Abstract
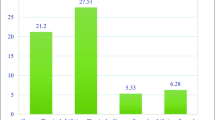
Kerala is one of the most progressive states in India in terms of women’s opportunities for higher education and employment. Despite these advancements in gender equality, intimate partner violence (IPV) against women remains high, with some studies finding increased rates of IPV in Kerala relative to other states. This study examines contributing factors to male-to-female IPV in Kerala. One hundred and thirty-four men were surveyed on perceived marital power, early exposure to violence, drinking habits, depression, and marital satisfaction in relation to current IPV. Forty percent of participants reported incidents of IPV in the past year. Batterers scored significantly higher on childhood abuse, drinking, depression, and marital dissatisfaction. These four predictor variables were all significantly correlated with male-to-female IPV, but perceived marital power was only partially correlated with IPV. Abuse in childhood emerged as the strongest predictor of current IPV. Implications and suggestions for further research are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
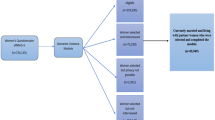
Please see Methods section for a full description of the Conflict Tactics Scales.
References
Bandura, A. (1978). Social learning theory of aggression. Journal of Communication, 28, 12–29.
Beck, A. T., & Beck, R. W. (1972). Screening depressed patients in family practice. Postgraduate Medicine, 52, 81–85.
Beck, A. T., Ward, C. H., Mendelson, M., Mock, J. E., & Erbaugh, J. K. (1961). An inventory for measuring depression. Archives of General Psychiatry, 4, 561–571.
Bell, K. M., & Naugle, A. E. (2007). Effects of social desirability on students’ self-reporting of partner abuse perpetration and victimization. Violence and Victims, 22(2), 243–256.
Berg, M. J., Kremelberg, D., Dwivedi, P., Verma, S., Schensul, J. J., Gupta, K., & Singh, S. K. (2010). The effects of husband’s alcohol consumption on married women in three low-income areas of greater Mumbai. AIDS and Behavior, 14, 126–135. doi:10.1007/s10461-010-9735-7.
Bernstein, D. P., & Fink, L. (1998). Childhood Trauma Questionnaire Manual. San Antonio: Harcourt Brace & Company.
Bernstein, D. P., et al. (1994). Initial reliability and validity of a new retrospective measure of child abuse and neglect. American Journal of Psychiatry, 151, 1132–1136.
Blood, R. O., & Wolfe, D. M. (1960). Husbands and wives. Glencoe: Free Press.
Brisibe, S., Ordinioha, B., & Dienye, P. O. (2012). Intersection between alcohol abuse and intimate partner’s violence in a rural ijaw community in bayelsa state, south-south nigeria. Journal of Interpersonal Violence, 27(3), 513–522. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0886260511421676
Census of India, Directorate of Census Operations. (2011). Census of India 2011: Summary of provisional population of Kerala. Retrieved from http://www.censusindia.gov.in/2011-prov results/data_files/kerala/ppt_at_a_glance_kerala.pdf
Center for Women’s Studies & Development. (2005). A situational analysis of domestic violence against women in Kerala. Retrieved from http://wcd.nic.in/research/Domestic%20Voilence-Kerala.pdf
Coleman, D. H., & Straus, M. A. (1986). Marital power, conflicts, and violence in a nationally representative sample of American couples. Violence and Victims, 1, 141–157.
Comijs, H. C., van Exel, E., van der Mast, R. C., Paauw, A., Voshaar, R. O., & Stek, M. L. (2013). Childhood abuse in late-life depression. Journal of Affective Disorders, 147(1–3), 241–246.
Downs, W. R., Smyth, N. J., & Miller, B. A. (1996). The relationship between childhood violence and alcohol problems among men who batter: an empirical review and synthesis. Aggression and Violent Behavior, 1, 327–344. doi:10.1016/S1359-1789(96)00006-7.
Fals-Stewart, W. (2003). The occurrence of partner physical aggression on days of alcohol consumption: a longitudinal diary study. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 71(1), 41–52. doi:10.1037/0022-006X.71.1.41.
Feldbau-Kohn, S., Heyman, R. E., & O’Leary, K. D. (1998). Major depressive disorder and depressive symptomatology as predictors of husband to wife physical aggression. Violence and Victims, 13(4), 347–360.
Felitti, V., Anda, R., Nordenbergm, D., Williamson, D., Spitz, A., Edwards, V., Koss, M., & Marks, J. (1998). Relationship of childhood abuse and household dysfunction to many of the leading causes of death in adults: the Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACE) study. American Journal of Preventative Medicine, 14(4), 245–258. doi:10.1016/S0749-3797(98)00017-8.
