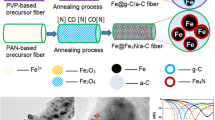
Abstract
The increasing excess electromagnetic wave (EMW) energies causes potential electromagnetic radiation pollution. It gives rise to more and more attention on designing environmentally friendly, efficient and suitable for large-scale industrial production of daily EMW absorbers. Carbon matrix composites modified with magnetic particles occupy the majority of these candidate absorbers. However, the preparation is still in its infancy. Here, we creatively mixed Fe(acac)3 with polyacrylonitrile (PAN) spinning solution, and then prepared magnetic carbon-based composites by in-situ pyrolysis of the obtained electrospun fibers (Fe(acac)3/PAN) at different temperatures. The SEM images display a fractured fibrous material with porous structure and uniform distribution of magnetic particles on the outer surface and inside. The XRD and XPS results indicate the composites consist of Fe3O4, Fe3C and carbon matrix. Besides, the thermal phase transition occurs with the pyrolysis temperature increasing from 300 to 1000 °C, and the formed Fe3O4 reacts with the carbon matrix to form Fe3C. As a result, the corresponding magnetic properties and electromagnetic properties improve. MCF-1000 exhibits enhanced EMW absorption performance with a minimum RL (\({RL}_{\mathrm{min}}\)) value of − 29.27 dB at a matching frequency (\({f}_{m}\)) of 11.68 GHz, a matching thickness (\({t}_{m}\)) as low as 1.50 mm, and an effective frequency bandwidth as broad as 4.50 GHz from 13.50 to 18.00 GHz at a fixed thickness as thin as 1.13 mm. Further investigations indicate that such good EMW absorption behavior is attributed to the optimal impedance matching and the weakened eddy current effect which are both benefited by the thermal phase transition effect. The results provide theoretical and practical experience for the industrial large-scale preparation of a kind of EMW absorbers.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Lan, Z. Zhao, Z. Gao, K. Kou, G. Wu, H. Wu, Porous high entropy alloys for electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 512, 167065 (2020)
Z. Lou, W. Wang, C. Yuan, Y. Zhang, Y. Li, L. Yang, Fabrication of Fe/C composites as effective electromagnetic wave absorber by carbonization of pre-magnetized natural wood fibers. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 4(1), 43–50 (2019)
P. Liu, S. Gao, Y. Wang, Y. Huang, W. He, W. Huang, J. Luo, Carbon nanocages with N-doped carbon inner shell and Co/N-doped carbon outer shell as electromagnetic wave absorption materials. Chem. Eng. J. 381, 122653 (2020)
W. Pei, W. Shang, C. Liang, X. Jiang, C. Huang, Q. Yong, Using lignin as the precursor to synthesize Fe3O4@lignin composite for preparing electromagnetic wave absorbing lignin-phenol-formaldehyde adhesive. Ind. Crop. Prod. 154, 112638 (2020)
D. Fabien, The different sources of electromagnetic fields: dangers are not limited to physical health. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 39, 166–175 (2020)
H. Lv, Y. Li, Z. Jia, L. Wang, X. Guo, B. Zhao, R. Zhang, Exceptionally porous three-dimensional architectural nanostructure derived from CNTs/graphene aerogel towards the ultra-wideband EM absorption. Compos. B 196, 108122 (2020)
Z. Jia, C. Wang, A. Feng, P. Shi, C. Zhang, X. Liu, K. Wang, G. Wu, A low-dielectric decoration strategy to achieve absorption dominated electromagnetic shielding material. Compos. B 183, 107690 (2020)
H. Lv, Z. Yang, H. Xu, L. Wang, R. Wu, An electrical switch-driven flexible electromagnetic absorber. Adv. Funct. Mater. 30, 1907251 (2020)
Z. Lou, Q. Wang, Y. Zhang, X. Zhou, R. Li, J. Liu, Y. Li, H. Lv, In-situ formation of low-dimensional, magnetic core-shell nanocrystal for electromagnetic dissipation. Compos. B 214, 108744 (2021)
Z. Shen, J. Chen, B. Li, G. Li, Z. Zhang, X. Hou, Recent progress in SiC nanowires as electromagnetic microwaves absorbing materials. J. Alloys Compd. 815, 152388 (2020)
