Abstract
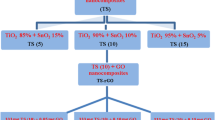
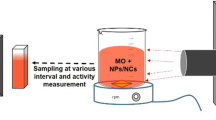
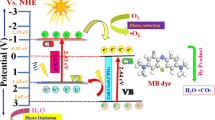
To enhance the degradation of colour and chemical oxygen demand using photocatalytic activity, Graphene–CuO–Co3O4 hybrid nanocomposites were synthesized using an in situ surfactant free facile hydrothermal method. The photocatalytic degradation of synthetic anionic dyes, methyl orange (MO) and Congo red (CR), and industrial textile wastewater dyes under visible light irradiation was evaluated. The synthesized nanocomposite was characterized structurally and morphologically using X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy, high-resolution transmission electron microscope, and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Evaluation of the colour indicated complete removal at 15 min of irradiation for the MO and CR dyes, with 99% degradation efficiency. The reaction time for the primary effluent wastewater dye was 60 min for 81% dye removal. In contrast, a longer reaction time was required to meet the national discharge regulation for the raw wastewater dye, 300 min for 60% dye removal. The mechanism for dye degradation using the Graphene–CuO–Co3O4 hybrid nanocomposite was elucidated using the Langmuir–Hinshelwood model, and the rate constant and half-life of the degradation process were calculated. The results demonstrate that photocatalytic degradation using a hybrid nanocomposite and visible light irradiation is a sustainable alternative technology for removing colour from wastewater dye.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. A. Ahmad and B. H. Hameed (2010). Effect of preparation conditions of activated carbon from bamboo waste for real textile wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 173, 487–493.
American Public Health Association (APHA) Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed (American Public Health Association, Washington, DC, 2005).
R. Asahi, T. Morikawa, T. Ohwaki, K. Aoki, and Y. Taga (2001). Visible-light photocatalysis in nitrogen-doped titanium oxides. Science 293, 269–271.
N. Azbar, T. Yonar, and K. Kestioglu (2004). Comparison of various advanced oxidation processes and chemical treatment methods for COD and color removal from a polyester and acetate fiber dyeing effluent. Chemosphere 55, 35–43.
X. Bai, L. Wang, and Y. Zhu (2012). Visible photocatalytic activity enhancement of ZnWO4 by graphene hybridization. ACS Catal. 2, 2769–2778.
E. Barrera, I. Gonzalez, and T. Viveros (1998). A new cobalt oxide electrodeposit bath for solar absorbers. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 51, 69–82.
E. Bi, H. Chen, X. Yang, W. Peng, M. Gratzel, and L. Han (2014). A quasi core-shell nitrogen- doped graphene/cobalt sulfide conductive catalyst for highly efficient dye- sensitized solar cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 7, 2637–2641.
Y. Bu, Z. Chen, W. Li, and B. Hou (2013). Highly efficient photocatalytic performance of graphene–ZnO quasi-shell–core composite material. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 5, 12361–12368.
O. T. Can, M. Kobya, E. Demirbas, and M. Bayramoglu (2006). Treatment of the textile wastewater by combined electrocoagulation. Chemosphere 62, 181–187.
H. Chen, G. Jhao, and Y. Liu (2013). Low-temperature solution synthesis of CuO nanorods with thin diameter. Mater. Lett. 93, 60–63.
X. K. Chen, J. C. Irwin, and J. P. Franck (1995). Evidence for a strong spin-phonon interaction in cupric oxide. Phys. Rev. B 52, R13130.
Y. S. Chen and P. V. Kamat (2014). Glutathione-capped gold nanoclusters as photosensitizers. Visible light-induced hydrogen generation in neutral water. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 6075–6082.
Datasheet of American Elements’ catalog. Available http://www.americanelements.com/copper-ii-ethoxide-2850-65-9.html. American Elements is a US Registered Trademark. Accessed 01 Jan 1998.
R. S. Dave and A. R. Patel (2010). Photochemical and photocatalytic of cypermethrin under UV radiation. Der Pharma Chem. 2, 152–158.
R. Esmaeli, A. H. Hassani, A. Eslami, M. Ahmadi Moghadam, and A. A. Safari (2011). Di-(2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate oxidative degradation by Fenton process in synthetic and real petrochemical wastewater. Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 8, 201–206.
I. Gulkaya, G. A. Surucu, and F. B. Dilek (2006). Importance of H2O2/Fe2+ ratio in Fenton’s treatment of a carpet dyeing wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 136, 763–769.
H. A. E. Hagelin-Weaver, G. B. Hoflund, D. M. Minahan, and G. N. Salaita (2004). Electron energy loss spectroscopic investigation of Co metal, CoO, and Co3O4 before and after Ar + bombardment. Appl. Surf. Sci. 235, 420–448.
L. He, L. Jing, Y. Luan, L. Wang, and H. Fu (2014). Enhanced visible activities of α-Fe2O3 by coupling N-doped graphene and mechanism insight. ACS Catal. 4, 990–998.
M. R. Hoffman, S. T. Martin, W. Choi, and D. W. Bahnemann (1995). Environmental applications of semiconductor photocatalysis. Chem. Rev. 95, 69–96.
