Abstract
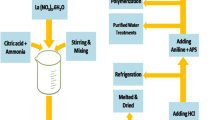
In this study, manganese zinc ferrite (MZF)-polyaniline (PANI) nanocomposites were synthesized by mixing route to investigate the impact of composites on microwave absorbing properties. The starting powder of MZF is synthesized using the microwave hydrothermal method and PANI/MZF is prepared using the synthesized ferrite nanoparticles. Structural analysis was performed using the X-ray diffraction method, while morphological information was obtained through transmission electron microscopy (TEM) studies. The results of the characterization studies confirmed the existence of the spinel phase of ferrite and the polymer phase in the composite samples. The TEM images revealed that the particles are in spherical morphology with sizes in the range of 40–50 nm. The magnetic properties of the composites were measured using magnetic hysteresis loops and observed the change in magnetic saturation with the percentage of polymer incorporated in the composites. The hysteresis loops confirm the soft magnetic nature of the composites. The complex permittivity (ε′ and ε″) and permeability (µ′ and µ″) of nanocomposite samples were measured in the frequency range of 2 to 18 GHz. The permittivity and permeability parameters are found to be increasing with ferrite volume concentration. The percentage of ferrite and polymer content also had a significant impact on the magneto-dielectric and microwave absorption properties of the composite materials in the measured frequency range. The composite MZF/PANI-50 exhibited a high reflection loss of − 52.8 dB at 10 GHz with bandwidth efficiency of more than 5 GHz. These composites’ enhanced microwave absorbing capability could be beneficial in designing microwave absorption filters for electromagnetic interference applications in both X-band and Ku-band frequency regions.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during the analysis the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
P. Mathur, S. Raman, Electromagnetic Interference (EMI), measurement and reduction techniques. J. Electron. Mater. 49, 2975–2998 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-020-07979-1
F.M. Oliveira, R. Gusmão, Recent advances in the electromagnetic interference shielding of 2D materials beyond Graphene. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2(10), 3048–3071 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaelm.0c00545
K. Tian, D. Hu, Q. Wei, Q. Fu, H. Deng, Recent progress on multifunctional electromagnetic interference shielding polymer composites. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 134, 106–131 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2022.06.031
N. Devi, S.S. Ray, Electromagnetic interference cognizance and potential of advanced polymer composites toward electromagnetic interference shielding: a review. Polym. Eng. Sci. 62(3), 591–621 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/pen.25876
Q. Wang, J. Liu, J. Li, A literature review of MOF derivatives of electromagnetic wave absorbers mainly based on pyrolysis. Int. J. Miner Metall. Mater. 30, 446–473 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-022-2562-9
Z. Lou, Q. Wang, U.I. Kara et al., Biomass-derived carbon heterostructures enable environmentally adaptive wideband electromagnetic wave absorbers. Nano-Micro Lett. 14, 11 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-021-00750-z
V. Shukla, Review of electromagnetic interference shielding materials fabricated by iron ingredients. Nanoscale Adv. 1, 1640–1671 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/C9NA00108E
E. Mikinka, M. Siwak, Recent advances in electromagnetic interference shielding properties of carbon-fibre-reinforced polymer composites—a topical review. J. Mater. Sci: Mater. Electron. 32, 24585–24643 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06900-8
M.T. Sebastian, R. Ubic, H. Jantunen, Microwave Materials and Applications, 1st edn. (John Wiley & Sons Ltd., Hoboken, 2017)
Ján. Kruželák, Andrea Kvasničáková, Klaudia Hložekováand, Ivan Hudec, Progress in polymers and polymer composites used asefficient materials for EMI shielding. Nanoscale Adv. 3, 123–172 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1039/D0NA00760A
H. Xiaodi Zhou, Y. Han, C. Wang, H. Zhang, Z. Lv, Lou, Silicon-coated fibrous network of carbon nanotube/iron towards stable and wideband electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 121, 199–206 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2022.03.002
H.L. Lv, H.Q. Zhang, J. Zhao, G.B. Ji, Y.W. Du, Achieving excellent bandwidth absorption by a mirror growth process of magnetic porous polyhedron structures. Nano Res. 9, 1813–1822 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-016-1074-1
L.S. Fu, J.T. Jiang, C.Y. Xu, L. Zhen, Synthesis of hexagonal Fe microflakes with excellent microwave absorption performance. Cryst. Eng. Comm. 14, 6827–6832 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CE25836F
