identifying and treating psychiatric illness in the elderly. Journal of the American Medical Association, 283(21), 2802–2809.
Nestadt, G., Samuels, J. F., Romanoski, A. J., Folstein, M. F., & McHugh, P. R. (1994). Obsessions and compulsions in the community. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica, 89(4), 219–224.
Kellam, S., Werthamer, L., Dolan, L. J., et al. (1991). Developmental epidemiologically based preventive trials: Baseline modeling of early target behaviors and depressive symptoms. American Journal of Community Psychology, 19(4), 563–584.
Thornicroft, G., & Breakey, W. R. (1991). The COSTAR programme.1: Improving social networks of the long-term mentally ill. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 159, 245–249.
Vlahov, D., Wang, C., Galai, N., et al. (2004). Mortality risk among new onset injection drug users. Addiction, 99(1), 946–954.
Valente, T., & Vlahov, D. (2001). Selective risk taking among needle exchange participants: Implications for supplemental interventions. American Journal of Public Health, 91(3), 406–411.
Brooner, R., Kidorf, M., King, V., Beilenson, P., Svikis, D., & Vlahov, D. (1998). Drug abuse treatment success among needle exchange participants. Public Health Reports, 113(Suppl 1), 129–139.
Brooner, R. K., Kidorf, M. S., King, V. L., et al. (2004). Behavioral contingencies improve counseling attendance in an adaptive treatment model. Journal of Substance Abuse and Treatment, 27(3), 223–232.
Sherman, S. G., Hua, W., & Latkin, C. A. (2004). Individual and environmental factors related to quitting heroin injection. Substance Use and Misuse, 39(8), 1199–1214.
Tong, W., Lima, J. A., Meng, Q., Flynn, E., & Lai, S. (2004). Long-term cocaine use is related to cardiac diastolic dysfunction in an African-American population in Baltimore, Maryland. International Journal of Cardiology, 97(1), 25–28.
Kuo, I., Sherman, S. G., Thomas, D. L., & Strathdee, S. A. (2004). Hepatitis B virus infection and vaccination among young injection and non-injection drug users: Missed opportunities to prevent infection. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 73(1), 69–78.
Gandhi, D., Jaffe, J., McNary, S., Kavanagh, G., Hayes, M., & Currens, M. (2003). Short-term outcomes after brief ambulatory opioid detoxification with buprenorphine in young heroin users. Addiction, 98(4), 453–462.
Tobin, K. E., & Latkin, C. A. (2003). The relationship between depressive symptoms and nonfatal overdose among a sample of drug users in Baltimore, Maryland. Journal of Urban Health, 80(2), 220–229.
Kuo, I., Brady, J., Butler, C., et al. (2003). Feasibility of referring drug users from a needle exchange program into an addiction treatment program: Experience with a mobile treatment van and LAAM maintenance. Journal of Substance Abuse and Treatment, 24(1), 67–74.
Riley, E. D., Safaeian, M., Strathdee, S. A., Brooner, R. K., Beilenson, P., & Vlahov, D. (2002). Drug user treatment referrals and entry among participants of a needle exchange program. Substance Use and Misuse, 37(14), 1869–1886.
Covi, L., Hess, J. M., Schroeder, J. R., & Preston, K. L. (2002). A dose response study of cognitive behavioral therapy in cocaine abusers. Journal of Substance Abuse and Treatment, 23(3), 191–197.
Riley, E. D., Wu, A. W., Junge, B., Marx, M., Strathdee, S. A., & Vlahov, D. (2002). Health services utilization by injection drug users participating in a needle exchange program. American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse, 28(3), 497–511.
Butz, A. M., Pulsifer, M., Marano, N., Belcher, H., Lears, M. K., & Royall, R. (2001). Effectiveness of a home intervention for perceived child behavioral problems and parenting stress in children with in utero drug exposure. Archives of Pediatric Adolescent Medicine, 155(9), 1029–1037.
Neumark, Y. D., Van Etten, M. L., & Anthony, J. C. (2000). “Drug dependence” and death: survival analysis of the Baltimore ECA sample from 1981 to 1995. Substance Use and Misuse, 35(3), 313–327.
Schwartz, R. P., Brooner, R. K., Montoya, I. D., Currens, M., & Hayes, M. (1999). A 12-year follow-up of a methadone medical maintenance program. American Journal of Addiction, 8(4), 293–299.
Kidorf, M., Brooner, R. K., & King, V. L. (1997). Motivating methadone patients to include drug-free significant others in treatment: A behavioral intervention. Journal of Substance Abuse and Treatment, 14(3), 23–28.
Weissman, M. M., & Johnson, J. (1991). Drug use and abuse in five US communities. New York State Journal of Medicine, 91(11 Suppl), 19S–23S.
Epstein, D. H., Hawkins, W. E., Covi, L., Umbricht, A., & Preston, K. L. (2003). Cognitive-behavioral therapy plus contingency management for cocaine use: Findings during treatment and across 12-month follow-up. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors: Journal of the Society of Psychologists in Addictive Behaviors, 17(1), 73–82.
