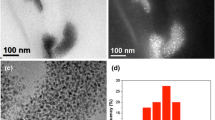
Abstract
The search for new more effective nanoparticles based antimicrobial agents has been under way in recent decades. Silver nanoparticles are hydrophobic and have a negative charge. We report on the preparation of Ag–Cu bimetallic nanoparticles with various silver contents synthesized by electric explosion of two twisted wires of the metals in argon atmosphere. The method allows to obtain nanoparticles of a given composition, has high performance and scalability. Nanoparticles were investigated using X-ray diffraction, high-resolution transmission electron microscopy, energy dispersive analysis and microelectrophoresis techniques. We evaluated the antibacterial activity of the nanoparticles against Gram-negative E. coli and Gram-positive methicillin resistance S. aureus MRSA. Our study showed that the synthesized nanoparticles have a positive zeta potential of about 30 mV at pH 7.2 and high antimicrobial activity against the tested bacteria strains, which is close to the activity of silver nanoparticles with a size of 20 nm. The high antimicrobial activity of the nanoparticles is due to the prolonged slow release of silver and copper ions, which makes nanoalloys more effective than Cu and Ag metallic nanoparticles. The synthesized nanoparticles have high antimicrobial activity and demonstrate the potential for their use as promising new generation antibacterial agents effective against resistant microorganisms.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Syed, N. Karthik, P. Bhat, N. Bisht, A. Prasad, S. Satish, and M. N. Prasad (2000). J. King Saud Univ. Sci.. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2018.01.008.
X. Wang, R. Li, Z. Li, R. Xiao, X. B. Chen, and T. Zhang (2019). J. Mater. Chem.. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9TB00148D.
C. E. Shi, L. Pan, C. R. Wang, Y. He, Y. F. Wu, and S. S. Xue (2016). JOM. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2008.10.002.
J. T. Lue (2001). J. Phys. Chem. Solid. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-3697(01)00099-3.
M. Auffan, J. Rose, M. R. Wiesner, and J. Y. Bottero (2009). Environ. Pollut.. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2008.10.002.
S. Shaikh, N. Nazam, S. M. D. Rizvi, K. Ahmad, M. H. Baig, E. J. Lee, and I. Choi (2019). Int. J. Mol. Sci.. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102468.
S.C. Sahu, A.W. Hayes Toxicol. Res. Appl. 1 2397847317726352(2017).
A. C. Burduşel, O. Gherasim, A. Grumezescu, L. Mogoantă, A. Ficai, and E. Andronescu (2018). Nanomaterials. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8090681.
S. Prabhu and E. K. Poulose (2012). Int. Nano Lett.. https://doi.org/10.1186/2228-5326-2-32.
I. Fratoddi (2018). Nanomaterials. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8010011.
M. Akter, M. T. Sikder, M. Rahman, A. A. Ullah, K. F. B. Hossian, S. Banik, T. Hosokawa, T. Saito, and M. Kurasaki (2018). J. Adv. Res.. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2017.10.008.
A. Panáček, L. Kvítek, M. Smékalová, R. Večeřová, M. Kolář, M. Röderová, F. Dyčka, M. Šebela, R. Prucek, O. Tomanec, and R. Zbořil (2018). Nat. Nanotechnol.. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-017-0013-y.
K. E. Alzahrani, A. A. Niazy, A. M. Alswieleh, R. Wahab, A. M. El-Toni, and H. S. Alghamdi (2018). Int. J. Nanomed.. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S154218.
S. Mohammadi, N.H. Jazani, M. Kouhkan, L.A. Babaganjeh, Iran J Microbiol 10 (2018).
L. Yang, L. Chen, Y. C. Chen, L. Kang, J. Yu, Y. Wang, C. Lu, T. Mashimo, A. Yoshiasa, and C. H. Lin (2019). Colloid Surf.. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.05.018.
E. Rivard, M. Trudeau, and K. Zaghib (2019). Materials. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12121973.
B. N. Mondal, S. Chabri, G. Sardar, D. N. Nath, and P. P. Chattopadhyay (2016). J. Magn. Magn. Mater.. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.03.084.
S. Li, T. Wei, M. Tang, F. Chai, F. Qu, and C. Wang (2018). Sensor Actuat.. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.08.159.
O. V. Bakina, E. A. Glazkova, N. V. Svarovskaya, N. G. Rodkevich, and M. I. Lerner (2019). Mater. Lett.. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2019.01.105.
S. Patel, M. Konar, H. Sahoo, and G. Hota (2019). Nanotechnology. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/ab045d.
M. Ashfaq, N. Verma, and S. Khan (2016). Mater. Sci. Eng.. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2015.10.079.
I. Ferreri, M. Henriques, J. T. M. De Hosson, A. Cavaleiro, and S. Carvalho (2016). Surf. Coat Technol.. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2016.04.019.
C. E. Santo, E. W. Lam, C. G. Elowsky, D. Quaranta, D. W. Domaille, C. J. Chang, and G. Grass (2011). Bacterial killing by dry metallic copper surfaces. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 77, (3), 794–802. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01599-10.
A. Kędziora, M. Speruda, E. Krzyżewska, J. Rybka, A. Łukowiak, and G. Bugla-Płoskońska (2018). Int. J. Mol. Sci.. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020444.
W. K. Jung, H. C. Koo, K. W. Kim, S. Shin, S. H. Kim, and Y. H. Park (2008). Appl. Environ. Microbiol.. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02001-07.
I. Matai, A. Sachdev, P. Dubey, S. U. Kumar, B. Bhushan, and P. Gopinath (2014). Colloid Surf.. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2013.12.005.
Acknowledgements
The works has been performed with the support of the Russian Science Foundation, project No. 17-79-20382. Antibacterial activity of colloidal silver nanoparticles were studied in the framework of the Program of Fundamental Scientific Studies of the State Science Academies for 2013–2020 (Direction No. III.23.2.10).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bakina, O., Glazkova, E., Pervikov, A. et al. Design and Preparation of Silver–Copper Nanoalloys for Antibacterial Applications. J Clust Sci 32, 779–786 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-020-01844-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-020-01844-1