P. Gairola, L.P. Purohit, S.P. Gairola, P. Bhardwaj, S. Kaushik, Enhanced electromagnetic absorption in ferrite and tantalum pentoxide based polypyrrole nanocomposite. Prog Nat. Sci. : Mater. Int. 29(2), 170–176 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnsc.2019.03.011
S. Geetha, K.K. Sateesh Kumar, C.R.K. Rao, M. Vijayan, D.C. Trivedi, EMI shielding: methods and materials-A review. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 112, 2073–2086 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1002/app.29812
P. Neelima, T. Ramesh, P. Raju et al., Structural and microwave behaviour of Dy3+ substituted Ni0.5Zn0.5DyxFe2-xO4 ferrites. J. Mater. Sci: Mater Electron 32, 1729–1740 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-04941-z
F.M. Idris, M. Hashim, I. Ismail et al., Microwave absorption characteristics of some ferrite-filled polymer composites. Adv Mat Res. 895, 298–304 (2014). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.895.298
B. Aziz, A. Shakoor, A.K. Qureshi et al., Structural, electrical, and magnetic Properties of Ferrite–Polymer Composites. J. Electron. Mater. 47, 6437–6442 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-018-6542-9
S. Maciej Jaroszewski, A.V. Thomas, Rane, Advanced Materials for Electromagnetic Shielding Fundamentals, Properties, and Applications (John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Hoboken, NJ, 2018)
B.G. Soares, G.M.O. Barra, T. Indrusiak, Conducting polymeric composites based on intrinsically conducting polymers as electromagnetic interference shielding/microwave absorbing materials-a review. J. Compos. Sci. 5(7), 173 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs5070173
K. Shahapurkar, M. Gelaw, V. Tirth et al., A comprehensive review on polymer composites as electromagnetic interference shielding materials. Polym. Polym. Compos. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1177/0967391122110212
Sumita Goswami, Suman Nandy, Elvira Fortunato, Rodrigo Martins, Polyaniline and its composites engineering: a class of multifunctional smartenergy materials. J. Solid State Chem. 317, 123679 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2022.123679
A.M.A. Henaish, M.M. Ali, D.E.E. Refaay, I.A. Weinstein, O.M. Hemeda, Synthesis, electric and magnetic characterization of nickel ferrite/pani nano-composite prepared by flash auto combustion method. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. 31, 731–740 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01737-w
K. Praveena, K. Sadhana, H.L. Liu, M. Bououdina, Microwave absorption studies of magnetic sublattices in microwave sintered Cr3+doped SrFe12O19. J. Magn. Magn. Mater 426, 604–614 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.11.013
K. Praveena, K. Sadhana, H.L. Liu, N. Maramu, G. Himanandini, Improved microwave absorption properties of TiO2 and Ni0.53Cu0.12Zn0.35Fe2O4nanocomposites potential for microwave devices. J. Alloys Compd. 681, 499–507 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.04.190
K. Praveena, K. Sadhana, H.L. Liu, S.R. Murthy, Effect of Zn substitution on structural, dielectric and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline Co1−xZnxFe2O4 for potential high density recording media. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron 27, 12680–11269 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-5402-8
K. Praveena, M. Bououdina, M. Penchal Reddy, S. Srinath, R. Sandhya, S. Katlakunta, Structural, magnetic, and electrical properties of microwave-sintered Cr3+-Doped Sr hexaferrites. J. Electron. Mater 44, 524–531 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-014-3453-2
T. Ramesh, B. Sravanthi, K.K. Ganta et al., Structural, magnetoelectric properties of multidoped Ni–Al ferrites for microwave circulator applications. Appl. Phys. A 128, 957 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-06103-w
K. Sadhana, K. Praveena, S.R. Murthy, Magnetic properties of xNi0.53Cu0.12Zn0.35Fe1.88O 4+ (1− x) BaTiO3 nanocomposites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322, 3729–3736 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2010.06.007
T. Ramesh, R.S. Shinde, S.R. Murthy, Nanocrystalline gadolinium iron garnet for circulator applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324(22), 3668–3673 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2012.05.029
W.B. Weir, Automatic measurement of complex dielectric constant and permeability at microwave frequencies. Proc. IEEE 62, 33–36 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1109/PROC.1974.9382
A.M. Nicolson, G.F. Ross, Measurement of intrinsic properties of materials by time domain techniques. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 19, 377–382 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.1970.4313932
S.B. Wilson, Modal analysis of the gap effect in waveguide dielectric measurements. IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory Tech. 36, 752–756 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1109/22.3581