Gruber, K., Chutuape, M. A., & Stitzer, M. L. (2000). Reinforcement-based intensive outpatient treatment for inner city opiate abusers: A short-term evaluation. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 57(3), 211–223.
Arria, A. M., Fuller, C., Strathdee, S. A., Latkin, C., & Vlahov, D. (2002). Drug dependence among young recently initiated injection drug users. Journal of Drug Issues, 32(4), 1089–1102.
Smith, L., Riley, E., Beilenson, P., Vlahov, D., & Junge, B. (1998). A focus group evaluation of drop boxes for safe syringe disposal. Journal of Drug Issues, 28(4), 905–920.
Cunningham, S., Kerrigan, D., Pillay, K., & Ellen, J. (2005). Understanding the role of perceived severity in STD-related care-seeking delays. Journal of Adolescent Health, 37(1), 69–74.
Plitt, S., Garfein, R., Gaydos, C., Strathdee, S., Sherman, S., & Taha, T. (2005). Prevalence and correlates of Chlamydia trachomatis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Trichomonas vaginalis infections, and bacterial vaginosis among a cohort of young injection drug users in Baltimore, Maryland. Sexually Transmitted Diseases, 32(7), 446–453.
Santelli, J., Davis, M., Celentano, D., Crump, A., & Burwell, L. (1995). Combined use of condoms with other contraceptive methods among inner-city Baltimore women. Family Planning Perspectives, 27(2), 74–78.
Plitt, S. S., Sherman, S. G., Strathdee, S. A., & Taha, T. E. (2005). Herpes simplex virus 2 and syphilis among young drug users in Baltimore, Maryland. Sexually Transmitted Infections, 81(3), 248–253.
Schillinger, J. A., Dunne, E. F., Chapin, J. B., et al. (2005). Prevalence of Chlamydia trachomatis infection among men screened in 4 U.S. cities. Sexually Transmitted Diseases, 32(2), 74–77.
Jennings, J., Glass, B., Parham, P., Adler, N., & Ellen, J. M. (2004). Sex partner concurrency, geographic context, and adolescent sexually transmitted infections. Sexually Transmitted Diseases, 31(12), 734–739.
Bernstein, K. T., Jacobson, L., Jennings, J., Olthoff, G., Erbelding, E. J., & Zenilman, J. (2004). Defining core gonorrhea transmission utilizing spatial data. American Journal of Epidemiology, 160(1), 51–58.
Mehta, K. M., Erbelding, E. J., Zenilman, J., & Rompalo, A. (2003). Gonorrhea reinfection in heterosexual STD clinic attendees: Longitudinal analysis of risks for first reinfection. Sexually Transmitted Infections, 79(2), 124–128.
Mehta, S. D., Rompalo, A., Rothman, R. E., Londner, M. S., & Zenilman, J. M. (2003). Generalizability of STD screening in urban emergency departments: Comparison of results from inner city and urban sites in Baltimore, Maryland. Sexually Transmitted Diseases, 30(2), 143–148.
Rogers, S. M., Miller, H. G., Miller, W. C., Zenilman, J. M., & Turner, C. F. (2002). NAAT-identified and self-reported gonorrhea and chlamydial infections: Different at-risk population subgroups? Sexually Transmitted Diseases, 29(10), 588–596.
Turner, C. F., Rogers, S. M., Miller, H. G., et al. (2002). Untreated gonococcal and chlamydial infection in a probability sample of adults. Journal of the American Medical Association, 287(6), 726–733.
Williams, P. B., & Ekundayo, O. (2001). Study of distribution and factors affecting syphilis epidemic among inner-city minorities of Baltimore. Public Health, 115(6), 387–393.
Rompalo, A. M., Shah, N., Mayer, K., et al. (2001). Influence of injection drug use behavior on reported antiretroviral therapy use among women in the HIV Epidemiology Research study: On-site versus referral care. Journal of the Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome, 28(1), 28–34.
Mehta, S. D., Rothman, R. E., Kelen, G. D., Quinn, T. C., & Zenilman, J. M. (2001). Unsuspected gonorrhea and chlamydia in patients of an urban adult emergency department: A critical population for STD control intervention. Sexually Transmitted Diseases, 28(1), 33–39.
Burstein, G. R., Zenilman, J. M., Gaydos, C. A., et al. (2001). Predictors of repeat Chlamydia trachomatis infections diagnosed by DNA amplification testing among inner city females. Sexually Transmitted Infections, 77(1), 26–32.
Jacobson, D. L., Peralta, L., Farmer, M., Graham, N. M., Gaydos, C. A., & Zenilman, J. (2000). Relationship of hormonal contraception and cervical ectopy as measured by computerized planimetry to chlamydial infection in adolescents. AIDS, 27(6), 313–319.
Burstein, G. R., Waterfield, G., Joffe, A., Zenilman, J. M., Quinn, T. C., & Gaydos, C. A. (1998). Screening for gonorrhea and chlamydia by DNA amplification in adolescents attending middle school health centers. Opportunity for early intervention. Sexually Transmitted Diseases, 25(1), 395–402.