M. Cao, X. Wang, M. Zhang, J. Shu, W. Cao, H. Yang, X. Fang, J. Yuan, Electromagnetic response and energy conversion for functions and devices in low-dimensional materials. Adv. Funct. Mater. 29, 1807398 (2019)
M.-S. Cao, Y.-Z. Cai, P. He, J.-C. Shu, W.-Q. Cao, J. Yuan, 2D MXenes: electromagnetic property for microwave absorption and electromagnetic interference shielding. Chem. Eng. J. 359, 1265–1302 (2019)
Z. Gao, Z. Jia, K. Wang, X. Liu, L. Bi, G. Wu, Simultaneous enhancement of recoverable energy density and efficiency of lead-free relaxor-ferroelectric BNT-based ceramics. Chem. Eng. J. 402, 125951 (2020)
B. Wen, H. Yang, Y. Lin, L. Wang, L. Ma, Y. Qiu, In situ anchoring carbon nanotubes on the Ni/C nanosheets with controllable thickness for boosting the electromagnetic waves absorption. Compos. A 138, 106044 (2020)
X. Zeng, X. Cheng, R. Yu, G.D. Stucky, Electromagnetic microwave absorption theory and recent achievements in microwave absorbers. Carbon 168, 606–623 (2020)
D.T. Chi, B.X. Khuyen, B.S. Tung, V.D. Lam, L.Y. Chen, Y. Lee, Progresses in metamaterials for advanced low-frequency perfect absorbers: a brief review. J. Electromagn. Wave Appl. 34, 2251–2265 (2020)
Y. Wang, H. Xu, C. Wang, M. Wang, S. Wang, Research progress of electromagnetic metamaterial absorbers. Acta Phys. Sin. Chin. Ed. 69, 134101 (2020)
S.K. Singh, M.J. Akhtar, K.K. Kar, Hierarchical carbon nanotube-coated carbon fiber: ultra lightweight, thin, and highly efficient microwave absorber. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 10, 24816–24828 (2018)
S.K. Singh, M.J. Akhtar, K.K. Kar, Synthesis of a lightweight nanocomposite based on polyaniline 3D hollow spheres integrated milled carbon fibers for efficient X-band microwave absorption. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 59, 9076–9084 (2020)
Y. Wang, X. Di, X. Wu, X. Li, MOF-derived nanoporous carbon/Co/Co3O4/CNTs/RGO composite with hierarchical structure as a high-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorber. J. Alloys Compd. 846, 156215 (2020)
Z. Lou, R. Li, J. Liu, Q. Wang, Y. Zhang, Y. Li, Used dye adsorbent derived N-doped magnetic carbon foam with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performance. J. Alloys Compd. 854, 157286 (2021)
C. Wang, V. Murugadoss, J. Kong, Z. He, X. Mai, Q. Shao, Y. Chen, L. Guo, C. Liu, S. Angaiah, Z. Guo, Overview of carbon nanostructures and nanocomposites for electromagnetic wave shielding. Carbon 140, 696–733 (2018)
M. Cao, C. Han, X. Wang, M. Zhang, Y. Zhang, J. Shu, H. Yang, X. Fang, J. Yuan, Graphene nanohybrids: excellent electromagnetic properties for the absorbing and shielding of electromagnetic waves. J. Mater. Chem. C 6, 4586–4602 (2018)
C. Jia, T. Xia, Y. Ma, N. He, Z. Yu, Z. Lou, Y. Li, Fe3O4/α-Fe decorated porous carbon-based composites with adjustable electromagnetic wave absorption: impedance matching and loading rate. J. Alloys Compd. 858, 157706 (2020)
Z. Lou, W. Wang, C. Yuan, Y. Zhang, Y. Li, L. Yang, Fabrication of Fe/C composites as effective electromagnetic wave absorber by carbonization of pre-magnetized natural wood fibers. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 4, 43–50 (2019)
B. Quan, G. Xu, D. Li, W. Liu, G. Ji, Y. Du, Incorporation of dielectric constituents to construct ternary heterojunction structures for high-efficiency electromagnetic response. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 498, 161–169 (2017)
Y. Niu, X. Li, W. Dong, C. Zhang, K. Zhao, F. Wang, H. Wang, Synthesis of N-doped carbon with embedded Fe/Fe3C particles for microwave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. 55, 11970–11983 (2020)
Y.X. Gong, L. Zhen, J.T. Jiang, C.Y. Xu, W.Z. Shao, Preparation of CoFe alloy nanoparticles with tunable electromagnetic wave absorption performance. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321, 3702–3705 (2009)
H. Zhao, Y. Cheng, H. Lv, G. Ji, Y. Du, A novel hierarchically porous magnetic carbon derived from biomass for strong lightweight microwave absorption. Carbon 142, 245–253 (2019)
