Abstract
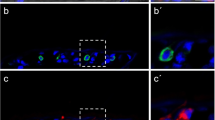
We describe the identification and characterization of two new cDNAs encoding pheromone-binding proteins (PBPs) from the male antennae of Sesamia nonagrioides, a species where no PBPs have been identified to date. Because PBPs are thought to participate in the first step of odor detection in a specific manner, we focused our investigation on this olfactory protein family using reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction strategies. The deduced amino acid sequences of SnonPBP1 and SnonPBP2 revealed mature proteins of 142 and 143 amino acids, respectively, with six cysteine residues in conserved positions relative to other known PBPs. The alignment of the two mature S. nonagrioides PBPs with other noctuid PBPs showed high sequence identity (70–80%) with other full-length sequences from GenBank. Sequence identity between SnonPBP1 and SnonPBP2 was only 46%, suggesting that the two proteins belong to different classes of PBPs already described from the Noctuidae. Furthermore, analyses of expression patterns of SnonPBP1 and SnonPBP2 were performed by in situ hybridization on antennae of both sexes, and these studies revealed the expression of the two PBPs at the bases of olfactory sensilla (basiconica or trichodea) from both sexes. The possible binding properties of these two new PBPs are discussed according to their homologies with other known PBPs and S. nonagrioides pheromone components.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham, D., Löfstedt, C., and Picimbon, J. F. 2003. Grp2-pheromone binding protein from Heliothis virescens. Direct GenBank submission no. AY301988.
Abraham, D., Löfstedt, C., and Picimbon, J. F. 2005. Molecular characterization and evolution of pheromone-binding protein genes in Agrotis moths. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 35:1100-1111.
Callahan, F. E., Vogt, R. G., Tucker, M. L., Dickens, J. C., and Mattoo, A. K. 2000. High level expression of “male specific” pheromone-binding proteins (PBPs) in the antennae of female noctuid moths. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 30:507–514.
Campanacci, V., Krieger, J., Bette, S., Sturgis, J. N., Lartigue, A., Cambillau, C., Breer, H., and Tegoni, M. 2001. Revisiting the specificity of Mamestra brassicae and Antheraea polyphemus pheromone-binding proteins with a fluorescence assay. J. Biol. Chem. 276:20078–20084.
Colazza, S. and Rosi, M. C. 2001. Differences in the searching behaviour of two strains of the egg parasitoid Telenomus busseolae (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae). Eur. J. Entomol. 98:47–52.
Colazza, S., Rosi, M. C., and Clemente, A. 1997. Response of the egg parasitoid Telenomus busseolae to sex pheromone of Sesamia nonagrioides. J. Chem. Ecol. 23:2437–2444.
Conti, E. and Bin, F. 2000. Parasitoids of concealed noctuid eggs and their potential in biological control of gramineae stemborers. Redia. 83:87–104.
Corpet, F. 1988. Multiple sequence alignment with hierarchical clustering. Nuc. Acids Res. 16:10881–10890.
Du, G. and Prestwich, G. D. 1995. Protein structure encodes the ligand binding specificity in pheromone-binding proteins. Biochemistry 34:8726–8732.
Giacometti, R. 1995. Rearing of Sesamia nonagrioides Lefevre on meridic diet (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Redia 78:19–27.
Györgyi, T. K., Roby-Shemkovitz, A. J., and Lerner, M. R. 1988. Characterization and cDNA cloning of the pheromone-binding protein from the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta: a tissue-specific developmentally regulated protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85:9851–9855.
Jacquin-Joly, E., Bohbot, J., Francois, M. C., Cain, A. H., and Nagnan-Le Meillour, P. 2000. Characterization of the general odorant-binding protein 2 in the molecular coding of odorants in Mamestra brassicae. Eur. J. Biochem. 267:6708–6714.
Jørgensen, K., Kvello, P., Almaas, T. J., and Mustaparta, H. 2006. Two closely located areas in the suboesophageal ganglion and the tritocerebrum receive projections of gustatory receptor neurons located on the antennae and the proboscis in the moth Heliothis virescens. J. Comp. Neurol. 496:121–134.
Kaissling, K. E. 2004. Physiology of pheromone reception in insects (an example of moths). ANIR 6:73–91.