Staat, M. A., Tang, Y. L., Fresia, A. E., Halsey, N., Kacergis, J., & Zenilman, J. (1998). Susceptibility to vaccine-preventable diseases in sexually transmitted disease clinic population. Sexually Transmitted Diseases, 25(7), 331–334.
Peek, M., & Zenilman, J. M. (1997). Sexually transmitted diseases in patients attending a Baltimore tuberculosis clinic. Assessment of use of multiple categoric services. Sexually Transmitted Diseases, 24(1), 8–10.
Spaulding, C. (1996). Adolescents’ use of levonorgestrel implants for contraception. The Journal of Family Practice, 42(4), 349.
Borenstein, P. E., Harvilchuck, J. D., Rosenthal, B. H., & Santelli, J. S. (1996). Patterns of ICD-9 diagnoses among adolescents using school-based clinics: Diagnostic categories by school level and gender. Journal of Adolescent Health, 18(3), 203–210.
Keyl, P. M., Hurtado, M. P., Barber, M. M., & Borton, J. (1996). School-based health centers. Students’ access, knowledge, and use of services. Archives of Pediatric Adolescent Medicine, 150(2), 175–180.
Bearss, N., Santelli, J. S., Papa, P. A pilot program of contraceptive continuation in six school-based clinics. Journal of Adolescent Health, 17(3), 178–183.
Thomas, D. L., Vlahov, D., Solomon, L., et al. (1995). Correlates of hepatitis C virus infections among injection drug users. Medicine (Baltimore), 74(4), 212–220.
Zenilman, J., Weisman, C. S., Rompalo, A., et al. (1995). Condom use to prevent incident STDs: The validity of self-reported condom use. Sexually Transmitted Diseases, 22(1), 15–21.
Hook, E. W. R., Reichart, C. A., Upchurch, D. M., Ray, P. A., Celentano, D., & Quinn, T. (1992). Comparative behavioral epidemiology of gonoccocal and chlamydial infections among patients attending a Baltimore, Maryland, sexually transmitted disease clinic. American Journal of Epidemiology, 136(6), 662–672.
Upchurch, D. M., Ray, P. A., Reichart, C. A., Celentano, D., Quinn, T., & Hook, E. W. R. (1992). Prevalence and patterns of condom use among patients attending a sexually transmitted disease clinic. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, 19(3), 175–180.
Beilenson, P., Garnes, A., Braithwaite, W., et al. (1996). Outbreak of primary and secondary syphilis—Baltimore City, Maryland, 1995. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, 45(8), 166–169.
Cabral, R. J., Galavotti, C., Gargiullo, P. M., et al. (1996). Paraprofessional delivery of a theory based HIV prevention counseling intervention for women. Public Health Reports, 111(Suppl 1), 75–82.
Wainwright, S., Buchanan, S., Mainzer, M., Parrish, G., & Sinks, T. (1999). Cardiovascular mortality—The hidden peril of heat waves. Prehospital and Disaster Medicine, 14(4), 222–231.
Young, D., Miller, K., Wilder, L., Yanek, L., & Becker, D. (1998). Physical activity patterns of urban African Americans. Journal of Community Health, 23(2), 99–112.
Pearte, C. A., Gary, T. L., & Brancati, F. L. (2004). Correlates of physical activity levels in a sample of urban African Americans with type 2 diabetes. Ethnicity and Disease, 14(2), 198–205.
LaVeist, T. A., Arthur, M., Morgan, A., Plantholt, S., & Rubinstein, M. (2003). Explaining racial differences in receipt of coronary angiography: The role of physician referral and physician specialty. Medical Care Research and Review, 60(4), 453–467; discussion 496–508.
Levine, D. M., Bone, L. R., Hill, M. N. et al. The effectiveness of a community/academic health center partnership in decreasing the level of blood pressure in an urban African-American population. Ethnicity and Disease, 13(3), 354–361.
LaVeist, T. A., Morgan, A., Arthur, M., Plantholt, S., & Rubinstein, M. (2002). Physician referral patterns and race differences in receipt of coronary angiography. Health Services Research, 37(4), 949–962.
Yanek, L. R., Becker, D. M., Moy, T. F., Gittelsohn, J., & Koffman, D. M. (2001). Project Joy: Faith based cardiovascular health promotion for African American women. Public Health Reports, 116(Suppl 1), 68–81.
Bone, L. R., Hill, M. N., Stallings, R., et al. (2000). Community health survey in an urban African-American neighborhood: Distribution and correlates of elevated blood pressure. Ethnicity and Disease, 10(1), 87–95.
Gelber, A. C., Wigley, F. M., Stallings, R. Y., et al. (1999). Symptoms of Raynaud’s phenomenon in an inner-city African-American community: Prevalence and self-reported cardiovascular comorbidity. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, 52(5), 441–446.
DeForge, B. R., Stewart, D. L., DeVoe-Weston, M., Graham, L., & Charleston, J. (1998). The relationship between health status and blood pressure in urban African Americans. J National Medical Association, 90(11), 658–664.