Friedrich, W., & Loftsgard, S. (1978). A comparison of the MacAndrew alcoholism scale and the Michigan alcoholism screening test in a sample of problem drinkers. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs, 39(11), 1940–1944.
Gratz, K. L., Paulson, A., Jakupcak, Tull, M. T. (2009). Exploring the relationship between childhood maltreatment and intimate partner abuse: gender differences in the mediating role of emotion dysregulation. Violence and Victims, 24(1), 68–82.
Hellmuth, J. C., Follansbee, K. W., Moore, T. M., & Stuart, G. L. (2008). Reduction of intimate partner violence in a gay couple following alcohol treatment. Journal of Homosexuality, 54(4), 439–448.
Henning, K., & Holdford, R. (2006). Minimization, denial, and victim blaming by batterers: how much does the truth matter? Criminal Justice and Behavior, 33(1), 110–130.
Henning, K., Leitenberg, H., Coffey, P., Bennett, T., & Jankowski, M. K. (1997). Long-term psychological adjustment to witnessing interparental physical conflict during childhood. Child Abuse and Neglect, 21, 501–51. doi:10.1016/S0145-2134(97)00009-4.
Holtzworth-Munroe, A., & Smutzler, N. (1996). Comparing the emotional reactions and behavioral intentions of violent and nonviolent husbands to aggressive, distressed, and other wife behaviors. Violence and Victims, 11(4), 319–339.
Holtzworth-Munroe, A., Bates, L., Smutzler, N., & Sandin, E. (1997a). A brief review of the research on husband violence (Part I: maritally violent versus nonviolent men). Aggression and Violent Behavior, 2, 65–99. doi:10.1016/S1359-1789(96)00015-8.
Holtzworth-Munroe, A., Smutzler, N., & Bates, L. (1997b). A brief review of the research on husband violence (Part III: sociodemographic factors, relationship factors, and differing consequences of husband and wife violence). Aggression and Violent Behavior, 3, 285–307. doi:10.1016/S1359-1789(96)00017-1.
Hornung, C. A., McCullough, B. C., & Sugimoto, T. (1981). Status relationships in marriage: risk factors in spouse abuse. Journal of Marriage & the Family, 43(3), 675–692. doi:10.2307/351768.
Hudson, W. W. (1982). The clinical measurement package: A field manual. Homewood: The Dorsey Press.
Information Technology Department of the Government of Kerala, Department of Information Technology, Ministry of Communications, & Information Technology. (2007). About Kerala: Demography. Retrieved from http://india.gov.in/knowindia/state_uts.php?id=37
Jewkes, R. K., Dunkle, K., Nduna, M., Jama, N., & Puren, A. (2008). Associations between childhood adversity and depression, substance abuse and HIV and HSV2 incident infections in rural South African youth. Child Abuse & Neglect, 34(11), 833–841.
Jewkes, R. K., Dunkle, K., Nduna, M., & Shai, N. (2010). Intimate partner violence, relationship power inequity, and incidence of HIV infection in young women in South Africa: a cohort study. The Lancet, 376(9734), 41–48. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60548-X.
Jin, X., & Keat, J. E. (2010). The effects of change in spousal power on intimate partner violence among Chinese immigrants. Journal of Interpersonal Violence, 25(4), 610–625. doi:10.1177/0886260509334283.
Jin, X., Eagle, M., & Keat, J. (2008). Hostile attributional bias, early abuse, and social desirability in reporting hostile attributions among Chinese immigrant batterers and non-violent Men. Violence and Victims, 23, 773–786. doi:10.1891/0886-6708.23.6.773.
Kacker, L., Varadan, S., & Kumar, P. (2007). Study on Child Abuse: INDIA 2007. Ministry of Women and Child Development, Government of India. Retrieved from http://wcd.nic.in/childabuse.pdf
Kaur, R., & Garg, S. (2010). Domestic violence against women: A qualitative study in a rural community. Asia-Pacific Journal of Public Health, 22(2), 242–251. Retrieved from http://search.proquest.com/docview/742978138?accountid=12261
Keiley, M. K., Keller, P. S., & El-Sheikh, M. (2009). Effects of physical and verbal aggression, depression, and anxiety on drinking behavior of married partners: a prospective and retrospective longitudinal examination. Aggressive Behavior, 35(4), 296–312. doi:10.1002/ab.20310.
Langeland, W., & Hartgers, C. (1998). Child sexual and physical abuse and alcoholism: a review. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs, 59(3), 336–348.
Lee, R. (2013). Behavioral and attitudinal factors differentiating male intimate partner violence perpetrators with and without a history of childhood family violence. Journal of Family Violence, 28(1), 85–94.
Magnusson, A., Lundholm, C., Goransson, M., Copeland, W., Heilig, M., & Pedersen, N. L. (2012). Familial influence and childhood trauma in female alcoholism. Psychological Medicine, 42(2), 381–389. doi:10.1017/S0033291711001310.