Kalinova, B., Hoskovec, M., Liblikas, I., Unelius, C. R., and Hansson, B. S. 2001. Detection of sex pheromone components in Manduca sexta (L.). Chem. Senses 26:1175–1186.
Krieger, J., Raming, K., and Breer, H. 1991. Cloning of genomic and complementary DNA encoding insect pheromone-binding proteins: evidence for microdiversity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1088:277–284.
Krieger, J., Gänβle, H., Raming, K., and Breer, H. 1993. Odorant-binding proteins of Heliothis virescens. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 23:449–456.
Leal, W. S. 2003. Proteins that make sense, pp. 447–476, in G. J. Blomquist and R. G. Vogt (eds.). Insect Pheromone Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. Elsevier Academic Press, Amsterdam.
Ljungberg, H., Anderson, P., and Hansson, B. S. 1993. Physiology and morphology of pheromone-specific sensilla on the antennae of male and female Spodoptera littoralis (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J. Insect Physiol. 39:253–260.
Maïbèche-Coisné, M., Sobrio, F., Delaunay, T., Lettere, M., Dubroca, J., Jacquin-Joly, E., and Nagnan-Le Meillour, P. 1997. Pheromone-Binding Proteins of the moth Mamestra brassicae: specificity of ligand binding. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 27:213–221.
Maïbèche-Coisné, M., Jacquin-Joly, E., François, M. C., and Nagnan-Le Meillour, P. 1998. Molecular cloning of two pheromone-binding proteins in the cabbage armyworm Mamestra brassicae. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 28:815–818.
Mida, R., Krieger, J., Gebauer, T., Lange, U., and Ziegelberger, G. 2000. Three pheromone-binding proteins in olfactory sensilla of the two silkmoth species Antheraea polyphemus and Antheraea pernyi. Eur. J. Biochem. 267:2899–2908.
Maida, R., Ziegelberger, G., and Kaissling, K. E. 2003. Ligand binding to six recombinant pheromone-binding proteins of Antheraea polyphemus and Antheraea pernyi. J. Comp. Physiol. 173:565–573.
Mazomenos, B. E. 1989. Sex pheromone components of corn stalk borer Sesamia nonagrioides (Lef.), Isolation, identification, and field tests. J. Chem. Ecol. 15:1241–1247.
Nielsen, H., Engelbrecht, J., Brunak, S., and Von Heijne, G. 1997. Identification of prokaryotic and eukaryotic signal peptides and prediction of their cleavage sites. Protein Eng. 10:1–6.
Picimbon, J.-F. and Gadenne, C. 2002. Evolution of noctuid pheromone-binding proteins: identification of PBP in the black cutworm moth, Agrotis ipsilon. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 32:839–846.
Picimbon, J.-F. 2003. Biochemistry and evolution of OBP and CSP proteins, pp. 539–566, in G. J. Blomquist and R. G. Vogt (eds.). Insect Pheromone Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. Elsevier Academic Press, Amsterdam.
Plettner, E., Lazar, J., Prestwich, E. G., and Prestwich, G. D. 2000. Discrimination of pheromone enantiomers by two pheromone-binding proteins from the gypsy moth Lymantria dispar. Biochemistry 39:8953–8962.
Pophof, B. 2002. Moth pheromone-binding proteins contribute to the excitation of olfactory receptor cells. Naturwissenschaften 89:515–518.
Pophof, B. 2004. Pheromone-binding proteins contribute to the activation of olfactory receptor neurons in the silkmoths Antheraea polyphemus and Bombyx mori. Chem. Senses 29:117–125.
Prestwich, G. D., Du, G., and Laforest, S. 1995. How is pheromone specificity encoded in proteins? Chem. Senses 20:461–469.
Quero, C., Bau, J., Guerrero, A., and Renou, M. 2004. Responses of the olfactory receptor neurons of the corn stalk borer Sesamia nonagrioides to components of the pheromone blend and their inhibition by a trifluoromethyl ketone analogue of the main component. Pest Manag. Sci. 60:719–726.
Raming, K., Krieger, J., and Breer, H. 1990. Primary structure of a pheromone-binding protein from Antheraea pernyi: homologies with other ligand-carrying proteins. J. Comp. Physiol. B 1160:503–509.
Renou, M. and Lucas, P. 1994. Sex pheromone reception in Mamestra brassicae L. (Lepidoptera): Responses of olfactory receptor neurons to minor components of the pheromone blend. J. Insect Physiol. 40:75–85.