H. Zhao, Y. Cheng, W. Liu, L. Yang, B. Zhang, L.P. Wang, G. Ji, Z.J. Xu, Biomass-derived porous carbon-based nanostructures for microwave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 11, 22 (2019)
H. Peng, X. Zhang, H. Yang, Z. Xiong, C. Liu, Y. Xie, Fabrication of core-shell nanoporous carbon@chiral polyschiff base iron(II) composites for high-performance electromagnetic wave attenuationin the low-frequency. J. Alloys Compd. 850, 156816 (2021)
L. Chai, Y. Wang, N. Zhou, Y. Du, X. Zeng, S. Zhou, Q. He, G. Wu, In-situ growth of core-shell ZnFe2O4 @ porous hollow carbon microspheres as an efficient microwave absorber. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 581, 475–484 (2021)
Y. Cheng, Y. Zhao, H. Zhao, H. Lv, X. Qi, J. Cao, G. Ji, Y. Du, Engineering morphology configurations of hierarchical flower-like MoSe2 spheres enable excellent low-frequency and selective microwave response properties. Chem. Eng. J. 372, 390–398 (2019)
Y. Cheng, J. Cao, H. Lv, H. Zhao, Y. Zhao, G. Ji, In situ regulating aspect ratio of bamboo-like CNTs via CoxNi1–x-catalyzed growth to pursue superior microwave attenuation in X-band. Inorg. Chem. Front. 6, 309–316 (2019)
W. Chu, C. Tian, Y. Wang, J. Chu, Z. Li, Y. Du, X. Han, Performance vs convenience of magnetic carbon-metal nanocomposites: a low-cost and facile citrate-derived strategy for Feco alloy/carbon composites with high-performance microwave absorption. Comment. Inorg. Chem. 37, 301–326 (2017)
M. Zhu, G. Diao, Review on the progress in synthesis and application of magnetic carbon nanocomposites. Nanoscale 3, 2748 (2011)
X. Zhang, J. Li, B. He, S. Yang, Y. Li, D. Chen, Y. Li, Y. Peng, Phase transformation and carbon precipitation of coal fly ash magnetospheres during a CVD process for microwave adsorption. Ceram. Int. 45, 18980–18981 (2019)
X. Cui, X. Liang, W. Liu, W. Gu, G. Ji, Y. Du, Stable microwave absorber derived from 1D customized heterogeneous structures of Fe3N@C. Chem. Eng. J. 381, 122589 (2020)
Z. Zhang, Z. Dong, X. Wang, Y. Dai, X. Cao, Y. Wang, R. Hua, H. Feng, J. Chen, Y. Liu, B. Hu, X. Wang, Synthesis of ultralight phosphorylated carbon aerogel for efficient removal of U(VI): batch and fixed-bed column studies. Chem. Eng. J. 370, 1376–1387 (2019)
C. Chen, E.B. Kennel, A.H. Stiller, P.G. Stansberry, J.W. Zondlo, Carbon foam derived from various precursors. Carbon 44, 1535–1543 (2006)
Y. Zhao, Y. Zhang, R. Li, Z. Wang, Z. Lou, Y. Li, Facile synthesis of ultralight and porous melamine-formaldehyde (MF) resin-derived magnetic graphite-like C3N4/carbon foam with electromagnetic wave absorption behavior. Curr. Comput.-Aided Drug Des. 10, 656 (2020)
Z. Lou, H. Han, M. Zhou, J. Han, J. Cai, C. Huang, J. Zou, X. Zhou, H. Zhou, Z. Sun, Synthesis of magnetic wood with excellent and tunable electromagnetic wave-absorbing properties by a facile vacuum/pressure impregnation method. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 6, 1000–1008 (2018)
Z. Lou, J. Sun, H. Lu, J. Cai, J. Zou, X. Li, Z. Sun, H. He, Fabrication of magnetic wood and its magnetic and electromagnetic wave absorption properties. J. For. Eng. 2, 24–29 (2017)
Z. Li, H. Lin, S. Ding, H. Ling, T. Wang, Z. Miao, M. Zhang, A. Meng, Q. Li, Synthesis and enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performances of Fe3O4@C decorated walnut shell-derived porous carbon. Carbon 167, 148–159 (2020)
R. Li, Z. Lou, S. Gu, Q. Wang, J. Liu, Y. Li, Preparation of magnetic carbon with microwave absorption property using bamboo powder. J. For. Eng. 6, 120–127 (2021)
J. Xiao, R. Hu, G. Chen, B. Xing, Facile synthesis of multifunctional bone biochar composites decorated with Fe/Mn oxide micro-nanoparticles: physicochemical properties, heavy metals sorption behavior and mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 399, 123067 (2020)
Z. Lou, Y. Li, H. Han, H. Ma, L. Wang, J. Cai, L. Yang, C. Yuan, J. Zou, Synthesis of porous 3D Fe/C composites from waste wood with tunable and excellent electromagnetic wave absorption performance. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 6, 15598–15607 (2018)
