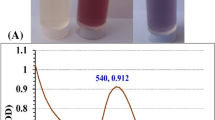
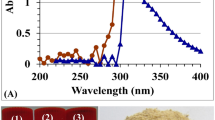
Abstract
Different growth stages of Penicillium notatum, P. purpurogenum and P. aculeatum were evaluated for their potential for zirconium nanoparticle (Zr-NP) biosynthesis by total protein content assay. Fungal secreted protein concentrations for all three species were higher at deceleration phase. For optimizing biosynthesis conditions with respect to Zr-NP size, different pH values and ZrCl4 concentrations were tested and analyzed. The artificial neural network (ANN) modeling was then applied to find the best conditions. A feed-forward ANN model was used to make a connection between the output as the size of Zr-NPs, with three input variables, including pH, ZrCl4 concentration and fungal species. An optimal multi-layer perceptron neural network was finally designed to model the experimental data for which the correlation coefficients R2 at each phase (training, validation and test sets) were calculated to be 0.9946, 0.9952 and 0.9997, respectively. The accuracy of the model was confirmed through validation experiments.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. O. Simbine, Ld. C. Rodrigues, J. Lapa-Guimaraes, E. S. Kamimura, C. H. Corassin, and C. AFd. Oliveira (2019). Application of silver nanoparticles in food packages: a review. Food Sci. Technol. 39, 793–802.
V. Bansal, D. Rautaray, A. Ahmad, and M. Sastry (2004). Biosynthesis of zirconia nanoparticles using the fungus Fusarium oxysporum. J. Mater. Chem. 14, 3303–3305.
K. AbdelRahim, S. Y. Mahmoud, A. M. Ali, K. S. Almaary, A.E.-Z.M. Mustafa, and S. M. Husseiny (2017). Extracellular biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Rhizopus stolonifer. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 24, 208–16.
A. C. Sergio Almeida, E. A. Nazario Franco, F. M. Peixoto, K. L. Ferreira Pessanha, and N. R. Melo (2015). Application of nanotechnology in food packaging. Polimeros-Ciencia E Tecnologia. 25, 89–97.
Y. Echegoyen and C. Nerín (2013). Nanoparticle release from nano-silver antimicrobial food containers. Food Chem. Toxicol. 62, 16–22.
C. Silvestre, D. Duraccio, and S. Cimmino (2011). Food packaging based on polymer nanomaterials. Progress Polym. Sci. 36, 1766–1782.
H. Barabadi (2017). Nanobiotechnology: a promising scope of gold biotechnology. Cell. Mol. Biol. 63, 3–4.
R. Pourrahim, S. Farzadfar, and A. Golnaraghi, Nanotechnology and Agriculture (Sepehr Co., Tehran, 2008).
A. P. Alivisatos (1996). Semiconductor clusters, nanocrystals, and quantum dots. Science. 271, 933–937.
A. N. Shipway, E. Katz, and I. Willner (2000). Nanoparticle arrays on surfaces for electronic, optical, and sensor applications. ChemPhysChem. 1, 18–52.
A. Ahmad, P. Mukherjee, D. Mandal, S. Senapati, M. I. Khan, R. Kumar, et al. (2002). Enzyme mediated extracellular synthesis of CdS nanoparticles by the fungus, Fusarium oxysporum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124, 12108–12109.
L. Addadi and S. Weiner (1992). Control and design principles in biological mineralization. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Eng. 31, 153–169.
S. Mann and G. A. Ozin (1996). Synthesis of inorganic materials with complex form. Nature. 382, 313–318.
H. Barabadi, H. Vahidi, K. D. Kamali, M. Rashedi, O. Hosseini, A. R. Golnaraghi-Ghomi, et al. (2020). Emerging theranostic silver nanomaterials to combat colorectal cancer: a systematic review. J. Clust. Sci. 31, 311–321.
N. Durán, P. D. Marcato, R. D. Conti, O. L. Alves, F. Costa, and M. Brocchi (2010). Potential use of silver nanoparticles on pathogenic bacteria, their toxicity and possible mechanisms of action. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 21, 949–959.