McAuley, T., Longabaugh, R., & Gross, H. (1978). Comparative effectiveness of self and family forms of the Michigan alcoholism screening test. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs, 39(9), 1622–1627.
Mihalic, S. W., & Elliott, D. (1997). Social learning theory model of marital violence. Journal of Family Violence, 12(1), 21–47.
Ministry of Woman and Child Development, Government of India (2007). Study on child abuse, India 2007. Retrived from http://wcd.nic.in/childabuse.pdf.
Murrell, A., Christoff, K., & Henning, K. (2007). Characteristics of domestic violence offenders: associations with childhood exposure to violence. Journal of Family Violence, 22(7), 523–532. doi:10.1007/s10896-007-9100-4.
Nair, M., Rajmohanan, K., Remadevi, S., Nair, S., Ghosh, C., & Leena, L. (2009). Child disciplining practices in Kerala. Indian Pediatrics, 46, S83–S85.
Pan, H. S., Neidig, P. H., & O’Leary, K. D. (1994). Predicting mild and severe husband-to-wife physical aggression. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 62(5), 975–981.
Paterson, J., Fairbairn-Dunlop, P., Esther, T. C., & Schluter, P. J. (2007). Maternal childhood parental abuse history and current intimate partner violence: Data from the pacific islands families study. Violence and Victims, 22(4), 474–88. Retrieved from http://search.proquest.com/docview/208556625?accountid=12261
Patriciu, I. O. (2003). The Social Distribution and Long-Term Effects of Childhood Maltreatment: An Analysis of the Moderating Effects of Social Status and Parental Support (Doctoral dissertation).
Rangul Askeland, I., Evang, A., & Heir, T. (2011). Association of violence against partner and former victim experiences: a sample of clients voluntarily attending therapy. Journal of Interpersonal Violence, 26(6), 1095–1110. doi:10.1177/0886260510368152.
Rocca, C. H., Rathod, S., Falle, T., Pande, R. P., & Krishnan, S. (2009). Challenging assumptions about women’s empowerment: social and economic resources and domestic violence among young married women in urban south India. International Journal of Epidemiology, 38(2), 577–85. doi:10.1093/ije/dyn226.
Rogers, W. S., Bidwell, J., & Wilson, L. (2005). Perception of and satisfaction with relationship power, sex, and attachment styles: a couples level analysis. Journal of Family Violence, 20(4), 241–251. doi:10.1007/s10896-005-5988-8.
Ross, E., Gavin, D. R., & Skinner, H. A. (1990). Diagnostic validity of the MAST and alcohol dependence scale in the assessment of DSM-III alcohol disorders. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 51, 506–513.
Schumacher, J. A., Feldbau-Kohn, S., Slep, A. M. S., & Heyman, R. E. (2001). Risk factors for male-to-female partner physical abuse. Aggression and Violent Behavior, 6, 281–352. doi:10.1016/S1359-1789(00)00027-6.
Selzer, M. (1971). The Michigan alcoholism screening test: the quest for a new diagnostic instrument. American Journal of Psychiatry, 127, 1653–1658.
Selzer, M. L., Vinokur, A., & van Rooijen, L. (1975). A self-administered short Michigan alcoholism screening test. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 36, 117–126.
Simister, J., & Mehta, P. S. (2010). Gender-based violence in India: long-term trends. Journal of Interpersonal Violence, 25(9), 1594–1611. doi:10.1177/0886260509354577.
Straus, M. A. (1979). Measuring intrafamily conflict and violence: the Conflict Tactics (CT) scales. Journal of Marriage and the Family, 41, 75–88.
Tilley, D. S., & Brackley, M. (2005). Men who batter intimate partners: a grounded theory study of the development of male violence in intimate partner relationships. Issues in Mental Health Nursing, 26(3), 281–297. doi:10.1080/01612840590915676.
Weiss, E., Longhurst, M., & Mazure, C. (1999). Childhood sexual abuse as a risk factor for depression in women: psychosocial and neurobiological correlates. American Journal of Psychiatry, 156, 816–828.
Whisman, M. A. (2001). In S. R. H. Beach (Ed.), The association between depression and marital dissatisfaction. United States: American Psychological Association.
Zhang, L. (2002). Marital conflicts in dual-earner families in Beijing: A gender perspective. Hong Kong Polytechnic University (Hong Kong)). ProQuest Dissertations and Theses. Retrieved from http://search.proquest.com/docview/252181548?accountid=12261
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, X., Doukas, A., Beiting, M. et al. Factors Contributing to Intimate Partner Violence among Men in Kerala, India. J Fam Viol 29, 643–652 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10896-014-9623-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10896-014-9623-4