Robertson, H. M., Martos, R., Sears, C. R., Todres, E. Z., Walden, K. K., and Nardi, J. B. 1999. Diversity of odourant-binding proteins revealed by an expressed sequence tag project on male Manduca sexta moth antennae. Insect Mol. Biol. 8:501–518.
Solinas, M. and Trona, F. 2002. Antennal sensilla of Sesamia nonagrioides (Lef.) (Lepidopterae: Noctuidae) Morphology and possible behavioural significance. Boll. Zool. Agrar. Bachic. Ser. II 34:321–345.
Steinbrecht, R. A., Ozaki, M., and Ziegelberger, G. 1992. Immunocytochemical localization of pheromone-binding protein in moth antennae. Cell Tissue Res. 270:287–302.
Steinbrecht, R. A., Laue, M., and Ziegelberger, G. 1995. Immunolocalization of pheromone-binding protein and general-odorant binding protein in olfactory sensilla of the silk moths Antheraea and Bombyx. Cell Tissue Res. 282:203–217.
Vinson, S. B. 1984. How parasitoids locate their hosts: a case of insect espionage, pp. 325–348, in T. Lewis (ed.). Insect Communication. 12th symposium of the Royal Entomological Society of London. Academic Press, London.
Vinson, S. B. 1998. The general host selection behavior of parasitoid Hymenoptera and a comparison of initial strategies utilised by larvaphagous and oophagous species. Biol. Control. 11:79–96.
Vogt, R. G. 2003. Biochemical diversity of odor detection: OBPs, ODEs and SNMPs, pp. 391–445, in G. J. Blomquist and R. G. Vogt (eds.). Insect Pheromone Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. Elsevier Academic Press, Amsterdam.
Vogt, R. G. and Riddiford, L. M. 1981. Pheromone binding and inactivation by moth antennae. Nature 293:161–163.
Vogt, R. G., Kohne, A. C., Dbnau, J. T., and Prestwich, G. D. 1989. Expression of pheromone-binding proteins during antennal development in the gypsy moth Lymantria dispar. J. Neurosci. 9:3332–3346.
Vogt, R. G., Prestwich, G. D., and Lerner, M. R. 1991. Odorant-binding-protein subfamilies associate with distinct classes of olfactory receptor neurons in insects. J. Neurobiol. 22:74–84.
Vogt, R. G., Callahan, F. E., Rogers, M. E., and Dickens, J. C. 1999. Odorant-binding protein diversity and distribution among insect orders, as indicated by LAP, an OBP-related protein of the true bug Lygus lineolaris (Hemiptera, Heteroptera). Chem. Senses 24:481–495.
Vogt, R. G., Rogers, M. E., Franco, M. D., and Sun, M. 2002. A comparative study of odorant binding protein genes: differential expression of the PBP1-GOBP2 gene cluster in Manduca sexta (Lepidoptera) and the organization of OBP genes in Drosophila melanogaster (Diptera). J. Exp. Biol. 205:719–744.
Willett, C. S. 2000a. Do pheromone-binding proteins converge in amino acid sequence when pheromones converge? J. Mol. Evol. 50:175–183.
Willett, C. S. 2000b. Evidence for directional selection acting on Pheromone-binding proteins in the genus Choristoneura. Mol. Biol. Evol. 17:553–562.
Wojtasek, H. and Lal, W. S. 1999. Conformational change in the pheromone-binding protein from Bombyx mori induced by pH and by interaction with membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 274:30950–30956.
Zhang, S.-G., Mida, R., and Steinbrecht, R. A. 2001. Immunolocalization of odorant-binding proteins in noctuid moths (Insecta, Lepidoptera). Chem. Senses 26:885–896.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by INRA, by the Integrated Action Program GALILEO no. 06914YG (Egide, France), and by a Marie Curie fellowship to F. de Santis. We are grateful to Chiaraluce Moretti and Roberto Bonaurio (DSAA-Patologia, Università degli Studi di Perugia) for useful suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Santis, F., François, MC., Merlin, C. et al. Molecular Cloning and in Situ Expression Patterns of Two New Pheromone-Binding Proteins from the Corn Stemborer Sesamia nonagrioides . J Chem Ecol 32, 1703–1717 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-006-9103-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-006-9103-2