Abstract
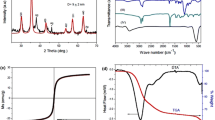
The broad application of organic dyes such as 4-nitrophenol (4-NP), rhodamine 6G (R6G), and methylene blue (MB) as raw materials in the manufacture of dyes, explosives, pesticides, preservatives, and pharmaceuticals caused serious damage to the environment, particularly aquatic ecosystems. In this study, silver nanoparticles decorated ZnO/Fe3O4 (Ag/ZnO/Fe3O4) nanocomposite was used as a catalyst to reduce 4-NP, R6G, and MB in the presence of sodium borohydride as a reducing agent. Silver nanoparticles decorated ZnO/Fe3O4 composite was synthesized via a simple and inexpensive chemical reduction method. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy dispersive X-ray analysis (EDX), and X-ray diffraction (XRD) were used to characterize the particles. The surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) activity of the nanocomposites due to AgNPs was used to monitor catalytic reactions with detailed spectral features using SERS. Thus, the catalytic transformation of 4-nitrothiophenol (4-NTP) into 4-aminothiophenol (4-ATP) was traced using SERS. The magnetic property of the nanocomposites enables its repeated use. Easy recovery of the particles from the reaction solution was achieved and run for fifteen cycles with no significant loss of its efficiency.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Das, V. S. Sypu, H. K. Paumo, M. Bhaumik, V. Maharaj, and A. Maity (2019). Silver decorated magnetic nanocomposite (Fe3O4@PPy-MAA/Ag) as highly active catalyst towards reduction of 4-nitrophenol and toxic organic dyes. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 244, 546–558.
Y. Wang, P. Gao, Y. Wei, Y. Jin, S. Sun, Z. Wang, and Y. Jiang (2021). Silver nanoparticles decorated magnetic polymer composites (Fe3O4@PS@Ag) as highly efficient reusable catalyst for the degradation of 4-nitrophenol and organic dyes. J. Environ. Manage. 278, 111473.
M. T. Alula, B. A. Aragaw, S. T. Modukanele, and J. Yang (2021). Enhanced catalytic activity of silver nanoparticles loaded into Fe3O4 nanoparticles towards reduction of 4-nitrophenol, degradation of organic dyes and oxidation of o-phenylenediamine. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 127, 108504.
M. H. Kahsay, D. RamaDevi, Y. P. Kumar, B. S. Mohan, A. Tadesse, G. Battu, and K. Basavaiah (2018). Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using aqueous extract of Dolichos lablab for reduction of 4-Nitrophenol, antimicrobial and anticancer activities. OpenNano 3, 28–37.
M. Nasrollahzadeh, M. Atarod, B. Jaleh, and M. Gandomirouzbahani (2016). In situ green synthesis of Ag nanoparticles on graphene oxide/TiO2 nanocomposite and their catalytic activity for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol, congo red and methylene blue. Ceram. Int. 42, 8587–8596.
H. Veisi, S. B. Moradi, A. Saljooqi, and P. Safarimehr (2019). Silver nanoparticle-decorated on tannic acid-modified magnetite nanoparticles (Fe3O4 @TA/Ag) for highly active catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol, Rhodamine B and Methylene blue. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 100, 445–452.
U. Kurtan and A. Baykal (2014). Fabrication and characterization of Fe3O4@APTES@ PAMAM-Ag highly active and recyclable magnetic nanocatalyst: catalytic reduction of 4- nitrophenol. Mater. Res. Bull. 60, 79–87.
P. D. Tomke and V. K. Rathod (2020). Facile fabrication of silver on magnetic nanocomposite (Fe3O4@Chitosan-AgNP nanocomposite) for catalytic reduction of anthropogenic pollutant and agricultural pathogens. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 149, 989–999.
M. R. Islam, M. Ferdous, M. I. Sujan, X. Mao, H. Zeng, and M. S. Azam (2020). Recyclable Ag-decorated highly carbonaceous magnetic nanocomposites for the removal of organic pollutants. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 562, 52–62.
G. Liao, Y. Gong, L. Zhong, J. Fang, L. Zhang, Z. Xu, H. Gao, and Baizeng Fang (2019). Unlocking the door to highly efficient Ag-based nanoparticles catalysts for NaBH4-assisted nitrophenol reduction. Nano Res. 12, 2407–2436.
C. Wen, A. Yin, and W.-L. Dai (2014). Recent advances in silver-based heterogeneous catalysts for green chemistry processes. Appl. Catal. B 160–161, 730–741.