D. Micheli et al., Broadband electromagnetic absorbers using carbon nanostructure-based composites. IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory Techn 59, 2633–2646 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMTT.2011.2160198
A. Davide Micheli, R. Vricella, M. Pastore, Marchetti, Synthesis and electromagnetic characterization of frequency selective radar absorbing materials using carbon nano powders. Carbon. 77, 756–774 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2014.05.080
S. Wang, Z. Tan, Y. Li, L. Sun, T. Zhang, Synthesis, characterization and thermal analysis of polyaniline/ZrO2 composites. Thermochim. Acta. 441(2), 191–194 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2005.05.020
K.H. Wu, C.M. Chao, C.H. Liu, T.C. Chang, Characterization and corrosion resistance of organically modified silicate–NiZn ferrite/polyaniline hybrid coatings on aluminum alloys. Corros. Sci. 49, 3001–3014 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2007.02.008
V.J. Angadi et al., Structural,electrical and magnetic properties of Sc3+ doped Mn-Zn ferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 424, 1–11 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.10.050
B.D. Cullity, Elements of X-ray Diffraction, 2nd edn. (Addison-Wesley, Reading, 1978)
R. Qindeel, N.H. Alonizan, Magnetic behavior of ferrite-polymer composites for hyperthermia applications. J. Mater. Sci: Mater. Electron. 31, 19672–19679 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-04493-2
A. Lekshmi Omana, R.E. Chandran, J.R. Wilson, K.C. George, N.V. Unnikrishnan, S.S. Varghese, G. George, S.M. Simon, I. Paul, Recent advances in polymer nanocomposites for electromagnetic interference shielding: a review. ACS Omega 7, 25921–25947 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.2c02504
N. Maruthi, M. Faisal, N. Raghavendra, Conducting polymer-based composites as efficient EMI shielding materials: a comprehensive review and future prospects. Synth. Met 272, 116664 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.synthmet.2020.116664
D. Jiang, V. Murugadoss, Y. Wang, J. Lin, T. Ding, Z. Wang, Q. Shao, C. Wang, H. Liu, N. Lu, R. Wei, A. Subramania, Z. Guo, Electromagnetic interference shielding polymers and nanocomposites - a review. Polym. Rev 59, 280–337 (2019)
T. Haibo Yang, Y. Ye, Lin, Microwave absorbing properties based on polyaniline/magnetic nanocomposite powders. RSC Adv. 5, 103488–103493 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA17576C
X. Li, J. Feng, Y. Du, J. Bai, H. Fan, H. Zhang, Y. Peng, F. Li, One-pot synthesis of CoFe2O4/graphene oxide hybrids and their conversion into FeCo/graphene hybrids for lightweight and highly efficient microwave absorber. J. Mater. Chem. 3(10), 5535–5546 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TA05718J
M. Mishra, A.P. Singh, B.P. Singh, V.N. Singh, S.K. Dhawan, Conducting ferrofluid: a high-performance microwave shielding material. J. Mater. Chem 2(32), 13159–13168 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TA01681E
D.L. Leslie-Pelecky, R.D. Rieke, Magnetic properties of nanostructured materials. Chem. Mater. 8, 1770–1783 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1021/cm960077f
Y.J. Chen, P. Gao, R.X. Wang, C.L. Zhu, L.J. Wang, M.S. Cao, H.B. Jin, Porous Fe3O4/SnO2 core/shell nanorods: synthesis and electromagnetic properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 113, 10061–10064 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp902296z
G. Viau, F. Fievet-Vincent, F. Fievet, P. Toneguzzo, F. Ravel, O. Acher, Size dependence of microwave permeability of spherical ferromagnetic particles. J. Appl. Phys. 81, 2749 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.363979
F. Wen, F. Zhang, Z. Liu, Investigation on microwave absorption properties for multiwalled carbon nanotubes/Fe/Co/Ni nano powders as lightweight absorbers. J. Phys. Chem. C 115, 14025–14030 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp202078p
J. Anjitha Thadathil, G.R. Kavil, C.P. Kovummal, Jijil, P. Periyat, Facile synthesis of Polyindole/Ni1–xZnxFe2O4 (x = 0,0.5,1) Nanocomposites and their enhanced microwave absorption and shielding Properties. ACS Omega. 7(13), 11473–11490 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.2c00824
Acknowledgements
Sadhana Katlakunta contributed to this article in a reasonable manner.
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TR synthesized the samples and took the measurements. KS helped in characterization of the present samples. KP wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare that they don’t have any Conflict of interest and all the authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ramesh, T., Sadhana, K. & Praveena, K. Enhanced microwave absorbing properties of manganese zinc ferrite: polyaniline nanocomposites. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 1245 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10651-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10651-z