Tielsch, J., Katz, J., Sommer, A., Quigley, H., & Javitt, J. (1995). Hypertension, perfusion pressure, and primary open-angle glaucoma: A population-based assessment. Archives of Ophthalmology, 113(2), 216–221.
Levine, D. M., Becker, D. M., & Bone, L. R. (1992). Narrowing the gap in health status of minority populations: A community-academic medical center partnership. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 8(5), 319–323.
Levine, D. M., Becker, D. M., Bone, L. R., et al. (1992). A partnership with minority populations: A community model of effectiveness research. Ethnicity and Disease, 2(3), 296–305.
Hill, M. N., Han, H. R., Dennison, C. R., et al. (2003). Hypertension care and control in underserved urban African American men: Behavioral and physiologic outcomes at 36 months. American Journal of Hypertension, 16(11), 906–913.
Stewart, K. J., Seemans, C. M., McFarland, L. D., & Weinhofer, J. J. (1997). Social learning versus traditional teaching in an elementary school cardiovascular health promotion program. American Journal of Health Promotion, 11(3), 194–197.
Tobin, K., Davey, M., & Latkin, C. (2005). Calling emergency medical services during drug overdose: An examination of individual, social and setting correlates. Addiction, 100(3), 397–404.
Reynolds, M. W., Fredman, L., Langenberg, P., & Magaziner, J. (1999). Weight, weight change, and mortality in a random sample of older community-dwelling women. Journal of American Geriatrics Society, 47(12), 1409–1414.
Kidorf, M., Disney, E., King, V., Kolodner, K., Beilenson, P., & Brooner, R. K. (2005). Challenges in motivating treatment enrollment in community syringe exchange participants. Journal of Urban Health, 82(3), 456–467.
Johnson, J. L., Wiechelt, S. A., Ahmed, A. U., & Schwartz, R. P. (2003). Outcomes for substance user treatment in women: Results from the Baltimore Drug and Alcohol Treatment Outcomes Study. Substance Use and Misuse, 38(11–13), 1807–1829.
King, V., Stoller, K. B., Hayes, M. et al. A multicenter randomized evaluation of methadone medical maintenance. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 65(2), 137–148.
Hanlon, T. E., Bateman, R. W., Simon, B. D., Carswell, S. B., & O’Grady, K. E. (2002). An early community-based intervention for the prevention of substance abuse and other delinquent behavior. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 31(3), 459–471.
Tommasello, A. C., Myers, C. P., Plumhoff, M., Gillis, L., & Treherne, L. L. (1999). Effectiveness of outreach to homeless substance abusers. Evaluation and Program Planning, 22(3), 295–303.
Katz, J., & Tielsch, J. (1996). Visual function and visual acuity in an urban adult population. Journal of Visual Impairment & Blindness, 90(5), 1367–1377.
Ekundayo, O. T., Bronner, Y., Johnson-Taylor, W. L., Dambita, N., & Squire, S. (2003). Formative evaluation of a men’s health center. American Journal of Public Health, 93(5), 717–719.
Quigley, H. A., Park, C. K., Tracey, P. A., & Pollack, I. P. (2002). Community screening for eye disease by laypersons: the Hoffberger program. American Journal of Ophthalmology, 133(3), 386–392.
Massof, R. W. A model of the prevalence and incidence of low vision and blindness among adults in the U.S. Optometry & Vision Science, 79(1), 31–38.
Preslan, M. W., & Novak, A. (1998). Baltimore vision screening project. Phase 2. Ophthalmology, 105(1), 150–153.
Katz, J., Tielsch, J. M., & Sommer, A. (1997). Prevalence and risk factors for refractive errors in an adult inner city population. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, 38(2), 334–340.
Rahmani, B., Tielsch, J. M., Katz, J., et al. (1996). The cause-specific prevalence of visual impairment in an urban population. The Baltimore Eye Survey. Ophthalmology, 103(11), 1721–1726.
Preslan, M. W., & Novak, A. (1996). Baltimore vision screening project. Ophthalmology, 103(1), 105–109.
Tielsch, J. M., Katz, J., Quigley, H. A., Javitt, J. C., & Sommer, A. (1995). Diabetes, intraocular pressure, and primary open-angle glaucoma in the Baltimore Eye Survey. Ophthalmology, 102(1), 48–53.
Katz, J., & Tielsch, J. M. (1993). Lifetime prevalence of ocular injuries from the Baltimore Eye Survey. Archives of Ophthalmology, 111(11), 1564–1568.
Dubowitz, H., Feigelman, S., Zuravin, S., Tepper, V., Davidson, N., & Lichenstein, R. (1992). The physical health of children in kinship care. American Journal of Diseases of Children, 146(5), 603–610.
Sommer, A., Tielsch, J. M., Katz, J., et al. (1991). Racial differences in the cause-specific prevalence of blindness in east Baltimore. New England Journal of Medicine, 325(20), 1412–1417.
Tielsch, J. M., Sommer, A., Katz, J., Royall, R. M., Quigley, H. A., & Javitt, J. (1991). Racial variations in the prevalence of primary open-angle glaucoma. The Baltimore Eye Survey. Journal of the American Medical Association, 266(3), 369–374.