Y. R. Mejía and N. K. R. Bogireddy (2022). Reduction of 4-nitrophenol using green-fabricated metal nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 12, 18661–18675.
H. Xu, L. Yan, Y. Yu, and Y. Xu (2018). Facile synthesis of carbon-supported silver nanoparticles for optical limiting. Appl. Surf. Sci. 457, 655–661.
Z. Ji, X. Shen, X. Yue, H. Zhou, J. Yang, Y. Wang, L. Ma, and K. Chen (2015). Facile synthesis of magnetically separable reduced graphene oxide/magnetite/silver nanocomposites with enhanced catalytic activity. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 459, 79–85.
E. Hariprasad and T. P. Radhakrishnan (2012). Palladium nanoparticle-embedded polymer thin film “dip catalyst” for Suzuki-Miyaura reaction. ACS Catal. 2, 1179–1186.
K. Zhang, C. Wang, Z. Rong, R. Xiao, Z. Zhou, and S. Wang (2017). Silver coated magnetic microflowers as efficient and recyclable catalysts for catalytic reduction. New J. Chem. 41, 14199–14208.
Q. Liu, L. Zhou, L. Liu, J. Li, S. Wang, H. Znad, and S. Liu (2020). Magnetic ZnO@Fe3O4 composite for self-generated H2O2 toward photo-Fenton-like oxidation of nitrophenol. Compos. Part B Eng. 200, 108345.
H. Koga, T. Kitaoka, and H. Wariishi (2009). In situ synthesis of silver nanoparticles on zinc oxide whiskers incorporated in a paper matrix for antibacterial applications. J. Mater. Chem. 19, 2135–2140.
M. T. Alula, P. Lemmens, L. Bo, D. Wulferding, J. Yang, and H. Spende (2019). Preparation of silver nanoparticles coated ZnO/Fe3O4 composites using chemical reduction method for sensitive detection of uric acid via surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Anal. Chim. Acta 1073, 62–71.
S. F. Chin, K. S. Iyer, and C. L. Raston (2009). Facile and green approach to fabricate gold and silver coated superparamagnetic nanoparticles. Cryst. Growth Des. 9, 2685–2689.
J. Xia, A. Wang, X. Liu, and Z. Su (2011). Preparation and characterization of bifunctional, Fe3O4 /ZnO nanocomposites and their use as photocatalysts. Appl. Surf. Sci. 257, 9724–9732.
M. T. Alula and J. Yang (2014). Photochemical decoration of magnetic composites with silver nanostructures for determination of creatinine in urine by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Talanta 130, 55–62.
R. He, X. Qian, J. Yin, and Z. Zhu (2002). Preparation of polychrome silver nanoparticles in different solvents. J. Mater. Chem. 12, 3783–3786.
M. T. Alula and J. Yang (2014). Photochemical decoration of silver nanoparticles on magnetic microspheres as substrates for the detection of adenine by surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Anal. Chim. Acta 812, 114–120.
M. T. Alula, M. L. Madingwane, H. Yan, P. Lemmens, L. Zhe, and M. Etzkorn (2022). Biosynthesis of bifunctional silver nanoparticles for catalytic reduction of organic pollutants and optical monitoring of mercury (II) ions using their oxidase-mimic activity. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21619-7.
N. Pradhan, A. Pal, and T. Pal (2002). Silver nanoparticle catalyzed reduction of aromatic nitro compounds. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 196, 247–257.
X. Chen, X. Chen, Z. Cai, and M. Oyama (2014). AuPd bimetallic nanoparticles decorated on graphene nanosheets: their green synthesis, growth mechanism and high catalytic ability in 4-nitrophenol reduction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2, 5668–5674.
Y. Liu, Y. Y. Zhang, Q. W. Kou, Y. Chen, D. L. Han, D. D. Wang, Z. Y. Lu, L. Chen, J. H. Yang, and S. Xing (2018). Eco-friendly seeded Fe3O4-Ag nanocrystals: a new type of highly efficient and low cost catalyst for methylene blue reduction. RSC Adv. 8, 2209–2218.
M. T. Alula, P. Lemmens, M. Madiba, and B. Present (2020). Synthesis of free-standing silver nanoparticles coated filter paper for recyclable catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol and organic dyes. Cellulose 27, 2279–2292.
Y. Qiu, Z. Ma, and P. Hu (2014). Environmentally benign magnetic chitosan/Fe3O4 composites as reductant and stabilizer for anchoring Au NPs and their catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. J. Mater. Chem. A 2, 13471–13478.
