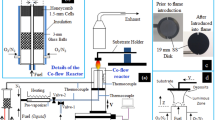
The authors present results of synthesis of superhydrophobic soot in flames of various hydrocarbons (methane, propane, butane, and polyethylene waste) using metallic catalysts of the gauze type from nichrome wire and of the honeycomb type from nickel plates, and also natural aluminosilicates. An analysis of hydrophobic characteristics of the obtained samples of soot has shown a substantial influence of the catalysts on its hydrophobic properties. The best samples of soot with a wetting angle larger than 160° were obtained during the combustion of gaseous hydrocarbons with the use of the honeycomb-type nickel catalyst. Soot samples obtained during the combustion of propane with a honeycomb-type nickel catalyst had a wetting angle within 160–165°, suggesting the presence of superhydrophobic properties in the soot. These samples were characterized by the large degree of graphitization (≈20%), which is due to the influence of metallic nickel on the structure of formed soot particles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z. A. Mansurov, Formation of soot from polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons as well as fullerenes and carbon nanotubes in the combustion of hydrocarbon, J. Eng. Phys. Thermophys., 84, No. 1, 84–125 (2011).
Z. Mansurov, Soot Formation, Kazakh University, Almaty (2015).
Long-Yue Meng and Soo-Jin Park, Superhydrophobic carbon-based materials: a review of synthesis, structure, and applications, Carbon Lett., 15, No. 2, 89–104 (2014).
Y. Zhou, B. Wang, X. Song, E. Li, G. Li, S. Zhao, and H. Yan, Control over the wettability of amorphous carbon films in a large range from hydrophilicity to super-hydrophobicity, Appl. Surf. Sci., 253, 2690–2694 (2006).
M. Nazhipkyzy, M. G. Solov′eva, A. E. Bakkara, G. T. Smagulova, G. O. Turesheva, B. T. Lesbaev, N. G. Prikhod′ko, E. T. Aliev, and Z. A. Mansurov, Obtaining of hydrophobic soot-based sand, in: Proc. VII Int. Symp. "The Physics and Chemistry of Carbon Materials. Nanoengineering," Almaty (2012), pp. 98–101.
Z. A. Mansurov, M. Nazhipkyzy, B. T. Lesbayev, N. G. Prikhodko, M. Auyelkhankyzy, and I. K. Puri, Synthesis of superhydrophobic carbon surface during combustion propane, Eurasian Chem.-Technol. J., 14, No. 1, 19–23 (2012).
B. T. Lesbaev, G. T. Smagulova, A. E. Bakkara, M. Nazhipkyzy, G. O. Turesheva, A. K. Kenzhegulov, E. S. Merkibaev, N. G. Prikhod′ko, E. T. Aliev, and Z. A. Mansurov, , Obtaining of superhydrophobic soot through the recycling of polyethylene waste, in: Proc. VII Int. Symp. "The Physics and Chemistry of Carbon Materials. Nanoengineering," Almaty (2012), pp. 190–193.
L. V. Furda, Catalytic Destruction of Polyethylene in the Presence of Natural and Synthetic Aluminosilicates, Candidate′s Dissertation in Chemistry, Ivanovo (2011).
V. A. Likholobov, Catalytic synthesis of carbon materials and their use in catalysis, Sorosovskii Obrazovat. Zh., No. 5, 35–42 (1997).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Inzhenerno-Fizicheskii Zhurnal, Vol. 91, No. 3, pp. 824–833, May–June, 2018.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smagulova, G.T., Nazhipkyzy, M., Lesbaev, B.T. et al. Influence of the Type of Catalysts on the Formation of a Superhydrophobic Carbon Nanomaterial in Hydrocarbon Flames. J Eng Phys Thermophy 91, 774–783 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10891-018-1800-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10891-018-1800-5