Tielsch, J., Sommer, A., Katz, J., Quigley, H., & Ezrine, S. (1991). Socioeconomic status and visual impairment among urban Americans: Baltimore eye survey research group. Archives of Ophthalmology, 109(5), 637–641.
Tielsch, J. M., Sommer, A., Witt, K., Katz, J., & Royall, R. M. (1990). Blindness and visual impairment in an American urban population. The Baltimore Eye Survey. Archives of Ophthalmology, 108(2), 286–290.
Tielsch, J. M. (1994). A population-based perspective on low-tension and classic primary open-angle glaucoma: The Baltimore Eye Survey. Chibret International Journal of Ophthalmology, 10, 1–5.
Gallo, J., Armenian, H., Ford, D., & Eaton, W. (2000). Major depression and cancer: The 13-year follow-up for the Baltimore’s epidemiologic catchment area sample. Cancer Causes and Control, 11(8), 751–758.
Bogner, H. (2004). Urinary incontinence and psychological distress in community-dwelling older African Americans and Whites. Journal of American Geriatrics Society, 52(11), 1870–1874.
Ensign, J. (2001). The health of shelter-based foster youth. Public Health Nursing, 18(1), 19–23.
Schwarz, K., Garrett, B., Lamoreux, J., Bowser, Y. D., Weinbaum, C., & Alter, M. J. (2005). Hepatitis B vaccination rate of homeless children in Baltimore. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition, 41(2), 225–229.
Atchison, K. A., Davidson, P. L., & Nakazono, T. T. (1997). Predisposing, enabling, and need for dental treatment characteristics of ICS-II USA ethnically diverse groups. Advances in Dental Research, 11(2), 223–234.
Eaton, W., Armenian, H., Gallo, J., Pratt, L. A., & Ford, D. (1996). Depression and risk for onset of type II diabetes: a prospective population-based study. Diabetes Care, 19(10), 1097–1102.
Lillie-Blanton, M., Mackenzie, E., & Anthony, J. C. (1991). Black-White differences in alcohol use by women: Baltimore survey findings. Public Health Reports, 106(2), 124–133.
Goepp, J. G., Chin, N. P., Massad, J., & Edwards, L. A. (2004). Pediatric emergency department outreach: solving medical problems or revealing community solutions? Journal of Health Care for the Poor and Underserved, 15(4), 522–529.
Chang, S. C., O’Brien, K. O., Nathanson, M. S., Mancini, J., & Witter, F. R. (2003). Characteristics and risk factors for adverse birth outcomes in pregnant black adolescents. Journal of Pediatrics, 143(2), 250–257.
Hill-Briggs, F., Gary, T. L., Hill, M. N., Bone, L. R., & Brancati, F. L. (2002). Health-related quality of life in urban African Americans with type 2 diabetes. Journal of General Internal Medicine, 17(6), 412–419.
Klassen, A. C., Smith, A. L., Meissner, H. I., Zabora, J., Curbow, B., & Mandelblatt, J. (2002). If we gave away mammograms, who would get them? A neighborhood evaluation of a no-cost breast cancer screening program. Preventive Medicine, 34(1), 13–21.
Kayrooz, K., Moy, T. F., Yanek, L. R., & Becker, D. M. (1998). Dietary fat patterns in urban African American women. Journal of Community Health, 23(6), 453–469.
Duckart, J. P. (1998). An evaluation of the Baltimore Community Lead Education and Reduction Corps (CLEAR Corps) program. Evaluation Review, 22(3), 373–402.
Eaton, W. W., Anthony, J. C., Gallo, J., et al. (1997). Natural history of Diagnostic Interview Schedule/DSM-IV major depression. The Baltimore Epidemiologic Catchment Area follow-up. Archives of General Psychiatry, 54(11), 993–999.
Huss, K., Winkelstein, M., Nanda, J., Naumann, P. L., Sloand, E. D., & Huss, R. W. (2003). Computer game for inner-city children does not improve asthma outcomes. Journal of Pediatric Health Care, 17(2), 72–78.
Kellam, S. G., & Anthony, J. C. (1998). Targeting early antecedents to prevent tobacco smoking: Findings from an epidemiologically based randomized field trial. American Journal of Public Health, 88(10), 1490–1495.
Voorhees, C. C., Stillman, F. A., Swank, R. T., Heagerty, P. J., Levine, D. M., & Becker, D. M. (1996). Heart, body, and soul: Impact of church-based smoking cessation interventions on readiness to quit. Preventive Medicine, 25(3), 277–285.
Santelli, J., Kouzis, A., & Newcomer, S. (1996). School-based health centers and adolescent use of primary care and hospital care. Journal of Adolescent Health, 19(4), 267–275.
Butz, A. M., Syron, L., Johnson, B., Spaulding, J., Walker, M., & Bollinger, M. E. (2005). Home-based asthma self-management education for inner city children. Public Health Nursing, 22(3), 189–199.