M. Mazhani, M. T. Alula, and D. Murape (2021). SERS assisted monitoring of catalytic reduction reaction using silver-magnetic nanocomposites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 265, 124487.
T. B. Nguyen, C. P. Huang, and R. A. Doong (2019). Enhanced catalytic reduction of nitrophenols by sodium borohydride over highly recyclable Au@graphitic carbon nitride nanocomposites. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 240, 337–347.
F. H. Lin and R. A. Doong (2014). Highly efficient reduction of 4-nitrophenol by heterostructured gold-magnetite nanocatalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 486, 32–41.
A. N. Chishti, L. Ni, F. Guo, X. Lin, Y. Liu, H. Wu, M. Chen, and G. W. Diao (2021). Magnetite-Silica core-shell nanocomposites decorated with silver nanoparticles for enhanced catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol and degradation of methylene blue dye in the water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 9, 104948.
H. Veisi, S. Razeghi, P. Mohammadi, and S. Hemmati (2019). Silver nanoparticles decorated on thiol-modified magnetite nanoparticles (Fe3O4 /SiO2 -Pr-S-Ag) as a recyclable nanocatalyst for degradation of organic dyes. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 97, 624–631.
U. Kurtan, M. Amir, A. Yildiz, and A. Baykal (2016). Synthesis of magnetically recyclable MnFe2O4 @SiO2 @Ag nanocatalyst: Its high catalytic performances for azo dyes and nitro compounds reduction. Appl. Surf. Sci. 376, 16–25.
M. T. Shah, A. Balouch, A. A. Sirajuddin, Abdullah Pathan, A. M. Mahar, S. Sabir, R. Khattak, and A. A. Umar (2017). SiO2 caped Fe3O4 nanostructures as an active heterogeneous catalyst for 4-nitrophenol reduction. Microsyst. Technol. 23, 5745–5758.
N. Esmaeili, P. Mohammadi, M. Abbaszadeh, and H. Sheibani (2019). Au nanoparticles decorated on magnetic nanocomposite (GO-Fe3O4/Dop/Au) as a recoverable catalyst for degradation of methylene blue and methyl orange in water. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 44, 23002–23009.
J. Shen, Y. Zhou, J. Huang, Y. Zhu, J. Zhu, X. Yang, W. Chen, Y. Yao, S. Qian, H. Jiang, and C. Li (2017). In-situ SERS monitoring of reaction catalyzed by multifunctional Fe3O4@TiO2@Ag-Au microspheres. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 205, 11–18.
W. Shen, Y. Qu, X. Pei, S. Li, S. You, J. Wang, Z. Zhang, and J. Zhou (2017). Catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol using gold nanoparticles biosynthesized by cell-free extracts of Aspergillus sp WL-Au. J. Hazard. Mater. 321, 299–306.
G. Zheng, L. Polavarapu, L. M. Liz-Marzán, I. Pastoriza-Santos, and J. Pérez-Juste (2015). Gold nanoparticle-loaded filter paper: a recyclable dip-catalyst for real-time reaction monitoring by surface enhanced Raman scattering. Chem. Commun. 51, 4572–4575.
P. Rajapandiyan and J. Yang (2012). Sensitive cylindrical SERS substrate array for rapid microanalysis of nucleobases. Anal. Chem. 84, 10277–10282.
K. He, N. Chen, C. Wang, L. Wei, and J. Chen (2018). Method for determining crystal grain size by X-ray diffraction. Cryst. Res. Technol. 53, 1700157.
Acknowledgements
The financial support for this project was obtained from Botswana International University of Science and Technology (BIUST) initiation grant (DVC/RDI/2/1/16I (48) that was awarded to MTA and we would like to thank BIUST for the financial assistance. The authors would also like to thank Prof. Amare Gessesse and Prof. Asfawossen Asrat Kassaye for editing the revised manuscript.
Funding
The financial support for this project was obtained from Botswana International University of Science and Technology (BIUST) initiation Grant (DVC/RDI/2/1/16I (48).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MTA: conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, investigation, writing—part of original draft, review & editing. HS: investigation. TAA: writing—review & editing. ANA: writing—part of original draft. BAA: formal analysis, Writing—review & editing. MM: investigation, analysis. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Alula, M.T., Spende, H., Aragaw, T.A. et al. A Highly Stable Silver Nanoparticle Loaded Magnetic Nanocomposite as a Recyclable Catalysts. J Clust Sci 34, 2205–2214 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-022-02386-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-022-02386-4