Abstract
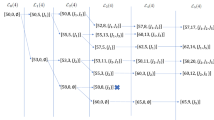
This paper considers the large-scale mixed job shop scheduling problem with general number of jobs on each route. The problem includes ordinary machines, batch machines (with bounded or unbounded capacity), parallel machines, and machines with breakdowns. The objective is to find a schedule to minimize the makespan. For the problem, we define a virtual problem and a corresponding virtual schedule, based on which our algorithm TVSA is proposed. The performance analysis of the algorithm shows the gap between the obtained solution and the optimal solution is O(1), which indicates the algorithm is asymptotically optimal.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bertsimas D, Gamarnik D (1999) Asymptotically optimal algorithms for job shop scheduling and packet routing. J Algorithms 33:296–318
Bertsimas D, Gamarnik D, Sethuraman J (2003) From fluid relaxations to practical algorithms for figh-multiplicity job-shop scheduling: the holding cost objective. Oper Res 51(5):798–813
Bertsimas D, Sethuraman J (2002) From fluid relaxations to practical algorithms for job shop scheduling: the makespan objective. Math Prog 92(1):61–102
Boudoukh T, Penn M, Weiss G (1998) Job-shop - an application of fluid approximation. In: Gilad I (ed) Proceedings of the tenth conference of industrial engineering and management, pp 254–258
Boudoukh T, Penn M, Weiss G (2001) Scheduling jobshops with some identical or similar jobs. J Sched 4:177–199
Chou M, Liu H, Queyranne M et al (2006) On the asymptotic optimality of a simple on-line algorithm for the stochastic single-machine weighted completion time problem and its extensions. Oper Res 54:464474
Dai JG, Weiss G (2002) A fluid heuristic for minimizing makespan in job shops. Oper Res 50(4):692–707
Fleischer L, Sethuraman J (2005) Efficient algorithms for separated continuous linear programs: the multicommodity flow problem with holding costs and extensions. Math Oper Res 30(4):916–938
Garey MR, Johnson DS, Sethi R (1976) The complexity of flowshop and jobshop scheduling. Math Oper Res 1(2):117–129
Gu M, Lu X (2011) Asymptotical optimality of WSEPT for stochastic online scheduling on uniform machines. Ann Oper Res 191(1):97–113
Gu M, Lu X (2013) The expected asymptotical ratio for preemptive stochastic online problem. Theoret Comput Sci 495:96–112
Masin M, Raviv T (2014) Linear programming-based algorithms for the minimum makespan high multiplicity jobshop problem. J Sched 17:321–338
Nazarathy Y, Weiss G (2009) A fluid approach to job shop scheduling: theory, software and experimentation. J Sched 13:509–529
Nazarathy Y, Weiss G (2010) A fluid approach to large volume job shop scheduling. J Sched 13:509–529
Penn M, Raviv T (2009) An algorithm for the maximum revenue jobshop problem. Eur J Oper Res 193:437–450
Weiss G (2008) A simplex based algorithm to solve separated continuous linear programs. Math Progr 115(1):151–198
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China(Grant Nos. 11201282, 11371137 and 61304209), Humanity and Social Science Youth Foundation of Ministry of Education of China(Grant no. 10YJCZH032), Innovation Program of Shanghai Municipal Education Commission (Grant No. 14YZ127).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
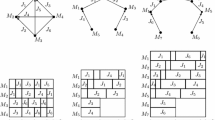
In each matrix, one line is for a route. Each line contains the number of jobs and the number of machines, listing the machine number and the processing load for each step of the route. The machines are numbered starting with 1.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, M., Lu, X. & Gu, J. An asymptotically optimal algorithm for large-scale mixed job shop scheduling to minimize the makespan. J Comb Optim 33, 473–495 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10878-015-9974-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10878-015-9974-7