A. Houas, H. Lachheb, M. Ksibi, E. Elaloui, C. Guillard, and J. Herrmann (2001). Photocatalytic degradation pathway of methylene blue in water. Appl. Catal. B 31, 145–157.
Y. W. Kang, M. J. Cho, and K. Y. Hwang (1999). Correction of hydrogen peroxide interference on standard chemical oxygen demand test. Water Res. 33, 1247–1251.
V. Kavitha and K. Palanivelu (2005). Destruction of cresols by Fenton oxidation process. Water Res. 39, 3062–3072.
M. Kobya, O. T. Can, and M. Bayramoglu (2003). Treatment of textile wastewaters by electrocoagulation using iron and aluminum electrodes. J. Hazard. Mater. 100, 163–178.
S. Kohtani, J. Hiro, N. Yamamoto, A. Kudo, K. Tokumura, and R. Nakagaki (2005). Adsorptive and photocatalytic properties of Ag-loaded BiVO4 on the degradation of 4-n-alkylphenols under visible light irradiation. Catal. Commun. 6, 185–189.
S. Kohtani, M. Koshiko, A. Kudo, K. Tokumura, Y. Ishigaki, A. Toriba, K. Hayakawa, and R. Nakagaki (2003). Photodegradation of 4-alkylphenols using BiVO4 photocatalyst under irradiation with visible light from a solar simulator. Appl. Catal. B 46, 573–586.
K. Krishnamoorthy, R. Mohan, and S. J. Kim (2011). Graphene oxide as a photocatalyst material. Appl. Phys. Lett. 98, 1–3.
A. Kudo, H. Kato, and I. Tsuji (2004). Strategies for the development of visible-light driven photo catalysts for water splitting. Chem. Lett. 33, 1534–1539.
M. R. Kumar (2009). Recycling of woven fabric dyeing wastewater practiced in Perundurai common effluent treatment plant. Mod. Appl. Sci. 3, 146–160.
R. Leary and A. Westwood (2011). Carbonaceous nanomaterials for the enhancement of TiO2 photocatalysis. Carbon 49, 741–772.
J. Lee, D. H. K. Jackson, T. Li, R. E. Winans, J. A. Dumesic, T. F. Kuech, and G. W. Huber (2014). Enhanced stability of cobalt catalysts by atomic layer deposition for aqueous-phase reactions. Energy Environ. Sci. 7, 1657–1660.
H. Liang, J. M. Raitano, L. Zhang, and S. W. Chan (2009). Controlled synthesis of Co3O4 nanopolyhedrons and nanosheets at low temperature. Chem. Commun., 7569–7571.
H. M. Liu, R. Nakamura, and Y. Nakato (2005). Bismuth–copper vanadate BiCu2VO6 as a novel photocatalyst for efficient visible-light-driven oxygen evolution. Chem. Phys. Chem. 6, 2499–2502.
M. Liu, R. Inde, M. Nishikawa, X. Qiu, D. Atarashi, E. Sakai, Y. Nosaka, K. Hashimoto, and M. Miyauchi (2014). Enhanced photoactivity with nanocluster-grafted titanium dioxide photocatalysts. ACS Nano 8, 7229–7238.
N. Manivasakam Industrial Effluents Origin, Characteristics, Effects, Analysis and Treatment (Sakthi Publications, Coimbatore, 2003).
L. Metcalf and H. P. Eddy Wastewater Engineering: Treatment and Reuse, 4th ed (McGraw-Hill, New York, 2004), pp. 93–94.
M. Niu, D. Cheng, and D. Cao (2014). Understanding the mechanism of photocatalysis enhancements in the graphene-like semiconductor sheet/TiO2 composites. J. Phys. Chem. C 118, 5954–5960.
M. Panizza and M. A. Oturan (2011). Degradation of Alizarin Red by electro-Fenton process using a graphite-felt cathode. Electrochim. Acta 56, 7084–7087.
S. K. Pardeshi and A. B. Patil (2008). A simple route for photocatalytic degradation of phenol in aqueous zinc oxide suspension using solar energy. Sol. Energy 82, 700–705.
K. M. Parida and S. Parija (2006). Photocatalytic degradation of phenol under solar radiation using microwave irradiated zinc oxide. Sol. Energy 80, 1048–1054.
P. S. Patil, L. D. Kadam, and C. D. Lokhande (1996). Preparation and characterization of spray pyrolysed cobalt oxide thin films. Thin Solid Films 272, 29–32.
Pham TA, Kim J, Kim JS, Jeong YT, Corrigendum to (2011) “One-step reduction of graphene oxide with 1-glutathione” [Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 384, 543–548], Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 384, 543.
J. J. Pignatello, E. Oliveros, and A. Mackay (2006). Advanced oxidation processes for organic contaminant destruction based on the Fenton reaction and related chemistry. J. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 36, 1–84.
W. H. Ryu, T. H. Yoon, S. H. Song, S. Jeon, Y. J. Park, and I. D. Kim (2013). Bifunctional composite catalysts using Co3O4 nanofibers immobilized on nonoxidized graphene nanoflakes for high-capacity and long-cycle-Li-O2 batteries. Nano Lett. 13, 4190–4197.