Lang, D. M., Butz, A. M., Duggan, A. K., & Serwint, J. R. (2004). Physical activity in urban school-aged children with asthma. Pediatrics, 113(4), e341–e346.
Jones, H., Svikis, D., & Tran, G. (2002). Patient compliance and maternal/infant outcomes in pregnant drug-using women. Substance Use and Misuse, 37(11), 1411–1422.
Bishai, D., McCauley, J., Trifiletti, L., et al. (2002). The burden of injury in preschool children in an urban medicaid managed care organization. Ambulatory Pediatrics, 2(4), 279–283.
Bartlett, S. J., Lukk, P., Butz, A., Lampros-Klein, F., & Rand, C. S. (2002). Enhancing medication adherence among inner-city children with asthma: Results from pilot studies. Journal of Asthma, 39(1), 47–54.
Clark, J. M., Bone, L. R., Stallings, R., et al. (2001). Obesity and approaches to weight in an urban African-American community. Ethnicity and Disease, 11(4), 676–686.
Erbelding, E. J., Hummel, B., Hogan, T., & Zenilman, J. (2001). High rates of depressive symptoms in STD clinic patients. Sexually Transmitted Diseases, 28(5), 281–284.
Comer, J. A., Tzianabos, T., Flynn, C., Vlahov, D., & Childs, J. E. (1999). Serologic evidence of rickettsialpox (Rickettsia akari) infection among intravenous drug users in inner-city Baltimore, Maryland. The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 60(6), 894–898.
Rule, J., Abrams, R., Miller, S., Gilner, M., Rubin, J., & Gunsolley, J. (1995). Caries in minority children ages 1–4 in Baltimore and Washington. Journal of the Maryland State Dental Association, 38(1), 14–16.
Serwint, J. R., Hall, B. S., Baldwin, R. M., & Virden, J. M. (1997). Outcomes of annual tuberculosis screening by Mantoux test in children considered to be at high risk: Results from one urban clinic. Pediatrics, 99(4), 529–533.
Forrest, C. B., Starfield, B., Riley, A. W., & Kang, M. (1997). The impact of asthma on the health status of adolescents. Pediatrics, 99(2), E1.
Holt, E., Guyer, B., Hughart, N., et al. (1996). The contribution of missed opportunities to childhood underimmunization in Baltimore. Pediatrics, 97(4), 474–480.
Lucas, S. R., Sexton, M., & Langenberg, P. (1996). Relationship between blood lead and nutritional factors in preschool children: A cross-sectional study. Pediatrics, 97(1), 74–78.
Burton, L. C., Paglia, M. J., German, P. S., Shapiro, S., & Damiano, A. M. (1995). The effect among older persons of a general preventive visit on three health behaviors: Smoking, excessive alcohol drinking, and sedentary lifestyle. The Medicare Preventive Services Research Team. Preventive Medicine, 24(5), 492–497.
Nordberg, B. J., Barlow, M. S., Chalew, S. A., & McCarter, R. J. (1993). Effect of third-party reimbursement on use of services and indexes of management among indigent diabetic patients. Diabetes Care, 16(8), 1076–1080.
Butz, A. M., Funkhouser, A., Caleb, L., & Rosenstein, B. J. (1993). Infant health care utilization predicted by pattern of prenatal care. Pediatrics, 92(1), 50–54.
Olson, G. L., Saade, G. R., & Nagey, D. A. (1997). Active recruitment into health care and its effect on birth weight and gestational age at delivery. Journal of Maternal-Fetal Investigation, 7(3), 122–125.
Farrell, K., Brophy, M., Chisolm, J. J., Rohde, C., & Strauss, W. (1998). Soil lead abatement and children’s blood lead levels in an urban setting. American Journal of Public Health, 88, 1837–1839.
Davis, H., Gergen, P. J., & Moore, R. M. (1997). Geographic differences in mortality of young children with sickle cell disease in the United States. Public Health Reports, 112(1), 52–58.
Blaum, C., Xue, Q., Michelon, E., Semba, R. D., & Fried, L. (2005). The association between obesity and the frailty syndrome in older women: The Women’s Health and Aging studies. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, 53(6), 927–934.
Minkovitz, C., Duggan, A., Fox, M., & Wilson, M. (1999). Use of social services by pregnant Medicaid eligible women in Baltimore. Maternal and Child Health Journal, 3(3), 117–127.
Caulfield, L., Gross, S., Bentley, M., et al. (1998). WIC-based interventions to promote breastfeeding among African-American women in Baltimore: Effects on breastfeeding initiation and continuation. Journal of Human Lactation, 14(1), 15–22.
O’Campo, P., Xue, X., Wang, M., & Coughy, M. (1997). Neighborhood risk factors for low birthweight in Baltimore: A multilevel analysis. American Journal of Public Health, 87(7), 1113–1118.
Read, K. M., Kufera, J. A., Jackson, M. C., & Dischinger, P. C. (2005). Population-based study of police-reported sexual assault in Baltimore, Maryland. American Journal of Emergency Medicine, 23(3), 273–278.