X. Wei, M. Luo, W. Li, L. Yang, X. Liang, L. Xu, et al. (2012). Synthesis of silver nanoparticles by solar irradiation of cell-free Bacillus amyloliquefaciens extracts and AgNO3. Bioresour. Technol. 103, 273–278.
P. Sonkusre, R. Nanduri, P. Gupta, and S. S. Cameotra (2014). Improved extraction of intracellular biogenic selenium nanoparticles and their specificity for cancer chemoprevention. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 5, 1.
N. Pantidos and L. E. JJo. N. Horsfall (2014). Nanotechnology. Biological synthesis of metallic nanoparticles by bacteria, fungi and plants. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 5, 5.
A. R. Golnaraghi-Ghomi, N. Asasian-Kolur, S. Sharifian, and A. Golnaraghi (2020). Biosorpion for sustainable recovery of precious metals from wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 8, 103996.
S. Sōmiya, N. Yamamoto, and H. Yanagida, Science and Technology of Zirconia (American Ceramic Society, Columbus, 1986).
R. C. Garvie, R. Hannink, and R. Pascoe (1975). Ceramic steel? Nature. 258, 703–704.
H. Xu, D.-H. Qin, Z. Yang, and H.-L. Li (2003). Fabrication and characterization of highly ordered zirconia nanowire arrays by sol–gel template method. Mater. Chem. Phys. 80, 524–528.
P. D. Southon, J. R. Bartlett, J. L. Woolfrey, and B. Ben-Nissan (2002). Formation and characterization of an aqueous zirconium hydroxide colloid. Chem. Mater. 14, 4313–4319.
H. Raihani (1994). Zirconia formation by reaction of zirconium sulfate in molten alkali-metal nitrates or nitrites. J. Mater. Chem. 4, 1331–1336.
H.-J. Noh, D.-S. Seo, H. Kim, and J.-K. Lee (2003). Synthesis and crystallization of anisotropic shaped ZrO2 nanocrystalline powders by hydrothermal process. Mater. Lett. 57, 2425–2431.
D. R. Lovley, J. F. Stolz, G. L. Nord, and E. J. Phillips (1987). Anaerobic production of magnetite by a dissimilatory iron-reducing microorganism. Nature. 330, 252–254.
S. V. Patwardhan, N. Mukherjee, M. Steinitz-Kannan, and S. J. Clarson (2003). Bioinspired synthesis of new silica structures. Chem Commun. https://doi.org/10.1039/b302056h.
F. N. Spagnoletti, C. Spedalieri, F. Kronberg, and R. J. Giacometti (2019). Extracellular biosynthesis of bactericidal Ag/AgCl nanoparticles for crop protection using the fungus Macrophomina phaseolina. J. Environ. Manag. 231, 457–466.
F. M. Mosallam, G. S. El-Sayyad, R. M. Fathy, and A. I. El-Batal (2018). Biomolecules-mediated synthesis of selenium nanoparticles using Aspergillus oryzae fermented Lupin extract and gamma radiation for hindering the growth of some multidrug-resistant bacteria and pathogenic fungi. Microbial. Pathogenesis. 122, 108–116.
S. A. Shafiq, R. H. Al-Shammari, H. Z. Majeed, and A. Studies (2016). Study of Biosynthesis silver nanoparticles by Fusarium graminaerum and test their antimicrobial activity. Int. J. Innov. Appl. Stud. 15, 43.
J. Kisała, K. Hęclik, A. Masłowska, M. Celuch, and D. Pogocki (2017). Natural environments for nanoparticles synthesis of metal, metal oxides, core–shell and bimetallic systems. Stud. Nat. Prod. Chem. 52, 1–67.
M. Shah, D. Fawcett, S. Sharma, S. K. Tripathy, and G. E. J. J. M. Poinern (2015). Green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles via biological entities. Materials. 8, 7278–308.
A. R. Golnaraghi-Ghomi, M. Mohammadi-Khanaposhti, H. Vahidi, F. Kobarfard, M. Ameri Shah-Reza, and H. Barabadi (2019). Fungus-mediated extracellular biosynthesis and characterization of zirconium nanoparticles using standard penicillium species and their preliminary bactericidal potential: a novel biological approach to nanoparticle synthesis. IJPR. 18, 2101.