R. Saito, M. Hofmann, G. Dresselhaus, A. Jorio, and M. S. Dresselhaus (2011). Raman spectroscopy of graphene and carbon nanotubes. Adv. Phys. 60, 413–550.
S. Sakthivel and H. Kisch (2003). Daylight photocatalysis by carbon- modified titanium dioxide. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 42, 4908–4911.
M. Shanmugam and R. Jayavel (2015). Synthesize of graphene-tin oxide nanocomposite and its photocatalytic properties for the degradation of organic pollutants under visible light. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 15, 7195–7201.
K. M. Srestha, C. M. Sorensen, and K. J. Klabunde (2010). Synthesis of CuO nanorods, reduction of CuO into Cu nanorods, and diffuse reflectance measurements of CuO and Cu nanomaterials in the near infrared region. J. Phys. Chem. C 114, 14368–14376.
Z. Sun, Y. Chen, Q. Ke, Y. Yang, and J. Yuan (2002). Photocatalytic degradation of a cationic azo dye by TiO2/bentonite nanocomposite. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 149, 169–174.
L. L. Tan, W. J. Ong, S. P. Chai, and A. R. Mohamed (2015). Noble metal modified reduced graphene oxide/TiO2 ternary nanostructures for efficient visible-light-driven photoreduction of carbon dioxide into methane. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 166–167, 251–259.
J. W. Tang, Z. G. Zou, and J. H. Ye (2004). Efficient photocatalytic decomposition of organic contaminants over CaBi2O4 under visible light-irradiation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 43, 4463–4466.
G. Tchobanoglous and F. L. Burton Wastewater Engineering: Treatment, Disposal and Reuse (Tata McGraw- Hill Publishing Co., Ltd., New Delhi, 1995).
F. Tuinstra and J. L. Koenig (1970). Raman spectrum of graphite. J. Chem. Phys. 53, 1126–1130.
D. Venieri, A. Fraggedaki, M. Kostadima, E. Chatzisymeon, V. Binas, A. Zachopoulos, G. Kiriakidis, and D. Mantzavinos (2014). Solar light and metal-doped TiO2 to eliminate water- transmitted bacterial pathogens: photocatalyst characterization and disinfection performance. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 154–155, 93–101.
B. Weng, J. Wu, N. Zhang, and Y. J. Xu (2014). Observing the role of graphene in boosting the two-electron reduction of oxygen in graphene–WO3 nanorod photocatalysts. Langmuir 30, 5574–5584.
Z. S. Wu, W. C. Ren, L. Wen, L. B. Gao, J. P. Zhao, Z. P. Chen, G. M. Zhou, F. Li, and H. M. Cheng (2010). Graphene anchored with Co3O4 nanoparticles as anode of lithium ion batteries with enhanced reversible capacity and cyclic performance. ACS Nano 4, 3187–3194.
Q. Xiang, J. Yu, and M. Jaroniec (2012). Graphene based semiconductor photocatalysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 41, 782–796.
C. Yang, X. Su, J. Wang, X. Cao, S. Wang, and L. Zhang (2013). Facile microwave-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of varied-shaped CuO nanoparticles and their gas sensing properties. Sens. Actuators B 185, 159–165.
H. Yu, H. Irie, and K. Hashimoto (2010). Conduction band energy level control of titanium dioxide: toward an efficient visible-light-sensitive photocatalyst. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132, 6898–6899.
J. Yuan, J. Zhu, H. Bi, X. Meng, S. Liang, L. Zhang, and X. Wang (2013). Graphene-based 3D composite hydrogel by anchoring Co3O4 nanoparticles with enhanced electrochemical properties. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 15, 12940–12945.
F. Zhang, A. Yamakata, K. Maeda, Y. Moriya, T. Takata, J. Kubota, K. Teshima, S. Oishi, and K. Domen (2012). Cobalt-modified porous single-crystalline LaTiO2N for highly efficient water oxidation under visible light. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 8348–8351.
H. Zhang, X. Chen, Z. Li, J. Kou, T. Yu, and Z. Zou (2007). Preparation of sensitized ZnS and its photocatalytic activity under visible light irradiation. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 40, 6846–6849.
J. Zhang, Z. Xiong, and X. S. Zhao (2011). Graphene-metal oxide composites for the degradation of dyes under visible light irradiation. J. Mater. Chem. 21, 3634–3640.
Y. C. Zhang, W. W. Chen, and X. Y. Hu (2007). Controllable synthesis and optical properties of Zn-doped CdS nanorods from single-source molecular precursors. Cryst. Growth Des. 7, 580–586.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (2017R1D1A3B03029814).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahalingam, S., Ramasamy, J. & Ahn, YH. Enhanced Photocatalytic Degradation of Synthetic Dyes and Industrial Dye Wastewater by Hydrothermally Synthesized G–CuO–Co3O4 Hybrid Nanocomposites Under Visible Light Irradiation. J Clust Sci 29, 235–250 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-017-1329-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-017-1329-3