Z. Lou, C. Yuan, Y. Zhang, Y. Li, J. Cai, L. Yang, W. Wang, H. Han, J. Zou, Synthesis of porous carbon matrix with inlaid Fe3C/Fe3O4 micro-particles as an effective electromagnetic wave absorber from natural wood shavings. J. Alloys Compd. 775, 800–809 (2019)
H. Han, Z. Lou, P. Wang, Q. Wang, R. Li, Y. Zhang, Y. Li, Synthesis of ultralight and porous magnetic g-C3N4/g-carbon foams with excellent electromagnetic Wave (EMW) absorption performance and their application as a reinforcing agent for 3D printing EMW absorbers. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 59, 7633–7645 (2020)
Z. Lou, R. Li, P. Wang, Y. Zhang, B. Chen, C. Huang, C. Wang, H. Han, Y. Li, Phenolic foam-derived magnetic carbon foams (MCFs) with tunable electromagnetic wave absorption behavior. Chem. Eng. J. 391, 123571 (2020)
W. Huang, Z. Tong, R. Wang, Z. Liao, Y. Bi, Y. Chen, M. Ma, P. Lyu, Y. Ma, A review on electrospinning nanofibers in the field of microwave absorption. Ceram. Int. 46, 26441–26453 (2020)
Y. Huo, K. Zhao, Z. Xu, Y. Tang, Electrospinning synthesis of SiC/carbon hybrid nanofibers with satisfactory electromagnetic wave absorption performance. J. Alloys Compd. 815, 152458 (2020)
Z. Lou, T. Yuan, Q. Wang, X. Wu, S. Hu, X. Hao, X. Liu, Y. Li, Fabrication of crack-free flattened bamboo and its macro-/micro-morphological and mechanical properties. J. Renew. Mater. 9(5), 959–977 (2021)
C.R. Vestal, Z.J. Zhang, Atom transfer radical polymerization synthesis and magnetic characterization of MnFe2O4/polystyrene core/shell nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124, 14312–14313 (2002)
S.K. Singh, M.J. Akhtar, K.K. Kar, Impact of Al2O3, TiO2, ZnO and BaTiO3 on the microwave absorption properties of exfoliated graphite/epoxy composites at X-band frequencies. Compos. B 167, 135–146 (2019)
G. Wu, Z. Jia, X. Zhou, G. Nie, H. Lv, Interlayer controllable of hierarchical MWCNTs@C@FexOy cross-linked composite with wideband electromagnetic absorption performance. Compos. A 128, 105687 (2020)
S.K. Singh, H. Prakash, M.J. Akhtar, K.K. Kar, Lightweight and high-performance microwave absorbing heteroatom-doped carbon derived from chicken feather fibers. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 6, 5381–5393 (2018)
W. Gua, J. Lv, B. Quan, X. Liang, B. Zhang, G. Ji, Achieving MOF-derived one-dimensional porous ZnO/C nanofiber with lightweight and enhanced microwave response by an electrospinning method. J. Alloys Compd. 806, 983–991 (2019)
B. Quan, W. Liu, G. Xu, G. Ji, Y. Du, Nano sulfur particles decorated bi-lamella composites for superior electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 543, 138–146 (2019)
P. Liu, V.M.H. Ng, Z. Yao, J. Zhou, Y. Lei, Z. Yang, H. Lv, L.B. Kong, Facile synthesis and hierarchical assembly of flowerlike NiO structures with enhanced dielectric and microwave absorption properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9, 16404–16416 (2017)
B. Lu, H. Huang, X.L. Dong, X.F. Zhang, J.P. Lei, J.P. Sun, C. Dong, Influence of alloy components on electromagnetic characteristics of core/shell-type Fe-Ni nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 104, 114313 (2008)
Acknowledgements
Financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61601227, 31971740), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2017M621598), Jiangsu Agriculture Science and Technology Innovation Fund (CX(20)3041), Nature Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20160939), Key University Science Research Project of Jiangsu Province (17KJA220004), Science and technology project of Jiangsu Province (BE2018391).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Y., Lou, Z., Wang, Q. et al. Thermal phase transition controlling electromagnetic wave absorption behavior of PAN fiber derived porous magnetic absorber. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32, 26007–26020 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-05864-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-05864-z