P. Shabanzadeh, R. Yusof, and K. J. R. A. Shameli (2015). Modeling of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles in Vitex negundo L. extract by artificial neural network. RSC Adv. 5, 87277–85.
A. Thapliyal, R. K. Khar, and A. J. C. N. Chandra (2018). Artificial neural network modelling of green synthesised silver nanoparticles in bentonite/starch bio-nanocomposite. Curr. Nanosci. 14, 239–251.
P. Shabanzadeh, R. Yusof, and K. Shameli (2015). Artificial neural network for modeling the size of silver nanoparticles’ prepared in montmorillonite/starch bionanocomposites. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 24, 42–50.
P. Shabanzadeh, N. Senu, K. Shameli, and M. M. Tabar (2013). Artificial intelligence in numerical modeling of silver nanoparticles prepared in montmorillonite interlayer space. J. Chem.
M. B. A. Rahman, N. Chaibakhsh, M. Basri, A. B. Salleh, and R. N. Rahman (2009). Application of artificial neural network for yield prediction of lipase-catalyzed synthesis of dioctyl adipate. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 158, 722–735.
S. Hamedi, S. A. Shojaosadati, S. Shokrollahzadeh, and S. Hashemi-Najafabadi (2014). Biotechnology. Extracellular biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using a novel and non-pathogenic fungus, Neurospora intermedia: controlled synthesis and antibacterial activity. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 30, 693–704.
R. Y. Sweeney, C. Mao, X. Gao, J. L. Burt, A. M. Belcher, G. Georgiou, et al. (2004). Bacterial biosynthesis of cadmium sulfide nanocrystals. Chem. Biol. 11, 1553–1559.
H. Fernández-Llamosas, L. Castro, M. L. Blázquez, E. Díaz, and M. J. M. Carmona (2016). Biosynthesis of selenium nanoparticles by Azoarcus sp. CIB. Microbial. Cell Fact. 15, 1–10.
C. Buerth, C. J. Heilmann, F. M. Klis, C. G. de Koster, J. F. Ernst, and D. J. M. Tielker (2011). Growth-dependent secretome of Candida utilis. Microbiol. Soc. 157, 2493–2503.
E. S. Shahid, M. Salari, M. Ehteshami, and S. N. Sheibani (2020). Artificial neural network (ANN) modeling of cavitation mechanism by ultrasonic irradiation for cyanobacteria growth inhibition. J. Environ. Treat. Tech. 8, 625–633.
P. Shabanzadeh, R. Yusof, and K. Shameli (2015). Modeling of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles in Vitex negundo L. extract by artificial neural network. RSC Adv. 5, 87277–85.
O. Roeva (2012). Real-World Applications of Genetic Algorithms. BoD–Books on Demand.
O. M. Darwesh, I. A. Matter, M. F. Eida, H. Moawad, and Y.-K.J.A.S. Oh (2019). Influence of nitrogen source and growth phase on extracellular biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using cultural filtrates of Scenedesmus obliquus. Appl. Sci. 9, 1465.
T. Ahmad, I. A. Wani, N. Manzoor, J. Ahmed, A. M. J. C. Asiri, and S. B. Biointerfaces (2013). Biosynthesis, structural characterization and antimicrobial activity of gold and silver nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B. 107, 227–234.
D. Lahiri, M. Nag, H. I. Sheikh, T. Sarkar, H. A. Edinur, S. Pati, et al. (2021). Microbiologically-synthesized nanoparticles and their role in silencing the biofilm signaling cascade. Front. Microbiol. 12, 1.
M. Guilger-Casagrande and Rd. Lima (2019). Synthesis of silver nanoparticles mediated by fungi: a review. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2019.00287.
M. Rostamizadeh and S. M. H. Rizi (2012). Predicting gas flux in silicalite-1 zeolite membrane using artificial neural networks. J. Membr. Sci. 403, 146–151.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank School of Pharmacy, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences (Tehran, Iran) for supporting this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Golnaraghi-Ghomi, A.R., Mohammadi-Khanaposhti, M., Sokhansanj, A. et al. Artificial Neural Network Modeling of Fungus-Mediated Extracellular Biosynthesis of Zirconium Nanoparticles Using Standard Penicillium spp.. J Clust Sci 33, 1907–1921 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-021-02111-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-021-02111-7