Maty, S. C., Fried, L. P., Volpato, S., Williamson, J., Brancati, F. L., & Blaum, C. S. (2004). Patterns of disability related to diabetes mellitus in older women. Journals of Gerontology: A Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences, 59(2), 148–153.
Rohm Young, D., & Voorhees, C. C. (2003). Personal, social, and environmental correlates of physical activity in urban African American women. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 25(3 Suppl 1), 38–44.
Orr, S. T., Miller, C. A., James, S. A., & Babones, S. (2000). Unintended pregnancy and preterm birth. Paediatric and Perinatal Epidemiology, 14(4), 309–313.
Zabin, L. S., Huggins, G. R., Emerson, M. R., & Cullins, V. E. (2000). Partner effects on a woman’s intention to conceive: ‘Not with this partner’. Family Planning Perspectives, 32(1), 39–45.
Bruner, A. B., Joffe, A., Duggan, A. K., Casella, J. F., & Brandt, J. (1996). Randomised study of cognitive effects of iron supplementation in non-anaemic iron-deficient adolescent girls. Lancet, 348, 992–996.
Jordan, E. A., Duggan, A. K., & Hardy, J. B. (1993). Injuries in children of adolescent mothers: home safety education associated with decreased injury risk. Pediatrics, 91(2), 481–487.
Harries, K., & Kovandzic, E. (1999). Persistence, intensity, and areal extent of violence against women: Baltimore City, 1992 to 1995. Violence Against Woman, 5(7), 813–828.
Baker, T. A. (2005). Chronic pain in older Black Americans: The influence of health and psychosocial factors. Ethnicity and Disease, 15(2), 179–186.
Fedder, D. O., Chang, R. J., Curry, S., & Nichols, G. (2003). The effectiveness of a community health worker outreach program on healthcare utilization of west Baltimore City Medicaid patients with diabetes, with or without hypertension. Ethnicity and Disease, 13(1), 22–27.
Feroli, K., & Hobson, S. (1995). Defining anemia in a preadolescent African American population. Journal of Pediatric Health Care, 9(5), 199–204.
Gary, T. L., Bone, L. R., Hill, M. N., et al. (2003). Randomized controlled trial of the effects of nurse case manager and community health worker interventions on risk factors for diabetes-related complications in urban African Americans. Preventive Medicine, 37(3), 23–32.
Torbenson, M., Kannangai, R., Astemborski, J., Strathdee, S. A., Vlahov, D., & Thomas, D. L. (2004). High prevalence of occult hepatitis B in Baltimore injection drug users. Hepatology, 39(1), 51–57.
Riley, E. D., Vlahov, D., Huettner, S., Beilenson, P., Bonds, M., & Chaisson, R. E. (2002). Characteristics of injection drug users who utilize tuberculosis services at sites of the Baltimore city needle exchange program. Journal of Urban Health, 79(1), 113–127.
Galai, N., Graham, N., Chaisson, R., Nelson, K., Vlahov, D., & Lewis, J. (1992). Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. New England Journal of Medicine, 327(16), 1172–1173.
Amin, R., & Sato, T. (2004). Impact of a school-based comprehensive program for pregnant teens on their contraceptive use, future contraceptive intention, and desire for more children. Journal of Community Health Nursing, 21(1), 39–47.
Gross, S. M., Caulfield, L. E., Bentley, M. E., et al. (1998). Counseling and motivational videotapes increase duration of breast-feeding in African-American WIC participants who initiate breast-feeding. Journal of the American Dietetic Association, 98(2), 143–148.
Neumark, Y. D., Van Etten, M. L., & Anthony, J. C. (2000). “Alcohol dependence” and death: Survival analysis of the Baltimore ECA sample from 1981 to 1995. Substance Use and Misuse, 35(4), 533–549.
Armenian, H., Pratt, L. A., Gallo, J., & Eaton, W. (1998). Psychopathology as a predictor of disability: A population-based follow-up study in Baltimore, Maryland. American Journal of Epidemiology, 148(3), 269–275.
D’Lugoff, M. I., Jones, W., Kub, J., Glass, N., Thompson, D., Brinkley, S., et al. (2002). Tuberculosis screening in an at-risk immigrant Hispanic population in Baltimore City: An academic health center/local health department partnership. Journal of Cultural Diversity, 9(3), 79–85.
Fielder, J. F., Chaulk, C. P., Dalvi, M., Gachuhi, R., Comstock, G. W., & Sterling, T. R. (2002). A high tuberculosis case-fatality rate in a setting of effective tuberculosis control: Implications for acceptable treatment success rates. The International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease, 6(12), 1114–1117.
Mess, S. E., Reese, P. P., Della Lana, D. F., Walley, A. Y., Ives, E. P., & Lee, M. C. (2000). Older, hypertensive, and hypercholesterolemic fairgoers visit more booths and differ in their health concerns at a community health fair. Journal of Community Health, 25(4), 315–329.
Garfein, R. S., Doherty, M. C., Monterroso, E. R., Thomas, D. L., Nelson, K. E., & Vlahov, D. (1998). Prevalence and incidence of hepatitis C virus infection among young adult injection drug users. Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes and Human Retrovirology, 18(Suppl 1), S11–S19.
O’Campo, P., Rao, R. P., Gielen, A. C., Royalty, W., & Wilson, M. (2000). Injury-producing events among children in low-income communities: The role of community characteristics. Journal of Urban Health, 77(1), 34–49.
Wood, N. P. J., Amanfo, J., Rodgers, D., et al. (1993). Intentional injury—homicide as a public health problem. Maryland Medical Journal, 42(8), 771–773.
Farfel, M. R., Orlova, A. O., Chaney, R. L., Lees, P. S., Rohde, C. A., & Ashley, P. J. (2005). Biosolids compost amendment for reducing soil lead hazards: A pilot study of Orgro amendment and grass seeding in urban yards. Science of the Total Environment, 340(1–3), 81–95.
Farfel, M. R., & Chisolm, J. J., Jr. (1991). An evaluation of experimental practices for abatement of residential lead-based paint: Report on a pilot project. Environmental Research, 55(2), 199–212.
O’Campo, P., Guyer, B., Squires, B., Weiss, J., Sweitzer, J., & Coyle, T. (1993). Needs assessment for reducing infant mortality in Baltimore City: The Healthy Start Program. Southern Medical Journal, 86(12), 1342–1349.
Ross, A., Kennedy, A., Holt, E., Guyer, B., Hou, W., & Hughart, N. (1998). Initiating the first DTP vaccination age-appropriately: A model for understanding vaccination coverage. Pediatrics, 101(6), 970–974.
Frank, R. G., Dewa, C. S., Holt, E., Hughart, N., Strobino, D., & Guyer, B. (1995). The demand for childhood immunizations: Results from the Baltimore Immunization Study. Inquiry, 32(2), 164–173.
Beilenson, P., & Santelli, J. (1992). An urban school-based voluntary MMR booster immunization program. Journal of School Health, 62(2), 71–73.
Mausner-Dorsch, H., & Eaton, W. W. (2000). Psychosocial work environment and depression: epidemiologic assessment of the demand-control model. American Journal of Public Health, 90(11), 1765–1770.
Yellowitz, J. A., Goodman, H. S., & Farooq, N. S. (1997). Knowledge, opinions, and practices related to oral cancer: Results of three elderly racial groups. Special Care in Dentistry, 17(3), 100–104.
Ewart, C. K., Young, D. R., & Hagberg, J. M. (1998). Effects of school-based aerobic exercise on blood pressure in adolescent girls at risk for hypertension. American Journal of Public Health, 88(6), 949–951.
Black, B. S., Rabins, P. V., & McGuire, M. H. (1998). Alcohol use disorder is a risk factor for mortality among older public housing residents. International Psychogeriatrics, 10(3), 309–327.
Schwartz, B., Glass, T., Bolla, K., et al. (2004). Disparities in cognitive functioning by race/ethnicity in the Baltimore Memory Study. Environmental Health Perspectives, 112(3), 314–320.
Stone, S., Erickson, B., Alexander, M., Dunning, R., Israel, E., & Dwyer, D. (1993). Characteristics of epidemic hepatitis A in Baltimore city: Implications for control measures. Maryland Medical Journal, 42(10), 995–1000.
Childs, J. E., Schwartz, B. S., Ksiazek, T. G., Graham, R. R., LeDuc, J. W., & Glass, G. E. (1992). Risk factors associated with antibodies to leptospires in inner-city residents of Baltimore: A protective role for cats. American Journal of Public Health, 82(4), 597–599.
Childs, J. E., Glass, G. E., Ksiazek, T. G., Rossi, C. A., Oro, J. G., & Leduc, J. W. (1991). Human-rodent contact and infection with lymphocytic choriomeningitis and Seoul viruses in an inner-city population. The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 44(2), 117–121.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Allison Roeser, a graduate student at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health (BSPH), who assisted with organizing the data abstraction process and leading the data entry efforts. Graduate students at BSPH who assisted the authors with abstracting data for this systematic review include Genevieve Birkby, Heidi Bramson, Kathy Byrd, Anisha Dharshi, Jessica Donaldson, Judy Easterbrook, Nadine Finigan, Tameka Gillum, Gursimran Grewal, Sabina Haberlen, James Ignas, Peter James, Christine Kang, Michelle Knowles, Dennis Kuo, Jia Liu, Sherry Madan, Craig Martinez, Mary Ellen McEvoy, Mpho Mogodi, Alejandro Necochea, Michael Oldham, Ibironke Olofin, Elizabeth Parker, Raj Punjabi, Anna Ricklin, James Saltsman, Myra Shapiro, Erica Shelton, Carol Strong, Andy Tan, Emma Tsui, Ellen Wells, and Jessika Zmuda.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tyus, N.C., Gibbons, M.C., Robinson, K.A. et al. In the Shadow of Academic Medical Centers: A Systematic Review of Urban Health Research in Baltimore City. J Community Health 35, 433–452 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10900-010-9258-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10900-010-9258-1